JUC源码分析-集合篇(六)LinkedBlockingQueue
1. 数据结构
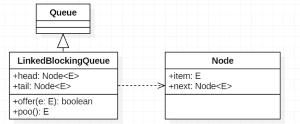
LinkedBlockingQueue 和 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 一样都是由 head 节点和 last 节点组成,每个节点(Node)由节点元素(item)和指向下一个节点(next)的引用组成,节点与节点之间就是通过这个 next 关联起来,从而组成一张链表结构的队列。默认情况下 head 节点存储的元素为空,last 节点等于 head 节点。和 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 不同的是 LinkedBlockingQueue 是基于 ReentrantLock 锁实现的,因此 head、last 以及 Node.item、Node.next 都不用 volatile 修辞。
// head.item == null
transient Node<E> head;
// last.next == null
private transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
}
默认情况下 head、last 都是空节点。
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
last = head = new Node<E>(null);
}
2. 基于 ReentrantLock 的实现
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
// 集合已空则调用notEmpty.await,等集合添加元素后调用notEmpty.singal
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
// 集合已满则调用notFull.await,等集合取出元素后调用notFull.singal
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
3. 入队 offer
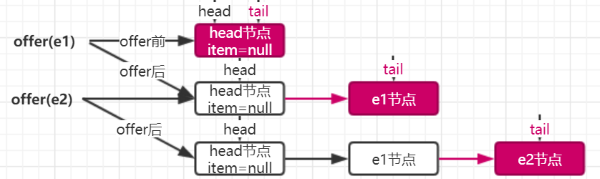
和 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 不同,last 是实时指向尾节点的,也就是每次插入元素时都会更新尾节点。代码如下
// offer 非阻塞
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == capacity)
return false;
// 1. c表示插入前元素的个数
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
// 2. 元素入队有2个操作:一是元素添加到last.next并更新last;
// 二是唤醒阻塞的put操作继续添加元素(只有put时会阻塞notFull.await)
if (count.get() < capacity) {
// 2.1 元素入队
enqueue(node);
// 2.2 c表示插入前元素的个数
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// 2.3 集合未满,唤醒put操作,继续添加元素
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
// 3. 插入前集合为空,则唤醒take操作,可以取元素了
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
return c >= 0;
}
元素入队 enqueue 有两个操作:一是 last.next 节点指向 node;二是 last 指向新的尾节点 node。也就是说 last 一定是指向尾节点的。
private void enqueue(Node<E> node) {
// assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert last.next == null;
last = last.next = node;
}
4. 出队 poll
// poll 非阻塞
public E poll() {
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
E x = null;
// 1. poll操作前元素的个数
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
// 2. 元素出队有2个操作:一是head.next出队
// 二是唤醒阻塞的take操作继续取出元素(只有take时会阻塞notEmpty.await)
if (count.get() > 0) {
// 2.1 head.next出队
x = dequeue();
// 2.2 c为poll前元素的个数
c = count.getAndDecrement();
// 2.3 集合中元素不为空,唤醒take操作,断续取元素
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
// 3. 取元素前集合已满,则唤醒put操作,可以继续添加元素
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}
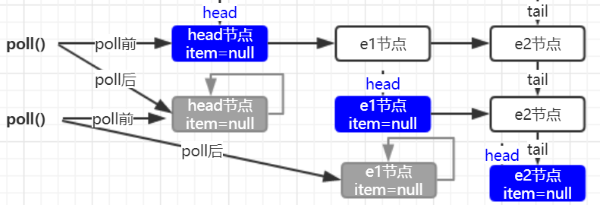
元素出队 dequeue 有三个操作:一是 head.next 出队;二是 head.next 指向自己,等待 GC 回收;三是修改 head 节点。
private E dequeue() {
// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert head.item == null;
Node<E> h = head;
Node<E> first = h.next;
h.next = h; // help GC
head = first;
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;
}
5. 删除元素 remove
// 删除指定 value 的元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
fullyLock();
try {
for (Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next;
p != null;
trail = p, p = p.next) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
// 删除指定节点 p,其中 trail 为 p 的前驱节点
unlink(p, trail);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
// 删除指定节点 p,其中 trail 为 p 的前驱节点
// 注意 p.next 没变
void unlink(Node<E> p, Node<E> trail) {
// assert isFullyLocked();
// p.next is not changed, to allow iterators that are
// traversing p to maintain their weak-consistency guarantee.
p.item = null;
trail.next = p.next;
if (last == p)
last = trail;
if (count.getAndDecrement() == capacity)
notFull.signal();
}
5. 将集合中的元素取出 drainTo
// 将集合中的全部元素取出到集合 c 中
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c) {
return drainTo(c, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
// 将集合中的 maxElements 个元素取出到集合 c 中
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) {
if (c == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (maxElements <= 0)
return 0;
boolean signalNotFull = false;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
int n = Math.min(maxElements, count.get());
// count.get provides visibility to first n Nodes
Node<E> h = head;
int i = 0;
try {
while (i < n) {
Node<E> p = h.next;
c.add(p.item);
p.item = null;
h.next = h;
h = p;
++i;
}
return n;
} finally {
if (i > 0) {
// assert h.item == null;
head = h;
signalNotFull = (count.getAndAdd(-i) == capacity);
}
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
if (signalNotFull)
signalNotFull();
}
}
每天用心记录一点点。内容也许不重要,但习惯很重要!