一、SparkStreaming
1.sparkcore模块的扩展,具有可扩展,高吞吐量,容错机制,针对实时数据流处理,数据可以来自于kafka,flume以及tcp套接字,可以使用更加复杂的函数来进行处理
如map reduce 和filter。数据可以推送到hdfs,mysql,针对数据流可以应用到机器学习以及图计算中

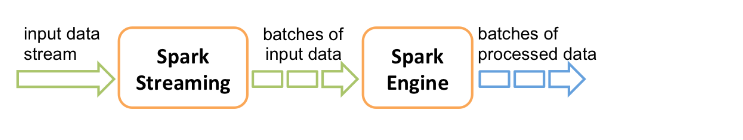
2.在内部,spark接收实时数据流,分成小批次,所以spark不是实时计算,是小批次计算,由spark引擎来进行处理,最终在每个批次中产生结果数据流。按照时间来划分批次。
计算完成之后就变成一小块的数据。sparkstreaming提供了一个高级的抽象称为discretized stream or DStream,离散流,代表的是连续的数据流。通过kafka或者flue实时输入数据流产生,也可以通过其他的DStream进行高阶变换产生。在内部,DStream也表现为RDD流。
3.体验sparkstreaming
(1)spark api编程
from pyspark import SparkContext from pyspark.streaming import StreamingContext # Create a local StreamingContext with two working thread and batch interval of 1 second sc = SparkContext("local[2]", "NetworkWordCount") #创建一个sparkStreaming上下文对象,local要大于1 ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 1)#指定一个上下文对象
# Create a DStream that will connect to hostname:port, like localhost:9999与主机创建连接,localhost是9999
lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
# Split each line into words,把每一个流切换成一个单词
words = lines.flatMap(lambda line: line.split(" "))
# Count each word in each batch,计算在队列中的每一个单词,变换成对偶
pairs = words.map(lambda word: (word, 1))
wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y)
# Print the first ten elements of each RDD generated in this DStream to the console,在控制台上打印10个元素
wordCounts.pprint()
ssc.start() # Start the computation开始计算
ssc.awaitTermination() # Wait for the computation to terminate,等待计算结束(2)启动nc服务器
nc -Ll -p 9999