1.1 实例化方式
l 3种bean实例化方式:默认构造、静态工厂、实例工厂
1.1.1 默认构造
|
<bean id="" class=""> 必须提供默认构造 |
1.1.2 静态工厂
l 常用与spring整合其他框架(工具)
l 静态工厂:用于生成实例对象,所有的方法必须是static
|
<bean id="" class="工厂全限定类名" factory-method="静态方法"> |
1.1.2.1 工厂-创建实例
|
public class MyBeanFactory { public static UserService createService(){ return new UserServiceImpl(); }} |
1.1.2.2 spring配置
|
<!-- 将静态工厂创建的实例交予spring class 确定静态工厂全限定类名 factory-method 确定静态方法名 --> <bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.c_inject.b_static_factory.MyBeanFactory" factory-method="createService"></bean> |
1.1.3 实例工厂
l 实例工厂:必须先有工厂实例对象,通过实例对象创建对象。提供所有的方法都是“非静态”的。
1.1.3.1 工厂
|
/** 实例工厂,所有方法非静态 创建实例 */ public class MyBeanFactory { public UserService createService(){ return new UserServiceImpl(); } } |
1.1.3.2 spring配置
|
<!-- 创建工厂实例 --> <bean id="myBeanFactoryId" class="com.itheima.c_inject.c_factory.MyBeanFactory"></bean> <!-- 获得userservice * factory-bean 确定工厂实例 * factory-method 确定普通方法--> <bean id="userServiceId" factory-bean="myBeanFactoryId" factory-method="createService"></bean> |
1.2 Bean种类
l 普通bean:之前操作的都是普通bean。<beanid="" class="A"> ,spring直接创建A实例,并返回
l FactoryBean:是一个特殊的bean,具有工厂生成对象能力,只能生成特定的对象。
bean必须使用 FactoryBean接口,此接口提供方法 getObject() 用于获得特定bean。
<bean id="" class="FB"> 先创建FB实例,使用调用getObject()方法,并返回方法的返回值
FB fb = new FB();
returnfb.getObject();
l BeanFactory 和 FactoryBean 对比?
BeanFactory:工厂,用于生成任意bean。
FactoryBean:特殊bean,用于生成另一个特定的bean。例如:ProxyFactoryBean ,此工厂bean用于生产代理。<bean id=""class="....ProxyFactoryBean"> 获得代理对象实例。AOP使用
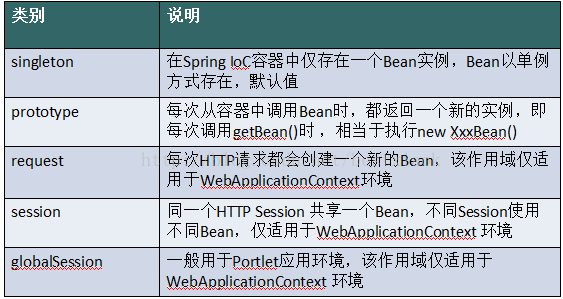
1.3 作用域
l 作用域:用于确定spring创建bean实例个数
l 取值:
singleton 单例,默认值。
prototype 多例,每执行一次getBean将获得一个实例。例如:struts整合spring,配置action多例。
l 配置信息
|
<bean id="" class="" scope=""> |
|
<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.d_scope.UserServiceImpl" scope="prototype" ></bean> |
1.4 生命周期-11个步骤
1.4.1 初始化和销毁
l 目标方法执行前后执行后,将进行初始化或销毁。
|
<bean id="" class="" init-method="初始化方法名称" destroy-method="销毁的方法名称"> |
1.4.1.1 目标类
|
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Override public void addUser() { System.out.println("e_lifecycle add user"); } public void myInit(){ System.out.println("初始化"); } public void myDestroy(){ System.out.println("销毁"); } } |
1.4.1.2 spring配置
|
<!-- init-method 用于配置初始化方法,准备数据等 destroy-method 用于配置销毁方法,清理资源等 --> <bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.e_lifecycle.UserServiceImpl" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestroy" ></bean> |
1.4.1.3 测试
|
@Test public void demo02() throws Exception{ //spring 工厂 String xmlPath = "com/itheima/e_lifecycle/beans.xml"; ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId"); userService.addUser(); //要求:1.容器必须close,销毁方法执行; 2.必须是单例的 // applicationContext.getClass().getMethod("close").invoke(applicationContext); // * 此方法接口中没有定义,实现类提供 applicationContext.close();
} |
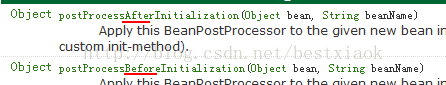
1.4.2 BeanPostProcessor 后处理Bean
l spring 提供一种机制,只要实现此接口BeanPostProcessor,并将实现类提供给spring容器,spring容器将自动执行,在初始化方法前执行before(),在初始化方法后执行after() 。 配置<bean class="">
l Factory hook(勾子) that allows for custom modification of new bean instances, e.g.checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.
l spring提供工厂勾子,用于修改实例对象,可以生成代理对象,是AOP底层。
模拟
A a =new A();
a = B.before(a) --> 将a的实例对象传递给后处理bean,可以生成代理对象并返回。
a.init();
a = B.after(a);
a.addUser(); //生成代理对象,目的在目标方法前后执行(例如:开启事务、提交事务)
a.destroy()
1.4.2.1 编写实现类
|
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("前方法: " + beanName); return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("后方法: " + beanName); // bean 目标对象 // 生成 jdk 代理 return Proxy.newProxyInstance( MyBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler(){ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("------开启事务"); //执行目标方法 Object obj = method.invoke(bean, args); System.out.println("------提交事务"); return obj; }}); } } |
1.4.2.2 配置
|
<!-- 将后处理的实现类注册给spring --> <bean class="com.itheima.e_lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean> |
l 问题1:后处理bean作用某一个目标类,还是所有目标类?
所有
l 问题2:如何只作用一个?
通过“参数2”beanName进行控制
1.5 属性依赖注入
l 依赖注入方式:手动装配 和 自动装配
l 手动装配:一般进行配置信息都采用手动
基于xml装配:构造方法、setter方法
基于注解装配:
l 自动装配:struts和spring 整合可以自动装配
byType:按类型装配
byName:按名称装配
constructor构造装配,
auto: 不确定装配。
1.5.1 构造方法
1.5.1.1 目标类
|
public class User { private Integer uid; private String username; private Integer age; public User(Integer uid, String username) { super(); this.uid = uid; this.username = username; } public User(String username, Integer age) { super(); this.username = username; this.age = age; } |
1.5.1.2 spring配置
|
<!-- 构造方法注入 * <constructor-arg> 用于配置构造方法一个参数argument name :参数的名称 value:设置普通数据 ref:引用数据,一般是另一个bean id值 index :参数的索引号,从0开始。如果只有索引,匹配到了多个构造方法时,默认使用第一个。 type :确定参数类型 --> <bean id="userId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.a_constructor.User" > <constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="1"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" type="java.lang.Integer" value="2"></constructor-arg> </bean> |
1.5.2 setter方法
|
<!-- setter方法注入 * 普通数据 <property name="" value="值"> 等效 <property name=""> <value>值 * 引用数据 <property name="" ref="另一个bean"> 等效 <property name=""> <ref bean="另一个bean"/> --> <bean id="personId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.b_setter.Person"> <property name="pname" value="阳志"></property> <property name="age"> <value>1234</value> </property> <property name="homeAddr" ref="homeAddrId"></property> <property name="companyAddr"> <ref bean="companyAddrId"/> </property> </bean> <bean id="homeAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.b_setter.Address"> <property name="addr" value="阜南"></property> <property name="tel" value="911"></property> </bean> <bean id="companyAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.b_setter.Address"> <property name="addr" value="北京八宝山"></property> <property name="tel" value="120"></property> </bean> |
1.5.3 P命令空间[了解]
l 对“setter方法注入”进行简化,替换<property name="属性名">,而是在
<beanp:属性名="普通值" p:属性名-ref="引用值">
l p命名空间使用前提,必须添加命名空间
|
<bean id="personId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.c_p.Person" p:pname="禹太璞" p:age="22" p:homeAddr-ref="homeAddrId" p:companyAddr-ref="companyAddrId"> </bean> <bean id="homeAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.c_p.Address" p:addr="DG" p:tel="东莞"> </bean> <bean id="companyAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.c_p.Address" p:addr="DG" p:tel="岛国"> </bean> |
1.5.4 SpEL[了解]
l 对<property>进行统一编程,所有的内容都使用value
<propertyname="" value="#{表达式}">
#{123}、#{'jack'} : 数字、字符串
#{beanId} :另一个bean引用
#{beanId.propName} :操作数据
#{beanId.toString()} :执行方法
#{T(类).字段|方法} :静态方法或字段
|
<!-- <property name="cname" value="#{'jack'}"></property> <property name="cname" value="#{customerId.cname.toUpperCase()}"></property> 通过另一个bean,获得属性,调用的方法 <property name="cname" value="#{customerId.cname?.toUpperCase()}"></property> ?. 如果对象不为null,将调用方法 --> <bean id="customerId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.d_spel.Customer" > <property name="cname" value="#{customerId.cname?.toUpperCase()}"></property> <property name="pi" value="#{T(java.lang.Math).PI}"></property> </bean> |
1.5.5 集合注入
|
<!-- 集合的注入都是给<property>添加子标签 数组:<array> List:<list> Set:<set> Map:<map> ,map存放k/v 键值对,使用<entry>描述 Properties:<props> <prop key=""></prop> 【】 普通数据:<value> 引用数据:<ref> --> <bean id="collDataId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.e_coll.CollData" > <property name="arrayData"> <array> <value>DS</value> <value>DZD</value> <value>屌丝</value> <value>屌中屌</value> </array> </property>
<property name="listData"> <list> <value>于嵩楠</value> <value>曾卫</value> <value>杨煜</value> <value>曾小贤</value> </list> </property> <property name="setData"> <set> <value>停封</value> <value>薄纸</value> <value>关系</value> </set> </property> <property name="mapData"> <map> <entry key="jack" value="杰克"></entry> <entry> <key><value>rose</value></key> <value>肉丝</value> </entry> </map> </property> <property name="propsData"> <props> <prop key="高富帅">嫐</prop> <prop key="白富美">嬲</prop> <prop key="男屌丝">挊</prop> </props> </property> </bean> |