1.寄存器:最快的存储区, 由编译器根据需求进行分配,我们在程序中无法控制.
2. 栈:方法执行时创建方法栈帧,存放基本类型的变量数据和对象的引用,但对象本身不存放在栈中,而是存放在堆(new 出来的对象)或者常量池中(字符串常量对象存放在常量池中。)
3. 堆:存放所有new出来的对象。
4. 静态域(方法区):存放静态成员(static定义的)
5. 常量池(方法区):存放字符串常量和基本类型常量(public static final)。
6. 非RAM存储:硬盘等永久存储空间
这里我们主要关心栈,堆和常量池,对于栈和常量池中的对象可以共享,对于堆中的对象不可以共享。栈中的数据大小和生命周期是可以确定的,当没有引用指向数据时,这个数据就会消失。堆中的对象的由垃圾回收器负责回收,因此大小和生命周期不需要确定,具有很大的灵活性。
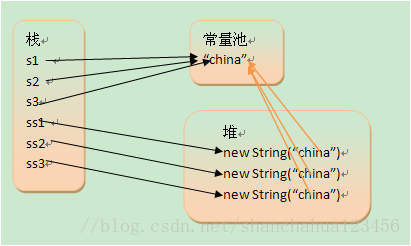
对于字符串:其对象的引用都是存储在栈中的,如果是编译期已经创建好(直接用双引号定义的)的就存储在常量池中,如果是运行期(new出来的)才能确定的就存储在堆中。对于equals相等的字符串,在常量池中永远只有一份,在堆中有多份。
如以下代码:
-
String s1 = "china";
-
String s2 = "china";
-
String s3 = "china";
-
String ss1 = new String("china");
-
String ss2 = new String("china");
-
String ss3 = new String("china");
这里解释一下黄色这3个箭头,对于通过new产生一个字符串(假设为”china”)时,会先去常量池中查找是否已经有了”china”对象,如果没有则在常量池中创建一个此字符串对象,然后堆中再创建一个常量池中此”china”对象的拷贝对象。这也就是有道面试题:String s = new String(“xyz”);产生几个对象?一个或两个,如果常量池中原来没有”xyz”,就是两个。
对于基础类型的变量和常量:变量和引用存储在栈中,常量存储在常量池中。
如以下代码:
-
int i1 = 9;
-
int i2 = 9;
-
int i3 = 9;
-
public static final int INT1 = 9;
-
public static final int INT2 = 9;
-
public static final int INT3 = 9;
对于成员变量和局部变量:成员变量就是方法外部,类的内部定义的变量;局部变量就是方法或语句块内部定义的变量。局部变量必须初始化。
形式参数是局部变量,局部变量的数据存在于栈内存中。栈内存中的局部变量随着方法的消失而消失。
成员变量存储在堆中的对象里面,由垃圾回收器负责回收。
如以下代码:
package com.study.stackheap; /** * @author mdl * @date 2019/11/15 */ public class BirthDate { private int day; private int month; private int year; public BirthDate(int d, int m, int y) { day = d; month = m; year = y; } /** * @return the day */ public int getDay() { return day; } /** * @param day the day to set */ public void setDay(int day) { this.day = day; } /** * @return the month */ public int getMonth() { return month; } /** * @param month the month to set */ public void setMonth(int month) { this.month = month; } /** * @return the year */ public int getYear() { return year; } /** * @param year the year to set */ public void setYear(int year) { this.year = year; } }
package com.study.stackheap; /** * @author mdl * @date 2019/11/15 * https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34467922/article/details/80790443 */ public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { int date = 9; Test test = new Test(); test.change(date); BirthDate d1 = new BirthDate(7, 7, 1970); System.out.println("date---" + date); } public void change(int i) { i = 1234; } }
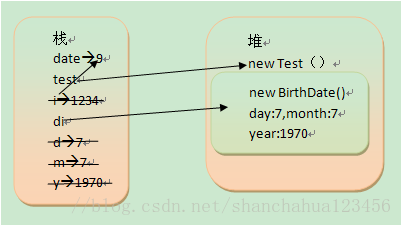
对于以上这段代码,date为局部变量,i,d,m,y都是形参为局部变量,day,month,year为成员变量。下面分析一下代码执行时候的变化:
1. main方法开始执行:int date = 9;
date局部变量,基础类型,引用和值都存在栈中。
2. Test test = new Test();
test为对象引用,存在栈中,对象(new Test())存在堆中。
3. test.change(date);
i为局部变量,引用和值存在栈中。当方法change执行完成后,i就会从栈中消失。
4. BirthDate d1= new BirthDate(7,7,1970);
d1为对象引用,存在栈中,对象(new BirthDate())存在堆中,其中d,m,y为局部变量存储在栈中,且它们的类型为基础类型,因此它们的数据也存储在栈中。day,month,year为成员变量,它们存储在堆中(new BirthDate()里面)。当BirthDate构造方法执行完之后,d,m,y将从栈中消失。
5.main方法执行完之后,date变量,test,d1引用将从栈中消失,new Test(),new BirthDate()将等待垃圾回收。