怎么安装解压kafka这里就不多说了,从配置文件说起
我这里搭建的是三节点集群 master slave1 slave2
修改server.properties 文件
把自己本地安装的zookeeper配置上

还有这个地方broker.id 我这里 master slave1 slave2 分别对于1 2 3,下图是以slave1的为例子

slave1的server.properties参考配置文件
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more # contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with # this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. # The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 # (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with # the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at # # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 # # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and # limitations under the License. # see kafka.server.KafkaConfig for additional details and defaults ############################# Server Basics ############################# # The id of the broker. This must be set to a unique integer for each broker. broker.id=2 ############################# Socket Server Settings ############################# # The port the socket server listens on port=9092 # Hostname the broker will bind to. If not set, the server will bind to all interfaces host.name=192.168.241.141 # Hostname the broker will advertise to producers and consumers. If not set, it uses the # value for "host.name" if configured. Otherwise, it will use the value returned from # java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName(). #advertised.host.name=<hostname routable by clients> # The port to publish to ZooKeeper for clients to use. If this is not set, # it will publish the same port that the broker binds to. #advertised.port=<port accessible by clients> # The number of threads handling network requests num.network.threads=3 # The number of threads doing disk I/O num.io.threads=8 # The send buffer (SO_SNDBUF) used by the socket server socket.send.buffer.bytes=102400 # The receive buffer (SO_RCVBUF) used by the socket server socket.receive.buffer.bytes=102400 # The maximum size of a request that the socket server will accept (protection against OOM) socket.request.max.bytes=104857600 ############################# Log Basics ############################# # A comma seperated list of directories under which to store log files log.dirs=/home/hadoop/app/kafka/kafka-logs # The default number of log partitions per topic. More partitions allow greater # parallelism for consumption, but this will also result in more files across # the brokers. num.partitions=5 # The number of threads per data directory to be used for log recovery at startup and flushing at shutdown. # This value is recommended to be increased for installations with data dirs located in RAID array. num.recovery.threads.per.data.dir=1 ############################# Log Flush Policy ############################# # Messages are immediately written to the filesystem but by default we only fsync() to sync # the OS cache lazily. The following configurations control the flush of data to disk. # There are a few important trade-offs here: # 1. Durability: Unflushed data may be lost if you are not using replication. # 2. Latency: Very large flush intervals may lead to latency spikes when the flush does occur as there will be a lot of data to flush. # 3. Throughput: The flush is generally the most expensive operation, and a small flush interval may lead to exceessive seeks. # The settings below allow one to configure the flush policy to flush data after a period of time or # every N messages (or both). This can be done globally and overridden on a per-topic basis. # The number of messages to accept before forcing a flush of data to disk #log.flush.interval.messages=10000 # The maximum amount of time a message can sit in a log before we force a flush #log.flush.interval.ms=1000 ############################# Log Retention Policy ############################# # The following configurations control the disposal of log segments. The policy can # be set to delete segments after a period of time, or after a given size has accumulated. # A segment will be deleted whenever *either* of these criteria are met. Deletion always happens # from the end of the log. # The minimum age of a log file to be eligible for deletion log.retention.hours=168 # A size-based retention policy for logs. Segments are pruned from the log as long as the remaining # segments don't drop below log.retention.bytes. #log.retention.bytes=1073741824 # The maximum size of a log segment file. When this size is reached a new log segment will be created. log.segment.bytes=1073741824 # The interval at which log segments are checked to see if they can be deleted according # to the retention policies log.retention.check.interval.ms=300000 # By default the log cleaner is disabled and the log retention policy will default to just delete segments after their retention expires. # If log.cleaner.enable=true is set the cleaner will be enabled and individual logs can then be marked for log compaction. log.cleaner.enable=false export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=false offsets.storage=kafka dual.commit.enabled=true delete.topic.enable=true ############################# Zookeeper ############################# # Zookeeper connection string (see zookeeper docs for details). # This is a comma separated host:port pairs, each corresponding to a zk # server. e.g. "127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002". # You can also append an optional chroot string to the urls to specify the # root directory for all kafka znodes. zookeeper.connect=master:2181,slave1:2181,slave2:2181 # Timeout in ms for connecting to zookeeper zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms=1000000
生成启动文件start.sh
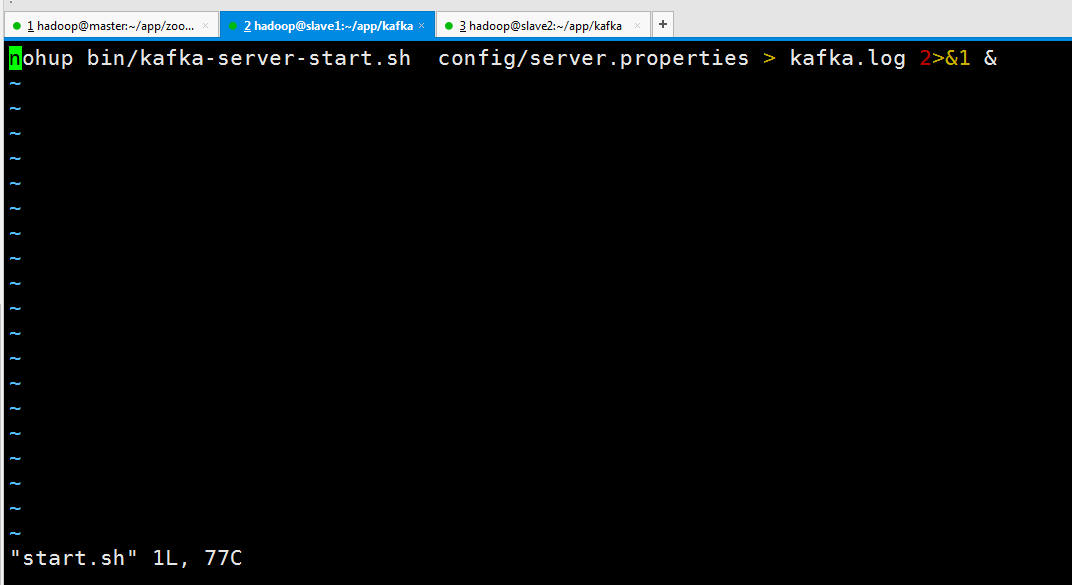
nohup bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties > kafka.log 2>&1 &
其他两节点也一样。
现在分别启动三个节点在zookeeper



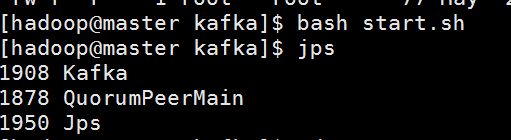
再启动kafka (slave1 slave2也一样)
创建topic操作,并且查看里面的topic
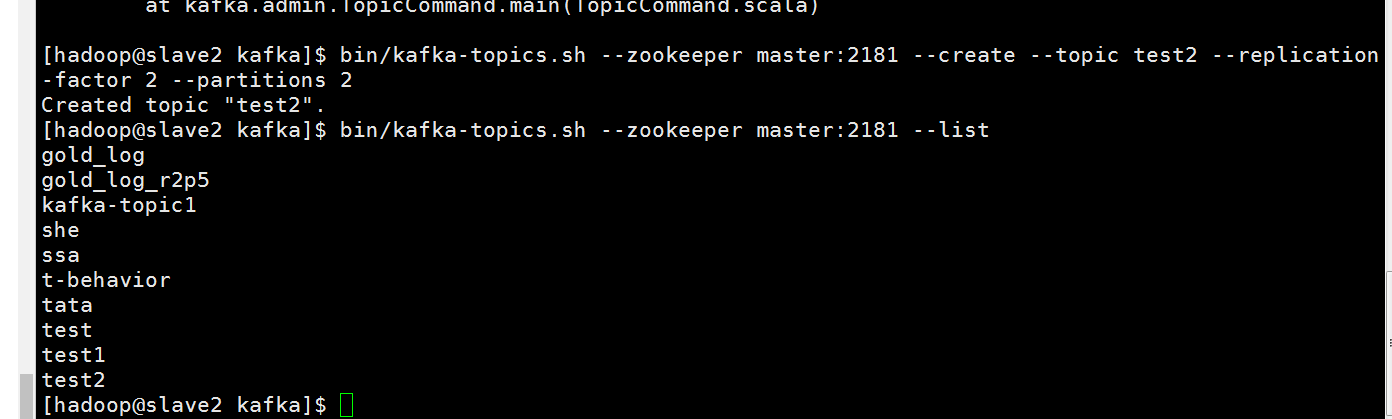
可以到zookeeper里面看看


通过describe命令查看topic是怎么存储的
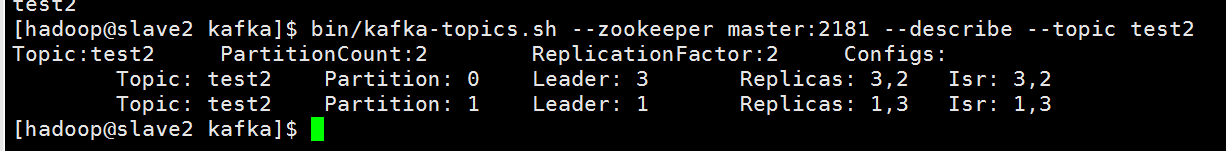
bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper master:2181 --describe --topic test2
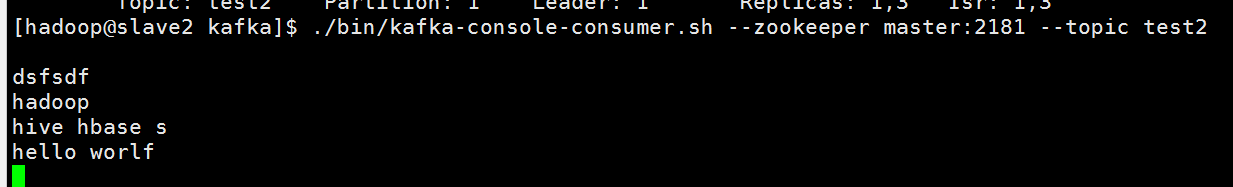
开启kafka consumer

./bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --zookeeper master:2181 --topic test2
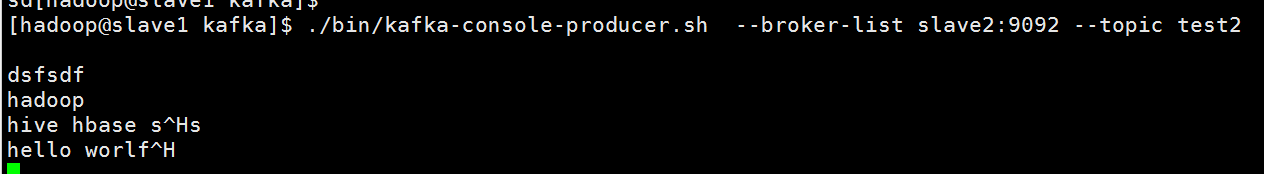
开启kafka producer

./bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list slave2:9092 --topic test2
在producer 敲人一下字母
可以在consumer这边看到