【目录】
一、布局相关的标签
二、盒子模型
三、浮动
四、定位
(有个即刻偷师学艺的方法——
在浏览器里,打开一个设计很棒的网页,鼠标点击右键,选择“检查”,即可查看网页的HTML+CSS代码和相对应的布局位置
调试自己写的网页时,也可以使用“检查”直接修改代码)
一、布局相关的标签
二、盒子模型
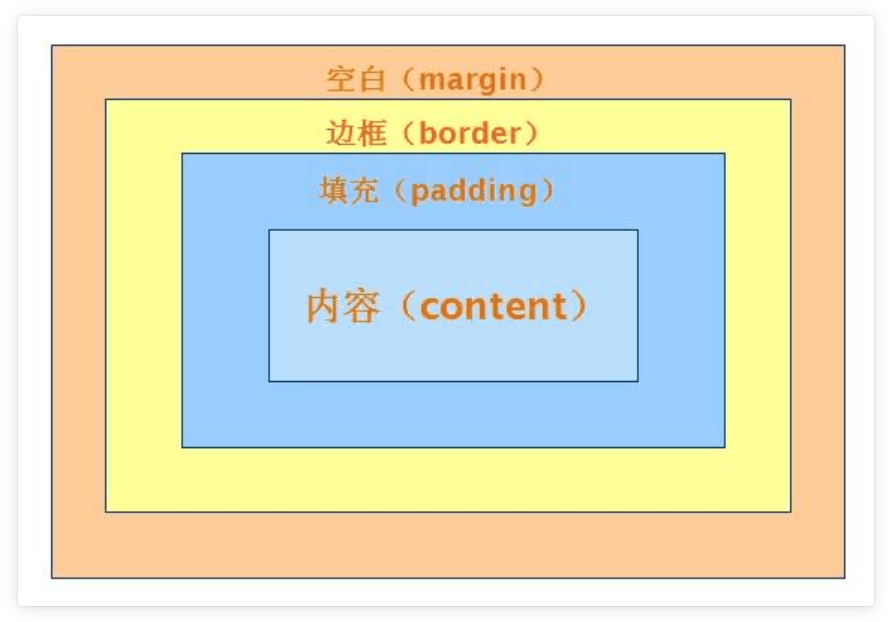
1、什么是盒子模型
# 就以快递盒为例
快递盒与快递盒之间的距离(标签与标签之间的距离 margin外边距)
盒子的厚度(标签的边框 border)
盒子里面的物体到盒子的距离(内容到边框的距离 padding内边距)
物体的大小(内容 content)
# 如果你想要调整标签与标签之间的距离 你就可以调整margin
# 浏览器会自带8px的margin,一般情况下我们在写页面的时候,上来就会先将body的margin去除

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <style> body { margin: 0; /*上下左右全是0 /*margin: 10px 20px; !* 第一个上下 第二个左右*!*/ /*margin: 10px 20px 30px; !*第一个上 第二个左右 第三个下*!*/ /*margin: 10px 20px 30px 40px; !*上 右 下 左*!*/ } /*p {*/ /* margin-left: 0;*/ /* margin-top: 0;*/ /* margin-right: 0;*/ /* margin-bottom: 0;*/ /*}*/ #d1 { margin-bottom: 50px; } #d2 { margin-top: 20px; /*不叠加 只取大的*/ } #dd { margin: 0 auto; /*只能做到标签的水平居中*/ } p { border: 3px solid red; /*padding-left: 10px;*/ /*padding-top: 20px;*/ /*padding-right: 20px;*/ /*padding-bottom: 50px;*/ /*padding: 10px;*/ /*padding: 10px 20px;*/ /*padding: 10px 20px 30px;*/ /*padding: 10px 20px 30px 40px;*/ /*规律和margin一模一样*/ } </style> </head> <body> <!-- <p style="border: 1px solid red;" id="d1">ppp</p>--> <!-- <p style="border: 1px solid orange;" id="d2">ppp</p>--> <!--<div style="border: 3px solid red;height: 400px; 400px">--> <!-- <div id='dd' style="border: 1px solid orange;height: 50px; 50px;background-color: blue;"></div>--> <!--</div>--> <p>ppp</p> </body> </html>
2、盒子模型相关的CSS属性
(1)布局属性
display 显示
| 值 | 描述 |
| ------------ | ---------------------------------------------------- |
| none | 此元素不会被显示。 |
| block | 此元素将显示为块级元素,此元素前后会带有换行符。 |
| inline | 默认。此元素会被显示为内联元素,元素前后没有换行符。 |
| inline-block | 行内块元素。(CSS2.1 新增的值) |
float 浮动
| 值 | 描述 |
| ------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
| left | 元素向左浮动。 |
| right | 元素向右浮动。 |
| none | 默认值。元素不浮动,并会显示在其在文本中出现的位置。 |
| inherit | 规定应该从父元素继承 float 属性的值。 |
clear 清除
| 值 | 描述 |
| ------- | ------------------------------------- |
| left | 在左侧不允许浮动元素。 |
| right | 在右侧不允许浮动元素。 |
| both | 在左右两侧均不允许浮动元素。 |
| none | 默认值。允许浮动元素出现在两侧。 |
| inherit | 规定应该从父元素继承 clear 属性的值。 |
visibility 可见
| 值 | 描述 |
| -------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| visible | 默认值。元素是可见的。 |
| hidden | 元素是不可见的。 |
| collapse | 当在表格元素中使用时,此值可删除一行或一列,但是它不会影响表格的布局。被行或列占据的空间会留给其他内容使用。
如果此值被用在其他的元素上,会呈现为 "hidden"。 |
| inherit | 规定应该从父元素继承 visibility 属性的值。 |
overflow 溢出
| 值 | 描述 |
| ------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| visible | 默认值。内容不会被修剪,会呈现在元素框之外。 |
| hidden | 内容会被修剪,并且其余内容是不可见的。 |
| scroll | 内容会被修剪,但是浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。 |
| auto | 如果内容被修剪,则浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。 |
| inherit | 规定应该从父元素继承 overflow 属性的值。 |
overflow-x
overflow-y
(2)尺寸

(3)内补白
![]()
(4)外边距

三、浮动——float
1、什么是浮动

2、设置浮动
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
#d1 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
float: left; /*浮动 浮到空中往左飘*/
}
#d2 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: greenyellow;
float: right; /*浮动 浮到空中往右飘*/
}
</style>
3、清除浮动
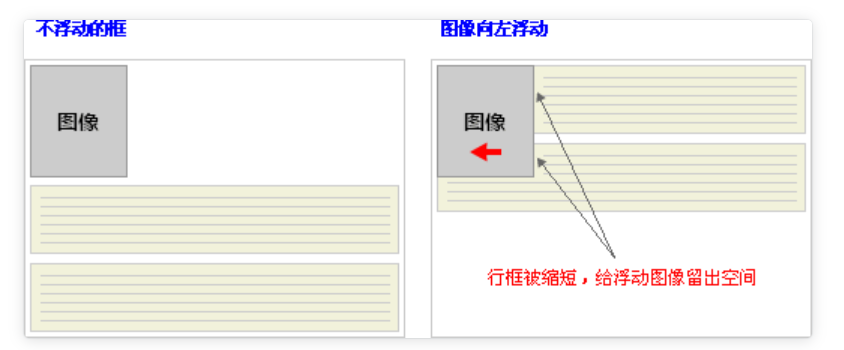
清除浮动的目的:
阻止行框围绕浮动框,一般使用行框的clear 属性(属性值 : left 、right、both、none ,表示框的哪一边不该挨着浮动框)
clear: both
clear: left
clear: right

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <style> body { margin: 0; } #d1 { border: 3px solid black; } #d2 { height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: red; float: left; } #d3 { height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: greenyellow; float: left; } #d4 { /*height: 100px;*/ clear: left; /*该标签的左边(地面和空中)不能有浮动的元素*/ } /* 万金油——前端框架必备CSS */ .clearfix:after { content: ''; display: block; clear:both; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="d1" class="clearfix"> <div id="d2"></div> <div id="d3"></div> <!-- <div id="d4"></div>--> </div> </body> </html>
清除方法二:
/* 万金油——前端框架必备CSS ——清除浮动*/ .clearfix:after { content: ''; display: block; clear:both;
四、定位——position (标签默认的状态是静态的(static))
# 不脱离文档流
1.相对定位
# 脱离文档流
1.浮动
2.绝对定位
3.固定定位
1、相对定位—relative

.box { position: relative; top: 10px; left: 20px; }
2、绝对定位— absolute

.box { position: absolute; top: 10px; left: 20px }
3、固定定位— fixed

.box { position: fixed; top: 10px; left: 20px; }

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <style> body { margin: 0; } #d1 { height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: red; left: 50px; /*从左往右 如果是负数 方向则相反*/ top: 50px; /*从上往下 如果是负数 方向则相反*/ /*position: static; !*默认是static无法修改位置*!*/ position: relative; /*相对定位 标签由static变为relative它的性质就从原来没有定位的标签变成了已经定位过的标签 虽然你哪怕没有动 但是你的性质也已经改变了 */ } #d2 { height: 100px; width: 200px; background-color: red; position: relative; /*已经定位过了*/ } #d3 { height: 200px; width: 400px; background-color: yellowgreen; position: absolute; left: 200px; top: 100px; } #d4 { position: fixed; /*写了fixed之后 定位就是依据浏览器窗口*/ bottom: 10px; right: 20px; height: 50px; width: 100px; background-color: white; border: 3px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <!-- <div id="d1"></div>--> <!--<div id="d2">--> <!-- <div id="d3"></div>--> <!--</div>--> <div style="height: 500px;background-color: red"></div> <div style="height: 500px;background-color: greenyellow"></div> <div style="height: 500px;background-color: blue"></div> <div id="d4">回到顶部</div> </body> </html>
4、空间位置 —属性 z-index

eg:百度登陆页面 其实是三层结构
1.最底部是正常内容(z=0) 最远的
2.黑色的透明区(z=99) 中间层
3.白色的注册区域(z=100) 离用户最近

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <style> body { margin: 0; } .cover { position: fixed; left: 0; top: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.5); z-index: 99; } .modal { background-color: white; height: 200px; width: 400px; position: fixed; left: 50%; top: 50%; z-index: 100; margin-left: -200px; margin-top: -100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div>这是最底层的页面内容</div> <div class="cover"></div> <div class="modal"> <h1>登陆页面</h1> <p>username:<input type="text"></p> <p>password:<input type="text"></p> <button>点我点我~</button> </div> </body> </html>
(PS: 浏览器的显示其实是建立在一个立体模型上的,屏幕的上方为 x轴,左边为y轴,z 轴 则是与用户的视线相对的,即像 垂直插在屏幕上的一根棍子,z 的值,代表着离用户视觉的距离,值越大,离用户越近。显示的效果就是 最先看到的内容,是z 值最大的标签部件。)
5、透明度
/* 它不单单可以修改颜色的透明度还同时修改字体的透明度
rgba只能影响颜色 (a的值用于设置透明度)
而opacity可以修改颜色和字体 */
opacity: 0.5;
参考阅读:
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoyuanqujing/articles/11670018.html

