Python 遗传算法实现字符串
流程
1. 初始化
2. 适应度函数
3. 选择
4. 交叉
5. 变异
适应度函数计算方法
计算个体间的差:分别计算每个元素与目标元素的差取平方和
种群:计算总体均值
| 操作 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 编码方式 | ASCII码 |
| 种群规模 | 5000 |
| 初始种群的个体取值范围 | !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! (33,33,33,33,33,33,33,33,33 ,33,33,33,33,33,33,33,33,33) ~ `````````````````` (126,126,126,126,126,126,126,126,126, 126,126,126,126,126,126,126,126,126) |
| 选择操作 | 个体选择概率 |
| 分配策略 | 根据概率保留对应个数 |
| 个体选择方法 | 锦标赛选择方法 |
| 交叉概率 | 0.7 |
| 交叉方式 | 多点交叉 |
| 变异方式 | 随机多点突变 |
| 最大迭代步数 | 500 |
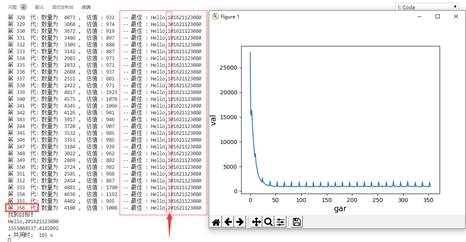
效果图
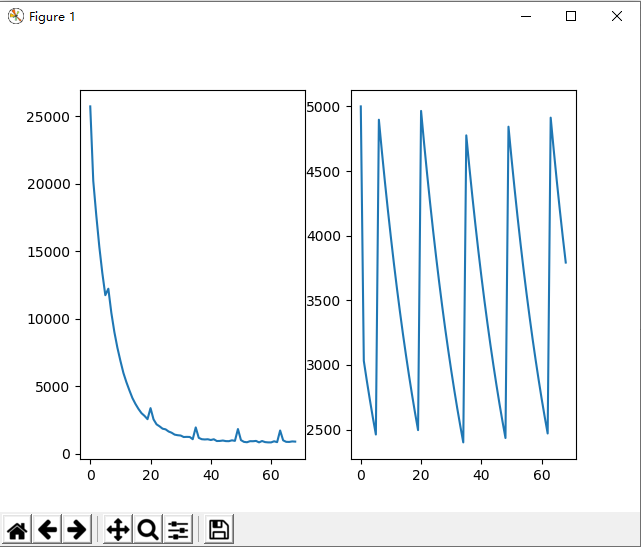

小结
-
一开始我设计的选择方法是把低于平均的个体淘汰,但是这样操作会导致陷入局部最优,循环500次依旧没有结果,很难找到最优个体。后面仔细看书,用书上的锦标赛算法,提高了随机性,可以找到了目标序列。
-
根据流程,我发现经过几轮的遗传,种群规模会迅速下降,因为中间补充的个体数量无法抵消淘汰的个体数量。于是我根据种群规模设计了阶梯式的概率,以便可以维持种群规模。

-
对于上面的问题,我开始想在选择后立即补充
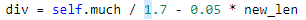
即 y=100/7+0.05x(x为选择后剩余的种群数量),但是补充的内容无法实现最后的功能:1.补充随机新个体,这就和选择前的操作无异,种群适应度没有太大变化。2.补充选择后的个体,会导致陷入局部最优,种群发展速度慢。3.综合 1 2 补充,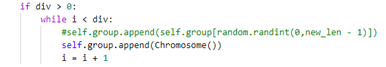
依旧没有明显效果。 -
书上的最优概率,(主要是突变的概率非常低)对于产生新个体的速度较慢,基因重组的效果感觉不够明显,很容易陷入局部最优和陷入一个死局面,需要许久才能跳出这个局面
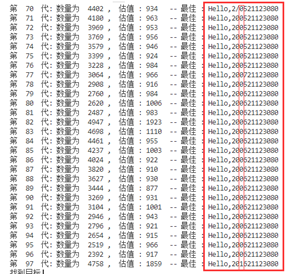
-
后面我自己修改了概率,依旧有这种问题,目前还没解决。
-
这次的代码写的比较不合理,高耦合。有许多地方可以改进,避免大量重复循环,以提高程序执行效率
补充
- 关于补充选择淘汰的个体,我发现可以在cross,即基因重组中改变他后代产生的children个数,直到恢复到设置的种群规模。在基因突变部分,不再是往种群中添加新的个体,而是修改现有种群的基因。
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
best = [72, 101, 108, 108, 111, 44, 105,99,106,98,64,102,111,120,109,97,105,108]
#最佳序列
def get_ran(b=33,e=126):
"""
获取随机字符值,默认从可显示字符开始(33-126)
"""
return random.randint(b,e)
def get_pos(cou=17):
"""
获取随机位置,默认到17
"""
return random.randint(0,cou)
class Chromosome:
"""
染色体类
"""
def __init__(self,dna=None):
"""
初始化,可指定DNA序列顺序,默认DNA为随机序列。
"""
if dna is not None:
self.dna = dna[:]
else :
self.dna = []
for i in range(18):
self.dna.append(get_ran())
def to_asc(self):
"""
将DNA序列由int转为str
"""
str = ''
for chrx in self.dna:
str = str + chr(chrx)
return str
def __str__(self):
"""
将DNA序列由int转为str
"""
str = ''
for chrx in self.dna:
str = str + chr(chrx)
return str
def mutation(self,which=-1):
"""
变异操作,默认产生随机个变异位点,突变为随机值,可指定突变位置
"""
if which == -1 :
i = get_pos()
for x in range(i):
self.dna[get_pos()] = get_ran()
else :
self.dna[which]=get_pos()
def comp(self,other):
"""
计算与指定序列DNA的平方差
"""
l = []
val = 0
for x in range(18):
#print(x)
d = self.dna[x] - other.dna[x]
d = pow(d,2)
l.append(d)
val = val + d
return l,val
def cross(self,other):
"""
该染色体与其他染色体基因重组,产生新染色体,采用多点交叉
"""
new = []
for i in range(18):
if get_pos(1) == 0:
new.append(self.dna[i])
else :
new.append(other.dna[i])
return Chromosome(new)
class Population:
"""
种群类
"""
def __init__(self,much=5000,aim=[72, 101, 108, 108, 111, 44, 105,99,106,98,64,102,111,120,109,97,105,108]):
"""
初始化种群,默认种群数量5000,指定序列为 Hello,icjb@foxmail
"""
self.group = []
self.best = Chromosome(aim)
i = 0
while i < much:
self.group.append(Chromosome())
i = i + 1
def choice(self,p=0.05):
"""
选择操作,采用锦标赛选择方法,默认保留0.05
"""
group = []
old = self.group[:]
count = int(self.group.__len__() * p)
once = int(self.group.__len__() / count)
t_b = old[0]
t = 0
for ch in old:
if t == once:
group.append(t_b)
t_b = ch
t = 0
_,v1 = t_b.comp(self.best)
_,v2 = ch.comp(self.best)
if v1 >= v2 :
t_b = ch
t = t + 1
self.group.clear()
self.group = group[:]
def cross(self,p=0.7):
"""
交叉操作,采用多点交叉
"""
count = int(self.group.__len__()*p)
i = 0
group = []
while i < count:
t = self.group.__len__()
group.append(self.group[get_pos(t-1)].cross(self.group[get_pos(t-1)]))
i = i + 1
self.group = self.group + group
def mutation(self,p=0.001):
"""
种群突变
"""
count = int(self.group.__len__()*p)
i = 0
t = self.group.__len__()
while i < count:
self.group[get_pos(t-1)].mutation()
i = i + 1
def have_the_best(self):
"""
判断是否存在目标序列
"""
for ch in self.group:
_,v = ch.comp(self.best)
if v == 0 :
return True
return False
def value(self):
"""
计算该种群的估值
"""
val = 0
for ch in self.group:
_,v = ch.comp(self.best)
val = val + v
return val / self.group.__len__()
def get_best(self):
"""
获取种群最优个体
"""
best_one = self.group[0]
_,val = best_one.comp(self.best)
for ch in self.group:
_,v = ch.comp(self.best)
if val >= v :
best_one = ch
val = v
return best_one
def big_up(self):
self.choice(0.9)
self.cross(1.5)
self.mutation(0.01)
def big_down(self):
self.choice()
self.cross()
self.mutation()
def main():
"""
主函数
"""
ch_b = Chromosome(best)
po = Population(5000)
i = 1
vals = []
popu = []
while i <= 500:
val = po.value()
leng = po.group.__len__()
str1 = '第 {:^4} 代: 数量为 {:^6}, 估值 :{:^6}'.format(i,leng,int(val))
str2 = ' -- 最佳 : {}'.format(po.get_best().to_asc())
if po.group.__len__() < 500:
#种群个体少于500,需要补充大量新个体以免灭亡
p1 = 0.8
p2 = 1
p3 = 0.12
elif po.group.__len__() < 2500:
p1 = 0.6
p2 = 0.99
p3 = 0.1
elif po.group.__len__() < 5000:
p1 = 0.5
p2 = 0.9
p3 = 0.09
elif po.group.__len__() < 8000:
p1 = 0.3
p2 = 0.82
p3 = 0.08
elif po.group.__len__() < 10000:
p1 = 0.2
p2 = 0.78
p3 = 0.05
else :
#默认操作
p1 = 0.05
p2 = 0.7
p3 = 0.001
# #但估值趋于稳定时,刺激种群
# if val < 1000 :
# p1 = p1 - 0.5
# if p1 <= 0 :
# p1 = 0.05
# p2 = p2 + 0.3
# p3 = p3 + 0.05
#模拟突增突降,可选
# if get_pos(100) < 5 :
# po.big_down()
# print('big-down')
# if get_pos(100) > 95 :
# po.big_up()
# print('big-up')
print(str1+str2)
#print(str2)
po.choice(p1)
if po.have_the_best() :
print('找到目标!')
print(ch_b.to_asc())
break
po.cross(p2)
po.mutation(p3)
vals.append(val)
popu.append(leng)
i = i + 1
#绘图
plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(121)
x = range(i-1)
y = vals[:]
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.subplot(122)
y = popu[:]
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
"""
"""
main()
input()
参考
【算法】超详细的遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm)解析 - 简书
遗传算法学习笔记(一):常用的选择策略 - 依然传奇 - 博客园
基于遗传算法的人工智能实例之拼图游戏(python实现) - 不基调的博客 - CSDN博客
另一版本实现方式,改自GITHUB:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
from random import (choice, random, randint)
__all__ = ['Chromosome', 'Population']
class Chromosome:
_target_gene = "Hello, icjb@foxmail.com"
def __init__(self, gene):
self.gene = gene
self.fitness = Chromosome._update_fitness(gene)
def mate(self, mate):
pivot = randint(0, len(self.gene) - 1)
gene1 = self.gene[:pivot] + mate.gene[pivot:]
gene2 = mate.gene[:pivot] + self.gene[pivot:]
return Chromosome(gene1), Chromosome(gene2)
def mutate(self):
gene = list(self.gene)
delta = randint(44, 122)
idx = randint(0, len(gene) - 1)
gene[idx] = chr((ord(gene[idx]) + delta) % 123)
return Chromosome(''.join(gene))
@staticmethod
def _update_fitness(gene):
fitness = 0
for a, b in zip(gene, Chromosome._target_gene):
fitness += abs(ord(a) - ord(b))
return fitness
@staticmethod
def gen_random():
gene = []
for x in range(len(Chromosome._target_gene)):
gene.append(chr(randint(44, 122)))
return Chromosome(''.join(gene))
class Population:
_tournamentSize = 3
def __init__(self, size=1024, crossover=0.8, elitism=0.1, mutation=0.3):
self.elitism = elitism
self.mutation = mutation
self.crossover = crossover
buf = []
for i in range(size): buf.append(Chromosome.gen_random())
self.population = list(sorted(buf, key=lambda x: x.fitness))
def _tournament_selection(self):
best = choice(self.population)
for i in range(Population._tournamentSize):
cont = choice(self.population)
if (cont.fitness < best.fitness): best = cont
return best
def _selectParents(self):
return (self._tournament_selection(), self._tournament_selection())
def evolve(self):
size = len(self.population)
idx = int(round(size * self.elitism))
buf = self.population[:idx]
while (idx < size):
if random() <= self.crossover:
(p1, p2) = self._selectParents()
children = p1.mate(p2)
for c in children:
if random() <= self.mutation:
buf.append(c.mutate())
else:
buf.append(c)
idx += 2
else:
if random() <= self.mutation:
buf.append(self.population[idx].mutate())
else:
buf.append(self.population[idx])
idx += 1
self.population = list(sorted(buf[:size], key=lambda x: x.fitness))
if __name__ == "__main__":
maxGenerations = 2000
t1 = time.time()
pop = Population(size=2000, crossover=0.7, elitism=0.05, mutation=0.9)
li = []
x = []
for i in range(1, maxGenerations + 1):
print("Generation %d Fitness:%d Result:%s" % (i, Chromosome._update_fitness(pop.population[0].gene),pop.population[0].gene) )
if pop.population[0].fitness == 0: break
else:pop.evolve()
li.append(Chromosome._update_fitness(pop.population[0].gene))
xx = 0
for p in range(pop.population.__len__()):
xx += Chromosome._update_fitness(pop.population[p].gene)
xx = xx / pop.population.__len__()
x.append(xx)
x.sort()
print(x[0])
print("Maximum generations reached without success.")
t2 = time.time()
t = int(t2 - t1)
print(f'+ 共用时: {t} s')
plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(111)
x = range(i-1)
y = li[:]
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.xlabel("generation",fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel("fitness",fontsize=12)
plt.show()