线程的创建和关闭需要花费时间,可能会浪费资源,所以可以通过让线程复用来解决这个问题。
线程池就是这样一个概念,当需要创建线程的时候直接从线程池中获取,当关闭线程的时候直接归还线程给线程池。

ThreadPoolExecutor就是JDK提供的这样一个类。
它继承AbstructExecutorService类,AbstructExecutorService类实现ExecutorSerive接口,ExecutorSerive接口继承Executor接口。
具体方法可以在API中自行查看。
看一下ThreadPoolExtcutor的构造方法:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) { if (corePoolSize < 0 || maximumPoolSize <= 0 || maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize || keepAliveTime < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize; this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize; this.workQueue = workQueue; this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime); this.threadFactory = threadFactory; this.handler = handler; }
下面是对它参数的解释:
corePoolSize:指定了线程池中线程的数量
maximumPoolSize:指定了线程池中线程的最大数量
keepAliveTime:当线程数量超过corePoolSize,多余线程的存活时间
TimeUnit:keepAliveTime的单位
workQueue:任务队列,被提交但还没执行的任务
threadFactory:用于创建线程
Handler:线程太多的拒绝策略
线程池有四个构造函数,其他三个只是把一些参数变成了默认而已,然后调用的这个构造函数。
对线程池类有点基本的了解之后接下来看看另一个类Extcutors。它是一个工厂类,可以从它获得特定功能的线程池。
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(xxxxxxx)
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(xxxx)
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(xxxxx)
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(xxxx)
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(xxxxx)
功能分别是获得固定线程数目的线程池,获得一个线程的线程池,获得线程数量可变的线程池,获得可在给定时间执行的单线程池,获得可在给定时间执行的多线程池。
对于前三个来说,它们只是根据参数不同对ThreadPoolExecutor进行了封装。
而ScheduledExecutorService则是继承自ExecutorService,又在它的基础上添加了一些功能。
写个小例子:
public class demo implements Runnable{ public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService es=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { es.submit(new Thread(new demo())); } } public void run() { System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
获得一个数量为2的固定线程数量线程池,在run里面每个线程sleep两秒,结果如下
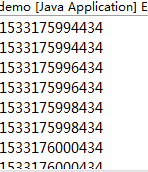
可以清楚地看到每两秒后两个线程被执行。
线程的逻辑调度如下:
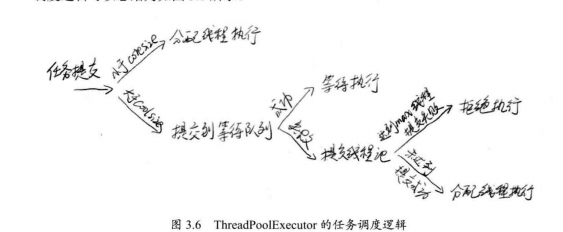
当线程池满,队列也满的时候,会采用拒绝策略,JDK提供了四种内置拒绝策略在线程池类里面:

具体的可以自行查找相关资料。
自此告一段落,线程池还有很多内容没有总结,后续再总结吧。