关于仙人掌的同构,主要是我太蒟蒻了QAQ,问了好几位大佬才弄好。
手撕仙人掌,你得先有手套 ,你得先了解以下基本知识
a.点双连通分量,没什么好说得,仙人掌上有环,判环用点双
b.树的hash点这里
c.仙人掌点这里
对于一棵仙人掌,我们通过一些方法来简化:
我们最讨厌的是环,假如说没有环,那么树的hash还是蛮简单的。
OK那么就是圆方树了,如果你还不知道什么是圆方树,请自行百度或者点这里。
当然对于判定仙人掌的同构,不需要一颗完整的圆方树,只需要在环中间建点
单纯地表示一个环,使用最小表示法(这部分内容我稍后补充QAQ)
单纯地表示一棵树,hash。
嗯,如果你觉得我上面说得十分模糊,那么是正确的,因为还没有开始呢 ^_^
(我其实是不会告诉你我没有用tarjan和完整的圆方树的)
e.g.一个只有一个环的仙人掌
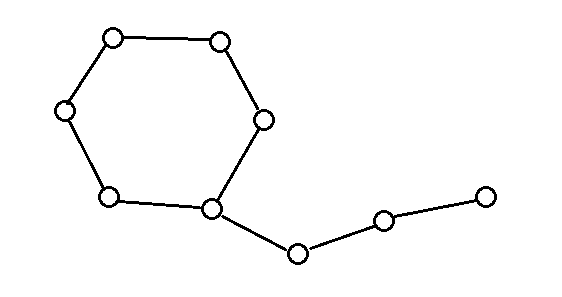
假设我们是这样搜索的
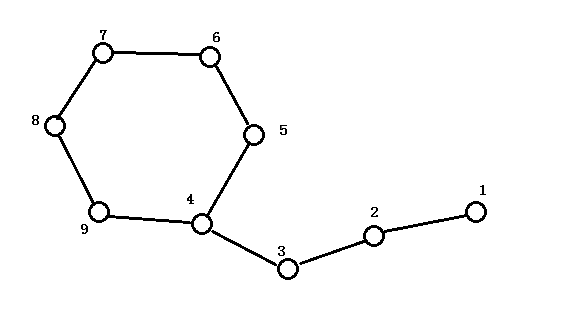
那么在dfs的过程中,要判定一个点在不在环上,记录它的父节点这样在回溯到4时,发现他有一个不是自己儿子的子节点(9)
哈,那就是环的另一端了。
这时抓出9,一直回溯父亲直到4被枚举到,整个环就被揪了出来。
新建一个节点,(在圆方树里则称方点)依次连边。
而对于非环上边直接连就好了
像这样就建立了一个独立出原图的树(一位大佬是这样描述的)
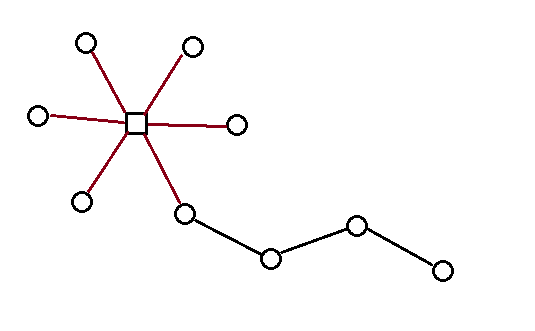
多么优雅的一棵树
好了,现在它是无根的找一下树的重心
新建一个根节点hash一下就好了^_^
你真的觉得这就完了
你太天真了
环是不能这样子搞的
正确打开方式:
别忘了真正的环上点是有顺序的
假如说这个环的方点(中间那个新建点)是根,跑最小表示法(然而我代码里没有这一项QAQ我改天加上)
对于一个普通树节点比如说这样
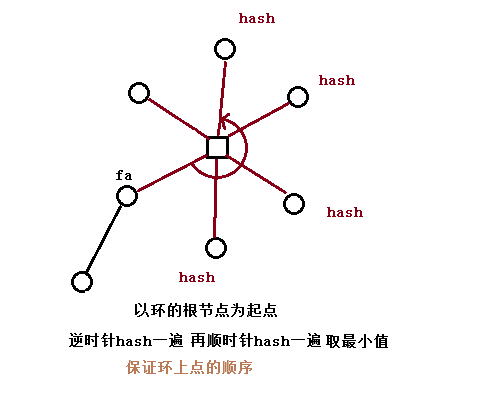
这样就可以了
代码实现
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef unsigned long long ult; 6 const ult seed1=1324983271ull; 7 const ult seed2=4327894239ull; 8 const ult lth1=9301248721ull; 9 const ult lth2=8317498371ull; 10 int nt,mt; 11 bool cmp(ult x,ult y) 12 { 13 return x<y; 14 } 15 struct pnt{ 16 int hd; 17 int sh; 18 int fa; 19 int wgt; 20 bool ong; 21 bool vis; 22 bool chkd; 23 ult has; 24 }; 25 struct ent{ 26 int twd; 27 int lst; 28 }; 29 struct Cactus{ 30 pnt p[300000]; 31 ent e[500000]; 32 ent r[500000]; 33 ult st[1000000]; 34 int rt[2]; 35 int n,m; 36 int sqn; 37 int cnt; 38 int cmt; 39 void e_ade(int f,int t) 40 { 41 cnt++; 42 e[cnt].twd=t; 43 e[cnt].lst=p[f].hd; 44 p[f].hd=cnt; 45 } 46 void r_ade(int f,int t) 47 { 48 cmt++; 49 r[cmt].twd=t; 50 r[cmt].lst=p[f].sh; 51 p[f].sh=cmt; 52 } 53 void tr_dfs(int x,int f) 54 { 55 p[x].vis=true; 56 for(int i=p[x].hd;i;i=e[i].lst) 57 { 58 int to=e[i].twd; 59 if((i^f)==1)continue; 60 if(!p[to].vis) 61 { 62 p[to].fa=x; 63 p[x].ong=false; 64 tr_dfs(to,i); 65 if(!p[x].ong) 66 { 67 r_ade(x,to); 68 r_ade(to,x); 69 } 70 }else{ 71 if(p[to].chkd)continue; 72 sqn++; 73 int u=x; 74 for(u=x;;u=p[u].fa) 75 { 76 r_ade(n+sqn,u); 77 r_ade(u,n+sqn); 78 p[u].ong=true; 79 if(u==to)break; 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 p[x].chkd=true; 84 } 85 void gravity(int x,int f) 86 { 87 p[x].wgt=1; 88 bool fl=true; 89 for(int i=p[x].sh;i;i=r[i].lst) 90 { 91 int to=r[i].twd; 92 if(to==f)continue; 93 gravity(to,x); 94 p[x].wgt+=p[to].wgt; 95 if(p[to].wgt*2>sqn+n) 96 fl=false; 97 } 98 if((sqn+n-p[x].wgt)*2>sqn+n) 99 fl=false; 100 if(fl) 101 { 102 if(rt[0]) 103 { 104 rt[1]=x; 105 }else{ 106 rt[0]=x; 107 } 108 } 109 } 110 void Hash(int x,int f) 111 { 112 int top=0; 113 for(int i=p[x].sh;i;i=r[i].lst) 114 { 115 int to=r[i].twd; 116 if(to==f)continue; 117 Hash(to,x); 118 } 119 if(x<=n) 120 { 121 for(int i=p[x].sh;i;i=r[i].lst) 122 { 123 int to=r[i].twd; 124 if(to==f)continue; 125 st[++top]=p[to].has; 126 } 127 sort(st+1,st+top+1,cmp); 128 p[x].has=seed1; 129 for(int i=1;i<=top;i++) 130 { 131 p[x].has=((p[x].has*lth1+st[i])^st[i])+st[i]; 132 } 133 }else{ 134 int i; 135 for(i=p[x].sh;i;i=r[i].lst) 136 { 137 if(r[i].twd==f) 138 break; 139 } 140 for(i=r[i].lst;i;i=r[i].lst) 141 { 142 int to=r[i].twd; 143 st[++top]=p[to].has; 144 } 145 for(i=p[x].sh;i;i=r[i].lst) 146 { 147 int to=r[i].twd; 148 if(to==f) 149 break; 150 st[++top]=p[to].has; 151 } 152 ult tmp1=seed2,tmp2=seed2; 153 for(i=1;i<=top;i++) 154 { 155 tmp1=((tmp1*lth2+st[i])^st[i])+st[i]; 156 } 157 for(i=top;i;i--) 158 { 159 tmp2=((tmp2*lth2+st[i])^st[i])+st[i]; 160 } 161 p[x].has=min(tmp1,tmp2); 162 p[x].has*=lth2; 163 } 164 } 165 ult solve(int nn,int mm) 166 { 167 n=nn; 168 m=mm; 169 cnt=1; 170 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 171 { 172 int x; 173 int y; 174 scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); 175 e_ade(x,y); 176 e_ade(y,x); 177 } 178 tr_dfs(1,0); 179 gravity(1,0); 180 r_ade(0,rt[0]); 181 if(rt[1]) 182 { 183 r_ade(0,rt[1]); 184 for(int i=p[rt[0]].sh;i;i=r[i].lst) 185 { 186 if(r[i].twd==rt[1]) 187 r[i].twd=0; 188 } 189 for(int i=p[rt[1]].sh;i;i=r[i].lst) 190 { 191 if(r[i].twd==rt[0]) 192 r[i].twd=0; 193 } 194 } 195 Hash(0,0); 196 return p[0].has; 197 } 198 }C[2]; 199 int main() 200 { 201 scanf("%d%d",&nt,&mt); 202 if(C[0].solve(nt,mt)==C[1].solve(nt,mt)) 203 { 204 printf("YES "); 205 }else{ 206 printf("NO "); 207 } 208 return 0; 209 }
大概就是这样了^_^