OSGi 系列(十)之 Blueprint
blueprint 是 OSGi 的一个规范,类似于 spring 的 IOC,用来处理 OSGi 的动态特性,可以大大简化服务的使用。
blueprint 是以 xml 文档来构建应用,但它也有采用 Annotation 的方式,我们在此只介绍 xml 的方式。
在 bundle 里,这个 xml 默认的位置在 OSGi-INF/blueprint 下,也可以在 MANIFEST.MF 里指定其它位置上的 xml 文档。
Bundle-Blueprint: OSGI-INF/blueprint/blueprint.xml
1. Blueprint XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<blueprint xmlns="http://www.osgi.org/xmlns/blueprint/v1.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.osgi.org/xmlns/blueprint/v1.0.0 https://osgi.org/xmlns/blueprint/v1.0.0/blueprint.xsd">
<!--1. 默认构造函数-->
<bean id="obj" class="java.lang.Object" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="name" value="MP4" />
<property name="type" ref="type1" />
</bean>
<!--2. 构造函数-->
<bean id="obj" class="java.lang.Object" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<argument value="..."/>
<argument value="..."/>
</bean>
<!--3. 工厂方法-->
<bean id="obj2" factory-ref="factory" factory-method="method"/>
</blueprint>
blueprint 的使用方法与 spring 差不多。
2. blueprint 的环境管理器注入
Blueprint Container 规范还定义了许多特殊的环境管理器,它们设置 ID 并提供对环境组件的访问。它们不具有 XML 定义,并且也不能被重写,因为它们的 ID 被保护起来,不能被其他管理器使用。环境管理器提供的对象只能被注入到使用引用的其他管理器中。Blueprint Container 规范定义了 4 种环境管理器:
blueprintBundle提供包的 Bundle(org.osgi.framework.Bundle) 对象。blueprintBundleContext提供包的 BundleContext(org.osgi.framework.BundleContext) 对象。blueprintContainer为包提供 BlueprintContainer(org.osgi.service.blueprint.container.BlueprintContainer) 对象。blueprintConverter为包提供 Converter(org.osgi.service.blueprint.container.Converter) 对象,提供了对 Blueprint Container 类型转换工具的访问
<bean id="" class="" init-method="">
<property name="bundle" ref="blueprintBundle" />
<property name="bundleContext" ref="blueprintBundleContext" />
</bean>
3. blueprint 复杂属性注入
<bean class="com.edu.osgi.blueprint.Order" init-method="init">
<property name="id" value="20160320" />
<property name="products">
<!--1. 集合、数组的注入-->
<list>
<ref component-id="mp4"/>
<ref component-id="dianshi"/>
</list>
</property>
<property name="map">
<!--2. map的注入-->
<map>
<entry key="createDate" value="20160320" />
<entry key="userId" value="101" />
</map>
</property>
</bean>
4. blueprint 注册、使用服务
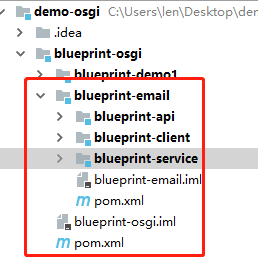
(1) 新建 3 个 bundle,目录结构如下:
(2) blueprint-api 为接口
package com.github.binarylei.email.api;
public interface EmailService {
void sendEmail(String to, String title, String content);
}
(3) blueprint-service 发布服务
package com.github.binarylei.email.service;
import com.github.binarylei.email.api.EmailService;
public class EmailServiceImpl implements EmailService {
public void sendEmail(String dest, String title, String content) {
System.out.println("OSGi email send. dest=" + dest + ",title=" + title + ",content=" + content);
}
}
在 OSGI-INF/blueprint 新建 blueprint.xml 文件,发布服务:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<blueprint xmlns="http://www.osgi.org/xmlns/blueprint/v1.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.osgi.org/xmlns/blueprint/v1.0.0 https://osgi.org/xmlns/blueprint/v1.0.0/blueprint.xsd">
<bean id="emailServiceImpl" class="com.github.binarylei.email.service.EmailServiceImpl"/>
<service interface="com.github.binarylei.email.api.EmailService" ref="emailServiceImpl">
<service-properties>
<entry key="vendor" value="163"/>
</service-properties>
</service>
</blueprint>
(3) blueprint-client 处理服务
package com.github.binarylei.email.client;
import com.github.binarylei.email.api.EmailService;
public class EmailClient {
private EmailService emailService;
public EmailService getEmailService() {
return emailService;
}
public void setEmailService(EmailService emailService) {
this.emailService = emailService;
}
public void init() {
emailService.sendEmail("binarylei@qq.com", "blueprint", "成功了");
}
}
在 OSGI-INF/blueprint 新建 blueprint.xml 文件,接收服务:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<blueprint xmlns="http://www.osgi.org/xmlns/blueprint/v1.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.osgi.org/xmlns/blueprint/v1.0.0 https://osgi.org/xmlns/blueprint/v1.0.0/blueprint.xsd">
<!--服务的引用-->
<reference id="emailService" interface="com.github.binarylei.email.api.EmailService"
filter="(vendor=163)"/>
<bean id="client" class="com.github.binarylei.email.client.EmailClient" init-method="init">
<property name="emailService" ref="emailService"/>
</bean>
</blueprint>
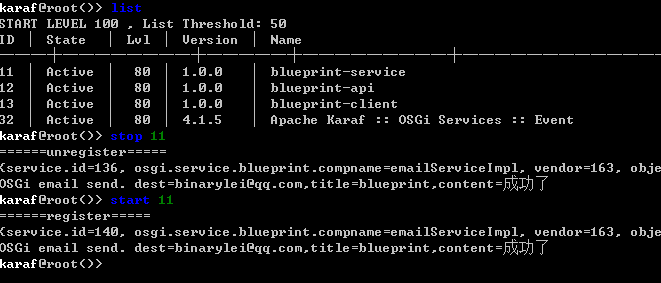
(4) 测试结果如下:

5. blueprint 服务的跟踪
(1) 在 blueprint-client 中编写一个监听类 EmailServiceListener
package com.github.binarylei.email.client;
import com.github.binarylei.email.api.EmailService;
import org.osgi.framework.ServiceReference;
import java.util.Map;
public class EmailServiceListener {
// member-type="service-object"
public void register(EmailService emailService, Map<?, ?> properties) {
System.out.println("======register=====");
System.out.println(properties);
emailService.sendEmail("binarylei@qq.com", "blueprint", "成功了");
}
/*public void register(EmailService emailService) {
}*/
// member-type="service-reference"
/*public void register(ServiceReference reference) {
}*/
public void unregister(EmailService emailService, Map<?, ?> properties) {
System.out.println("======unregister=====");
System.out.println(properties);
emailService.sendEmail("binarylei@qq.com", "blueprint", "成功了");
}
}
(2) blueprint.xml 配制文件
<!--服务的跟踪-->
<reference-list interface="com.github.binarylei.email.api.EmailService" member-type="service-object">
<reference-listener ref="emailServiceListener" bind-method="register" unbind-method="unregister"/>
</reference-list>
<bean id="emailServiceListener" class="com.github.binarylei.email.client.EmailServiceListener"/>
(3) 测试结果如下: