这几天正在对SSM框架的知识进行一个回顾加深,有很多东西学的囫囵吞枣,所以利用一些时间进一步的学习。首先大概了解一下mybatis的使用,再通过一个案例来学习它。
什么是MyBatis
Mybatis(前身是iBatis)是一个支持普通SQL查询、存储过程以及高级映射的持久层框架,它消除了几乎所有的JDBC代码和参数的手动设置以及对结果集的检索,
并使用简单的XML或注解进行配置和原始映射,用以将接口和Java的POJO(Plain Old Java Object,普通Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录,使得Java开发人员可以使用面向对象的编程思想来操作数据库。
MyBatis框架也称之为ORM(Object/Relational Mapping,即对象关系映射)框架。所谓的ORM框架就是一种为了解决面向对象与关系型数据库中数据类型不匹配的技术,
它通过描述Java对象与数据库表之间的映射关系,自动将Java应用程序中的对象持久化到关系型数据库的表中。
当前的ORM框架有很多,常见的ORM框架有Hibernate和MyBatis。这两个框架的主要区别如下:
-
Hibernate:是一个全表映射框架。通常开发者只需要定义好持久化对象到数据库表的映射关系,就可以通过Hibernate 提供的方法完成持久层操作。
开发者并不需要熟练地掌握SQL语句的编写,Hibernate会根据制定的存储逻辑,自动生成对应的SQL,并调用JDBC接口来执行,所以其开发效率会高于MyBatis。
然而Hibernate自身也存在着一些缺点,例如它在多表关联时,对SQL查询的支持比较差;更新数据时,需要发送所有字段;不支持存储过程;不能通过优化SQL来优化性能等。
这些问题导致其只适合在场景不太复杂且对性能要不高的项目中使用。 -
MaBatis:是一个半自动映射的框架。这里所谓的“半自动化”是相对于Hibernate全表映射而言的,MyBatis需要手动匹配提供POJO、SQL和映射关系,而Hibernate只需要提供POJO和映射关系即可。
与Hibernate相比,虽然使用MyBatis手动编写SQL要比使用Hibernate的工作量大,但MyBatis可以配置动态SQL并优化SQL,可以通过配置决定SQL的映射规则,它还支持存储过程等。
对于一些复杂的和需要优化性能的项目来说,显然使用Mybatis更加合适。
我是比较喜欢用MyBatis,所以会更加深入的去学习,而Hibernate我只是了解了点,没有学习很多。
MyBatis的下载和使用
下载MyBatis可以到GitHub网址进行下载,如下图所示:

下载第一个框架压缩包就可以了,使用MyBatis很简单,只需要在应用程序中引入MyBatis的核心包和lib目录下的依赖包就可以了。
MyBatis的工作原理
简单的了解MyBatis的工作原理如下图所示:
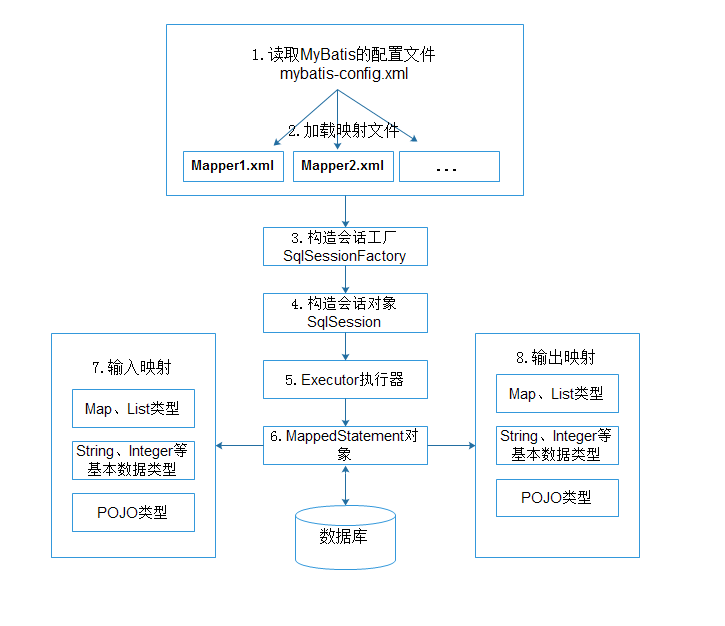
从图中可以看出,MyBatis在操作数据库时,大体经过了8个步骤。
1.读取MyBatis的配置文件mybatis-config.xml。mybatis-config.xml作为MyBatis的全局配置文件,配置了MyBatis的运行环境等信息,其中主要内容是获取数据库连接。
2.加载映射文件Mapper.xml。Mapper.xml文件即SQL映射文件,该文件中配置了操作数据库的SQL语句,需要在mybatis-config.xml中加载才能执行。mybatis-config.xml可以加载多个配置文件,每个配置文件对应数据库中的一张表。
3.构建会话工厂。通过MyBatis的环境等配置信息构建会话工厂SqlSessionFactory。
4.创建SqlSession对象。由会话工厂创建SqlSession对象,该对象中包含了执行SQL的所有方法。
5.MyBatis底层定义了一个Executor接口来操作数据库,它会根据SqlSession传递的参数动态地生成需要执行的SQL语句,同时负责查询缓存的维护。
6.在Executor接口执行方法中,包含一个MappedStatement类型的参数,该参数是对映射信息的封装,用于存储要映射的SQL语句的id、参数等。
Mapper.xml文件中一个SQL对应一个MappedStatement对象,SQL的id即是MappedStatement的id。
7.输入类型映射。在执行方法时,MappedStatement对象会对用户执行SQL语句的输入参数进行定义(可以定义为Map、List类型、基本类型和POJO类型),
Executor执行器会通过MappedStatement对象在执行SQL前,将输入的Java对象映射到SQL语句中。这里对输入参数的映射过程就类似于JDBC编程中对preparedStatement对象设置参数的过程。
8.输出结果映射。在数据库中执行完SQL语句后,MappedStatement对象会对SQL执行输出的结果进行定义(可以定义为Map、List类型、基本类型和POJO类型),
Executor执行器会通过MappedStatement对象在执行SQL后,将输出结果映射至Java对象中。这种将输出结果映射到Java对象的过程就类似于JDBC编程中对结果的解析处理过程。
MyBatis的入门案例
开发工具:idea
Java环境: jdk1.8.0_121
数据库:SQLServer
1.新建数据库,表
use mybatis
create table t_customer (
id int identity(1,1) PRIMARY key,
username varchar(50),
jobs varchar(50),
phone varchar(16)
)
insert into t_customer values ('joy','doctor','13745874847');
insert into t_customer values ('jack','teacher','1376874847');
insert into t_customer values ('tom','worker','13745874858');
2.在idea中新建项目,并添加所需的包,如下图:
3.创建log4j.properties文件,编辑以下内容:
log4j.rootLogger=Error, stdout
log4j.logger.com.itheima=DEBUG
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
4.创建持久化类Customer,声明属性。
package com.itheima.po;
/**
* @author mz
* @version V1.0
* @Description: 客户实体类
* @create 2017-10-31 13:04
*/
public class Customer {
private Integer id; //主键
private String username; //客户名称
private String jobs; //职业
private String phone; //电话
//省略setter和getter方法
}
5.新建CustomerMapper.xml文件添加基础的增删改查语句。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace表示命名空间-->
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.CustomerMapper">
<!--根据客户编号获取客户信息-->
<select id="findCustomerById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer where id = #{id}
</select>
<!--根据名称查询-->
<select id="findCustomerByName" parameterType="String" resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer where username like '%${value}%'
</select>
<!--添加客户-->
<insert id="addCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
insert into t_customer(username,jobs,phone)
values (#{username},#{jobs},#{phone})
</insert>
<!--更新客户信息-->
<update id="updateCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
update t_customer set username=#{username}, jobs=#{jobs}, phone=#{phone}
where id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteCustomer" parameterType="Integer">
delete from t_customer where id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
6.编写MyBatis的核心配置文件:mybatis-config.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!--配置环境,默认的环境id为sqlserver-->
<environments default="sqlserver">
<!--配置id为sqlserver的数据库环境-->
<environment id="sqlserver">
<!--使用JDBC的事务管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--数据库连接池-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:sqlserver://IP加端口;DatabaseName=mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="sa"/>
<property name="password" value="输入自己的密码"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--配置mapper的位置-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/itheima/mapper/CustomerMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
7.编写测试类MyBatisTest
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.po.Customer;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author mz
* @version V1.0
* @Description: Mybatis测试
* @create 2017-10-31 13:20
*/
public class MybatisTest {
/**
* 根据客户编号查询客户信息
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void findCustomerByIdTest() throws Exception {
//读取配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,返回结果映射结果
Customer customer = sqlSession.selectOne("com.itheima.mapper.CustomerMapper.findCustomerById", 1);
System.out.println(customer.toString());
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 模糊匹配查询
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void findCustomerByNameTest() throws Exception {
//读取配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,返回结果映射结果
List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.itheima.mapper.CustomerMapper.findCustomerByName", "j");
for (Customer customer : customers) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 添加客户
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void addCustomerTest() throws Exception {
//读取配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//创建对象,添加数据
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("rose");
customer.setJobs("student");
customer.setPhone("1335848798");
//SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,返回结果映射结果
int rows = sqlSession.insert("com.itheima.mapper.CustomerMapper.addCustomer", customer);
if (rows > 0) {
System.out.println("你已经成功插入了"+ rows +"条数据!");
} else {
System.out.println("failed");
}
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 更新客户
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void updateCustomerTest() throws Exception {
//读取配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//创建对象,更新数据
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setId(4);
customer.setUsername("rose");
customer.setJobs("programmer");
customer.setPhone("13111111111");
//执行更新语句
int rows = sqlSession.update("com.itheima.mapper.CustomerMapper.updateCustomer", customer);
if (rows > 0){
System.out.println("你成功修改了"+ rows+"条数据!");
} else {
System.out.println("failed");
}
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 删除用户
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void deleteCustomerTest()throws Exception {
//读取配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
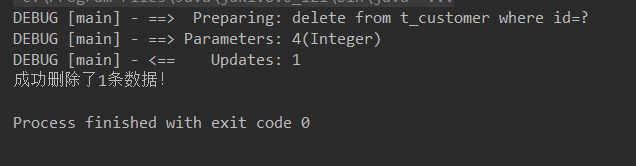
int rows = sqlSession.delete("com.itheima.mapper.CustomerMapper.deleteCustomer", 4);
if (rows > 0) {
System.out.println("成功删除了"+rows+"条数据!");
} else {
System.out.println("failed");
}
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
}
以上的代码我都已经实现的,都是可以运行的,可以根据自己的喜好创建这些文件,包,类等。
部分运行结果图:
MybatisUtils工具类和db.properties
上面的测试代码中有很多的重复代码,可以抽取出来封装成一个工具类,数据库的配置信息可以单独建一个properties文件,然后在mybatis-config文件中添加properties元素。
MybatisUtils工具类
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.Reader;
/**
* @author mz
* @version V1.0
* @Description: mybatis工具类
* @create 2017-11-01 10:02
*/
public class MybatisUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
//初始化SqlSessionFactory对象
static {
try {
//使用M主Batis提供的Resources类加载MyBatis的配置文件
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
//构建SqlSessionFactory工厂
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取SqlSession对象的静态方法
* @return
*/
public static SqlSession getSession() {
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
测试代码就可以修改成以下的样子了:
@Test
public void addCustomerTest() throws Exception {
/*//读取配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//根据配置文件构建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();*/
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSession();
//创建对象,添加数据
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("rose");
customer.setJobs("student");
customer.setPhone("1335848798");
//SqlSession执行映射文件中定义的SQL,返回结果映射结果
int rows = sqlSession.insert("com.itheima.mapper.CustomerMapper.addCustomer", customer);
if (rows > 0) {
System.out.println("你已经成功插入了"+ rows +"条数据!");
} else {
System.out.println("failed");
}
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
db.properties文件
jdbc.driver=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
jdbc.url=jdbc:sqlserver://IP端口;DatabaseName=mybatis
jdbc.username=sa
jdbc.password=
mybatis-config.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="db.properties"/>
<!--配置环境,默认的环境id为sqlserver-->
<environments default="sqlserver">
<!--配置id为sqlserver的数据库环境-->
<environment id="sqlserver">
<!--使用JDBC的事务管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--数据库连接池-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--配置mapper的位置-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/itheima/mapper/CustomerMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
小结
主要是熟悉了MyBatis的工作原理,并能够使用MyBatis框架完成基本的数据库操作。这是我自己在看书学习的,
以上大部分内容是根据Java EE企业级应用开发教程(Spring+Spring MVC+MyBatis)做的一些笔记和总结。如果你喜欢,可以去买这本书看看,个人觉得挺好的。