这篇将基于jdk1.7对HashMap部分重要代码做下分析
一、存储结构
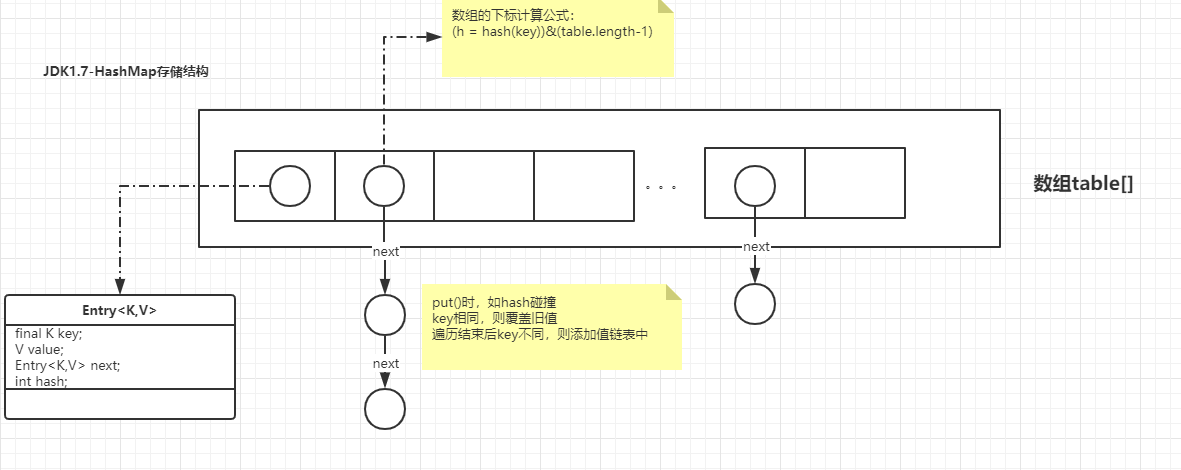
HashMap的数据结构是数组+链表(哈希表,也称散列表)的组合
二、原理
成员变量
/** * 构造函数不指定容量时,默认容量16 */ static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 /** * 最大指定容量,2^30,最接近整数的最大值 */ static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /** * 默认负载因子0.75,例如容量为16时,在put超过16 * 0.75 = 12将扩容 */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /** * 空数组 */ static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {}; /** * 实际存储数据的数组,默认为空 */ transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE; /** * 实际存储的元素个数 */ transient int size; /** * 临界值,当前数组最大存储的元素个数,超过将扩容 */ int threshold; /** * 负载因子 */ final float loadFactor; /** * 修改次数 */ transient int modCount; /** * 整数最大值*/ static final int ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD_DEFAULT = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
元素结点
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; V value; /** * 记录下一个结点 */ Entry<K,V> next; int hash; /** * 构造赋值 */ Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n; key = k; hash = h; } ... ... }
构造函数
构造时并不会初始化数组table,而是在第一次put时通过 inflateTable() 初始化(用Map来初始化例外)
/** * 指定容量、加载因子 */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) // 如果指定容量超过2^30,则设定为2^30 initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; // 临界值此时为容量大小,在初始化table时将重新设置 threshold = initialCapacity; // 这个init()方法其实是个模板方法设计模式,看看LinkedHashMap就知道了 init(); } public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); } public HashMap() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); } public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1, DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); inflateTable(threshold); putAllForCreate(m); }
put方法
public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { // 这个时候初始化数组 inflateTable(threshold); } // 1. key为空时,数组index为0,将添加或覆盖到table[0]处 if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); // 2. key不为空,找出下标,并遍历链表 int hash = hash(key); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { // 已经存在这个key值了,覆盖旧值 V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; // table[i]中没有存储这个key、value,那就放到table[i]的链表头处 // 至于为什么说是头插法,请看addEntry方法 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; } /** * 添加元素至table[bucketIndex] */ void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { // 扩容,重新hash resize(2 * table.length); // 扩容后,这个要插入的元素槽位也要重新计算 hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); } /** * 记录插入前table[bucketIndex]位置的元素,将它作为要插入元素的next, * 由此可见,jdk1.7链表的插入方式是头插法 */ void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; }
get方法
public V get(Object key) { if (key == null) // 遍历table[0]的链表,取值 return getForNullKey(); Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key); return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue(); } private V getForNullKey() { if (size == 0) { return null; } for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) return e.value; } return null; } final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { if (size == 0) { return null; } int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) // hash、key都相等,取元素 return e; } return null; }
扩容机制
void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { // 当前table的容量已经是最大的了,将临界值调至最大 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } // 构造新数组,数量为传入的数量(一般是当前长度的两倍做扩充) Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; // rehash transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); table = newTable; threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); } /** * 重新整理元素,这是最消耗性能的点 */ void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } }
扩容极其消耗性能,所以如果我们预知元素的个数,构造函数预设容量将有效提高性能。