rsync语法:
Local: rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [DEST] #<===本地传输数据 Access via remote shell: #<===借助通道传输数据,本地-远程主机;远程主机-本地 Pull: rsync [OPTION...] [USER@]HOST:SRC... [DEST] #<===从远程主机拉取数据到本地 Push: rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [USER@]HOST:DEST #<===从本地推数据到远程主机 Access via rsync daemon: #<===通过守护进程(socket网络套接字)传输数据---重点 Pull: rsync [OPTION...] [USER@]HOST::SRC... [DEST] #<===注意daemon模式下传输数据,使用的是自定义的模块的名称 Push: rsync [OPTION...] SRC... [USER@]HOST::DEST
本地传输模式和借助通道传输模式使用实例
[root@meinv01 ~]# rsync /etc/hosts /tmp/ #<==本地到本地
[root@meinv01 ~]# ls /tmp/
hosts
ssh-NFCFOdb882
[root@meinv01 ~]# rsync -avz /etc/hosts -e 'ssh -p 22' root@192.168.81.169:~ #<==借助ssh通道,拷贝本地文件到远程主机,如果是远程拉取数据到本地,调换一下位置即可
root@192.168.81.169's password:
sending incremental file list
sent 30 bytes received 12 bytes 12.00 bytes/sec
total size is 158 speedup is 3.76
[root@meinv02 ~]# ll
total 44
-rw-------. 1 root root 1116 Aug 1 12:58 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 158 Aug 1 12:35 hosts
注意点:源路径如果是一个目录的话,带上尾随斜线和不带尾随斜线是不一样的,不带尾随斜线表示的是整个目录包括目录本身,带上尾随斜线表示的是目录中的文件,不包括目录本身
如:
[root@xuexi ~]# rsync -a /etc /tmp #<==表示把etc这个目录及其目录下的文件和目录拷贝到tmp下 [root@xuexi ~]# rsync -a /etc/ /tmp #<==只把etc下的文件及目录拷贝到tmp
rsync的常用参数说明:(-avzP相当于-vzrtopgDlP,脚本内用az即可)
-v --verbose 输出传输时的进度信息 -z --compress 传输时进行压缩传输以提高效率 --compress-level=NUM可按级别压缩 -a --archive 归档模式,递归方式传输并保持所有文件属性,等价于--rtopgDl -r --recursive 对子目录以递归模式传输,小写r参数 -t --times 保持文件时间信息 -o --owner 保持文件属主信息 -p --perms 保持文件权限信息 -g --group 保持文件属组信息 -P --progress 显示同步的过程及传输的进度等信息 -D --devices 保持文件设备信息 -l --links 保持软链接信息 -e --rsh=command 指定使用的信道协议,指定替换的rsh的shell程序,如ssh --exclude=pattern 指定排除不需要的传输的文件模式 --exclude-from=file 排除指定文件内容中的文件 --bwlimit=RATE 传输时进行限速(整数) --delete 同步参数(慎用
rsync通过守护进程socket传输数据图解:
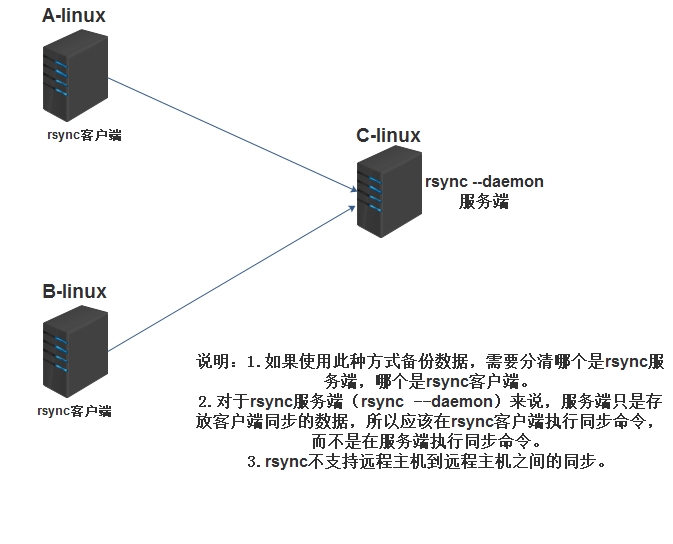
rsync服务端配置:
[root@C-linux ~]# uname -r #<==查看版本号 2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64 [root@C-linux ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS release 6.5 (Final) [root@C-linux ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables status #<==停止防火墙 iptables: Firewall is not running. [root@C-linux ~]# getenforce #<==关闭selinux Disabled [root@C-linux ~]# rpm -qa|grep rsync #<==服务端和客户端和要保证rsync软件包已安装 rsync-3.0.6-9.el6_4.1.x86_64 [root@C-linux ~]# rsync --version #<==查看rsync版本号 rsync version 3.0.6 protocol version 30 [root@C-linux ~]# rz -y rz waiting to receive. ???a? zmodem ′???£ °′ Ctrl+C ???£ ??′?? rsyncd.conf... 100% 562 bytes 562 bytes/s 00:00:01 0 ′? ?[root@C-linux ~]# ls rsyncd.conf [root@C-linux ~]# cp rsyncd.conf /etc/ [root@C-linux ~]# useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin rsync #<==添加指定用户作为传输时使用的用户 [root@C-linux ~]# id rsync uid=502(rsync) gid=502(rsync) 组=502(rsync) [root@C-linux ~]# vi /etc/rsyncd.conf [root@C-linux ~]# cat /etc/rsyncd.conf #<==rsync服务端配置文件具体配置 #rsync_configuration #port=873 # 指定rsync端口。默认873(没有特殊需求,使用默认端口即可) uid = rsync # rsync服务的运行用户,默认是nobody,文件传输成功后属主将是这个uid gid = rsync # rsync服务的运行组,默认是nobody,文件传输成功后属组将是这个gid use chroot = no # rsync daemon在传输前是否切换到指定的path目录下,并将其监禁在内 max connections = 200 # 指定最大连接数量,0表示没有限制 timeout = 300 # 链接超时时间,确保rsync服务器不会永远等待一个崩溃的客户端,0表示永远等待 pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid # 指定rsync daemon的pid文件 lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock # 指定锁文件 log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log # 指定rsync的日志文件存放,而不把日志发送给syslog
[data] # 模块ID ,传输数据时指定模块ID,就会将数据传输到模块指定对应的目录下 path = /data/ # 指定该模块的路径,该参数必须指定。启动rsync服务前该目录必须存在。rsync请求访问模块本质就是访问该路径 ignore errors # 忽略某些IO错误信息 read only = false # 指定该模块是否可读写,即能否上传文件,false表示可读写,true表示可读不可写。所有模块默认不可上传 #write only = false # 指定该模式是否支持下载,设置为true表示客户端不能下载。所有模块默认可下载 list = false # 客户端请求显示模块列表时,该模块是否显示出来,设置为false则该模块为隐藏模块。默认true hosts allow = 10.0.0.0/24 # 指定允许连接到该模块的机器,多个ip用空格隔开或者设置区间 hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32 # 指定不允许连接到该模块的机器 auth users = rsync_backup # 指定连接到该模块的用户列表,只有列表里的用户才能连接到模块,用户名和对应密码保存在secrts file中, # 这里使用的不是系统用户,而是虚拟用户。不设置时,默认所有用户都能连接,但使用的是匿名连接 secrets file = /etc/rsync.password # 保存auth users用户列表的用户名和密码,每行包含一个username:passwd。由于"strict modes", # 默认为true,所以此文件要求非rsync daemon用户不可读写。只有启用了auth users该选项才有效 #rsync_config_______________end #[test] # 以下定义的是第二个模块(根据情况加载即可) :wq #<==保存退出
[root@C-linux ~]# mkdir /data #<==创建rsync模块所存放的目录 [root@C-linux ~]# chown -R rsync.rsync /data #<==授权 [root@C-linux ~]# echo 'rsync_backup:123456' >/etc/rsync.password #<==指定密码文件 [root@C-linux ~]# cat /etc/rsync.password rsync_backup:123456 [root@C-linux ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password #<==此文件权限需为600,否则出错 [root@C-linux ~]# ll /etc/rsync.password -rw------- 1 root root 20 1月 31 13:16 /etc/rsync.password
[root@C-linux ~]# rsync --daemon #<==启动rsync服务 [root@C-linux ~]# netstat -lntup|grep rsync #查看服务是否起来 [root@C-linux ~]# echo 'rsync --daemon' >>/etc/rc.local
以上是服务端(rsync --damon)的配置,下面
配置客户端
[root@A-linux ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables stop [root@A-linux ~]# getenforce Disabled
[root@A-linux ~]# rpm -qa|grep rsync [root@A-linux ~]# echo '123456' >/etc/rsync.password [root@A-linux ~]# cat /etc/rsync.password #<===客户端密码文件只需要保留密码即可,无需将用户一起保留 123456 [root@A-linux ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password [root@A-linux ~]# ll /etc/rsync.password -rw------- 1 root root 7 1月 31 13:28 /etc/rsync.password
配置完成后,需要注意2个地方:
1. 数据的流向是从客户端到服务端,在客户端进行拉/推操作数据流向
2. 所有操作(备份)都是在客户端,服务端只是守护进程
3. 配置好rsync --daemon服务端后,在客户端推拉数据的时候,就不用借用通道了,直接是使用服务端侦听的端口传输数据
测试验证:
客户端推数据到服务端
[root@A-linux ~]# rsync -avz /tmp/ rsync_backup@10.0.0.4::data --password-file=/etc/rsync.password sending incremental file list ./ hosts .ICE-unix/ ssh-hBbdsD1500/ ssh-hBbdsD1500/agent.1500 sent 253 bytes received 41 bytes 588.00 bytes/sec total size is 166 speedup is 0.56
服务端查看数据
[root@C-linux ~]# ll /data/ 总用量 8 -rw-r--r-- 1 rsync rsync 166 1月 31 10:36 hosts drwx------ 2 rsync rsync 4096 1月 31 13:27 ssh-hBbdsD1500
如果出现报错信息,查看日志排错即可! 更多rsync知识及原理深入了解,请查看好友博客