转自
SkiaSharp 中的矩阵转换
利用多样的转换矩阵深入了解 SkiaSharp 转换
应用于该对象的所有转换 SKCanvas 都在结构的单个实例中合并 SKMatrix 。 这是标准的 3 x 3 变换矩阵,与所有新式2D 图形系统中的矩阵类似。
正如您所看到的,可以在 SkiaSharp 中使用转换,而无需知道转换矩阵,但是转换矩阵对于理论观点非常重要,在使用变换来修改路径或处理复杂的触摸输入时,这两种情况都非常重要。

SKCanvas通过访问只读属性,可以随时使用应用于的当前转换矩阵 TotalMatrix 。 您可以使用方法设置新的转换矩阵 SetMatrix ,还可以通过调用将该转换矩阵还原为默认值 ResetMatrix 。
SKCanvas直接使用画布的矩阵转换的另一个成员是 Concat 通过将两个矩阵相乘在一起来连接两个矩阵。
默认转换矩阵为恒等矩阵,其中包含对角单元中的1个,其他所有位置均为0。
| 1 0 0 | | 0 1 0 | | 0 0 1 |
您可以使用静态方法创建一个标识矩阵 SKMatrix.MakeIdentity :
SKMatrix matrix = SKMatrix.MakeIdentity();
SKMatrix默认构造函数不 not 返回恒等矩阵。 它将返回一个矩阵,其中所有单元格均设置为零。 SKMatrix除非你计划手动设置这些单元格,否则不要使用构造函数。
1,这里讲默认转换,变换后结果不变。
将第三列设为1,等于轴永远是1,弱化为平面。
矩阵乘法就是把第一个矩阵的横和第二个矩阵的竖排相应位相称,将结果相加。
当 SkiaSharp 呈现图形对象时,每个点 (x,y) 会有效地转换为第三列中的 1 x 3 矩阵:
| x y 1 |
这一 3 x 3 的矩阵表示一个三维点,其中 Z 坐标设置为1。 (稍后将介绍一些数学原因) 二维矩阵转换需要在三个维度中工作。 您可以将此 1 x 3 矩阵视为表示3D 坐标系中的一个点,但始终在 Z 等于1的2D 平面上。
然后,这一 3 x 3 的矩阵与变换矩阵相乘,结果是在画布上呈现的点:
| 1 0 0 |
| x y 1 | × | 0 1 0 | = | x' y' z' |
| 0 0 1 |
使用标准矩阵乘法,转换后的点如下所示:
x' = x
y' = y
z' = 1
这是默认转换。
2,下面讲坐标转换
对 Translate 对象调用方法时 SKCanvas , tx 方法的和参数将 ty Translate 成为转换矩阵的第三行中的前两个单元格:
| 1 0 0 | | 0 1 0 | | tx ty 1 |
乘法现在如下所示:
| 1 0 0 |
| x y 1 | × | 0 1 0 | = | x' y' z' |
| tx ty 1 |
下面是转换公式:
x' = x + tx
y' = y + ty
3,缩放
缩放系数的默认值为1。 在对 Scale 新对象调用方法时 SKCanvas ,生成的转换矩阵包含 sx sy 对角单元格中的和参数:
| sx 0 0 |
| x y 1 | × | 0 sy 0 | = | x' y' z' |
| 0 0 1 |
转换公式如下所示:
x' = sx · x
y' = sy · y
4,将skew自由变形拉伸
在调用后,转换矩阵 Skew 包含两个自变量的矩阵单元中的两个参数:
│ 1 ySkew 0 │
| x y 1 | × │ xSkew 1 0 │ = | x' y' z' |
│ 0 0 1 │
转换公式为:
x' = x + xSkew · y
y' = ySkew · x + y
5, 旋转
对于 RotateDegrees α角度的或的调用 RotateRadians ,转换矩阵如下所示:
│ cos(α) sin(α) 0 │
| x y 1 | × │ –sin(α) cos(α) 0 │ = | x' y' z' |
│ 0 0 1 │
下面是转换公式:
x' = cos(α) · x - sin(α) · y
y' = sin(α) · x - cos(α) · y
当α为0度时,表示为恒等矩阵。 当α为180度时,转换矩阵如下所示:
| –1 0 0 | | 0 –1 0 | | 0 0 1 |
180度旋转等效于水平和垂直翻转对象,这也是通过设置–1的缩放因子来完成的。
所有这些类型的转换都分类为 仿射 转换。 仿射转换从不涉及矩阵的第三列,这将保留默认值0、0和1。 非仿射转换一文介绍了非仿射转换。
矩阵相乘
使用转换矩阵的一个明显优势是,可通过矩阵乘法获取复合转换,这在 SkiaSharp 文档中通常称为 " 串联"。 在中,许多与转换相关的方法是 SKCanvas 指 "串联" 或 "预先连接"。 这是指乘法的阶数,这一点非常重要,因为矩阵乘法不能交换。
例如,该方法的文档 Translate 指出它 "用指定的翻译预 concats 当前矩阵",而该方法的文档 Scale 指出它 "用指定的刻度预 concats 当前矩阵"。
这意味着由方法调用指定的转换是左操作数 (的乘数) 并且当前的转换矩阵是右操作数) (被乘数。
假设 Translate 调用后跟 Scale :
canvas.Translate(tx, ty);
canvas.Scale(sx, sy);
Scale转换乘以 Translate 复合转换矩阵的转换:
| sx 0 0 | | 1 0 0 | | sx 0 0 | | 0 sy 0 | × | 0 1 0 | = | 0 sy 0 | | 0 0 1 | | tx ty 1 | | tx ty 1 |
Scale``Translate如下所示:
canvas.Scale(sx, sy);
canvas.Translate(tx, ty);
在这种情况下,乘法的顺序会反转,缩放因子有效地应用于翻译因素:
| 1 0 0 | | sx 0 0 | | sx 0 0 | | 0 1 0 | × | 0 sy 0 | = | 0 sy 0 | | tx ty 1 | | 0 0 1 | | tx·sx ty·sy 1 |
下面是 Scale 具有透视点的方法:
canvas.Scale(sx, sy, px, py);
这等效于以下转换和缩放调用:
canvas.Translate(px, py);
canvas.Scale(sx, sy);
canvas.Translate(–px, –py);
这三个变换矩阵按照其在代码中的显示方式的相反顺序进行相乘:
| 1 0 0 | | sx 0 0 | | 1 0 0 | | sx 0 0 | | 0 1 0 | × | 0 sy 0 | × | 0 1 0 | = | 0 sy 0 | | –px –py 1 | | 0 0 1 | | px py 1 | | px–px·sx py–py·sy 1 |
SKMatrix 结构
SKMatrix结构定义了九种类型的读/写属性,这些属性 float 对应于转换矩阵的九个单元:
│ ScaleX SkewY Persp0 │ │ SkewX ScaleY Persp1 │ │ TransX TransY Persp2 │
SKMatrix 还定义了一个名为 Values 的类型的属性 float[] 。 此属性可用于在顺序、、、、、、、和中的一次拍摄中设置或获取九个值 ScaleX SkewX TransX SkewY ScaleY TransY Persp0 Persp1 Persp2 。
Persp0 Persp1 Persp2 非仿射转换一文中讨论了、和单元。 如果这些单元格的默认值为0、0和1,则转换将乘以坐标点,如下所示:
│ ScaleX SkewY 0 │
| x y 1 | × │ SkewX ScaleY 0 │ = | x' y' z' |
│ TransX TransY 1 │
x' = ScaleX · x + SkewX · y + TransX
y' = SkewX · x + ScaleY · y + TransY
z' = 1
这是完整的二维仿射转换。 仿射转换保留了平行线,这意味着不会将矩形转换为平行四边形以外的任何内容。
SKMatrix结构定义了若干用于创建值的静态方法 SKMatrix 。 这些都是返回 SKMatrix 值:
- MakeTranslation
- MakeScale
MakeScale使用透视点MakeRotation以弧度表示的角度MakeRotation对于具有透视点的以弧度表示的角度- MakeRotationDegrees
MakeRotationDegrees使用透视点- MakeSkew
SKMatrix 还定义了多个连接两个矩阵的静态方法,这意味着将它们相乘。 这些方法的名称分别为 Concat 、 PostConcat 和 PreConcat ,每个都有两个版本。 这些方法没有返回值;相反,它们 SKMatrix 通过参数引用现有值 ref 。 在下面的示例中 A , B R "result" ) 的、和 (都是 SKMatrix 值。
这两种 Concat 方法的调用方式如下:
SKMatrix.Concat(ref R, A, B);
SKMatrix.Concat(ref R, ref A, ref B);
这会执行以下乘法操作:
R = B × A
其他方法只有两个参数。 第一个参数已修改,从方法调用返回时,将包含两个矩阵的乘积。 这两种 PostConcat 方法的调用方式如下:
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref A, B);
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref A, ref B);
这些调用执行以下操作:
A = A × B
这两种 PreConcat 方法类似:
SKMatrix.PreConcat(ref A, B);
SKMatrix.PreConcat(ref A, ref B);
这些调用执行以下操作:
A = B × A
这些具有所有参数的方法的版本 ref 在调用基础实现方面稍有提高,但它可能会使阅读你的代码的人员感到困惑,并假设具有参数的任何内容 ref 都由方法修改。 而且,传递作为方法之一结果的参数通常很方便 Make ,例如:
SKMatrix result;
SKMatrix.Concat(result, SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(100, 100),
SKMatrix.MakeScale(3, 3));
这将创建以下矩阵:
│ 3 0 0 │ │ 0 3 0 │ │ 100 100 1 │
这是转换转换后的缩放变换。 在此特定情况下, SKMatrix 结构使用名为的方法提供快捷方式 SetScaleTranslate :
SKMatrix R = new SKMatrix();
R.SetScaleTranslate(3, 3, 100, 100);
这是可以安全使用构造函数的几个时间之一 SKMatrix 。 SetScaleTranslate方法设置矩阵的所有九个单元格。 将 SKMatrix 构造函数用于静态 Rotate 和方法也是安全的 RotateDegrees :
SKMatrix R = new SKMatrix();
SKMatrix.Rotate(ref R, radians);
SKMatrix.Rotate(ref R, radians, px, py);
SKMatrix.RotateDegrees(ref R, degrees);
SKMatrix.RotateDegrees(ref R, degrees, px, py);
这些方法 不会 将旋转转换连接到现有转换。 方法设置矩阵的所有单元格。 它们在功能上与 MakeRotation 和方法相同, MakeRotationDegrees 不同之处在于它们不会实例化 SKMatrix 该值。
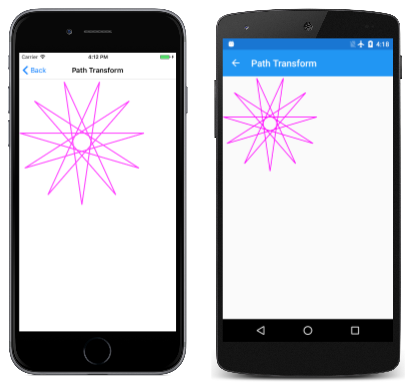
假设你有一个 SKPath 要显示的对象,但你希望它具有稍有不同的方向或不同的中心点。 可以通过调用 Transform 具有参数的的方法来修改该路径的所有坐标 SKPath SKMatrix 。 " 路径转换 " 页演示了如何执行此操作。 PathTransform类引用 HendecagramPath 字段中的对象,但使用其构造函数将转换应用于该路径:
public class PathTransformPage : ContentPage
{
SKPath transformedPath = HendecagramArrayPage.HendecagramPath;
public PathTransformPage()
{
Title = "Path Transform";
SKCanvasView canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
SKMatrix matrix = SKMatrix.MakeScale(3, 3);
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref matrix, SKMatrix.MakeRotationDegrees(360f / 22));
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref matrix, SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(300, 300));
transformedPath.Transform(matrix);
}
...
}
HendecagramPath对象的中心位于 (0,0) ,星号的11个点从该中心向外延伸,方向为100个单位。 这意味着路径具有正坐标和负坐标。 路径转换 页面首选使用星形三次,并具有所有正坐标。 此外,它也不希望星形上的一个点直接指向。 它需要改用星号的一个点来向下直接指向。 (因为星形包含11个点,所以不能同时具有这两个点。 ) 这需要将星形旋转360度除以22。
构造函数 SKMatrix 使用方法从三个单独的转换生成一个对象 PostConcat ,该方法采用以下模式,其中 A、B 和 C 是的实例 SKMatrix :
SKMatrix matrix = A;
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref A, B);
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref A, C);
这是一系列连续的祖,因此结果如下:
A × B × C
连续的祖有助于了解每个转换的用途。 缩放转换会将路径坐标的大小增加3倍,因此,坐标范围为–300到300。 旋转变换围绕其原点旋转星形。 然后,转换转换向右和向下移动了300像素,因此所有坐标都变为正值。
还有其他序列产生同一矩阵。 下面是另一种:
SKMatrix matrix = SKMatrix.MakeRotationDegrees(360f / 22);
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref matrix, SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(100, 100));
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref matrix, SKMatrix.MakeScale(3, 3));
这会先围绕中心旋转路径,然后将其向右和向下平移100像素,以使所有坐标为正值。 然后,该星形相对于其新的左上角的大小增加,这是 (0,0) 的点。
PaintSurface处理程序可以简单地呈现以下路径:
public class PathTransformPage : ContentPage
{
...
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
paint.Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke;
paint.Color = SKColors.Magenta;
paint.StrokeWidth = 5;
canvas.DrawPath(transformedPath, paint);
}
}
}
它显示在画布的左上角:
此程序的构造函数将矩阵应用到具有以下调用的路径:
transformedPath.Transform(matrix);
该路径 不 会将此矩阵保留为属性。 相反,它会将转换应用于路径的所有坐标。 如果 Transform 再次调用,将再次应用该转换,而您可以返回的唯一方法是应用另一个撤消转换的矩阵。 幸运的是,该 SKMatrix 结构定义了一个 TryInvert 方法,该方法可获取反向给定矩阵的矩阵:
SKMatrix inverse;
bool success = matrix.TryInverse(out inverse);
将调用方法 TryInverse ,因为并非所有矩阵都是可逆的,但是不可能将不可逆矩阵用于图形转换。
您还可以将矩阵转换应用于 SKPoint 值、点数组、 SKRect 甚至只是程序中的单个数字。 此 SKMatrix 结构使用以单词开头的方法集合(如下所示)来支持这些操作 Map :
SKPoint transformedPoint = matrix.MapPoint(point);
SKPoint transformedPoint = matrix.MapPoint(x, y);
SKPoint[] transformedPoints = matrix.MapPoints(pointArray);
float transformedValue = matrix.MapRadius(floatValue);
SKRect transformedRect = matrix.MapRect(rect);
如果使用最后一种方法,请记住, SKRect 结构不能表示旋转矩形。 此方法仅适用于 SKMatrix 表示转换和缩放的值。
交互式试验
获得仿射转换的一种方法是在屏幕上以交互方式移动位图的三个角并查看转换结果。 这是 " 显示仿射矩阵 " 页面背后的概念。 此页需要另外两个也用于其他演示的类:
TouchPoint类显示可在屏幕上拖动的半透明圆圈。 TouchPoint 要求作为的 SKCanvasView 父级的或元素 SKCanvasView 具有 TouchEffect 附加的。 将 Capture 属性设置为 true。 在 TouchAction 事件处理程序中,程序必须 ProcessTouchEvent TouchPoint 为每个实例调用中的方法 TouchPoint 。 true如果触摸事件导致触摸点移动,则方法返回。 而且, PaintSurface 处理程序必须 Paint 在每个实例中调用方法 TouchPoint ,并向其传递 SKCanvas 对象。
TouchPoint 演示 SkiaSharp 视觉对象可以在单独的类中封装的常见方法。 类可定义用于指定视觉对象特性的属性,并且具有参数的名为 Paint 的方法 SKCanvas 可以呈现视觉对象。
的 Center 属性 TouchPoint 指示对象的位置。 此属性可设置为初始化位置;当用户在画布上拖动圆圈时,属性将发生变化。
" 显示仿射矩阵" 页 还需要 MatrixDisplay 类。 此类显示对象的单元格 SKMatrix 。 它有两个公共方法: Measure 若要获取呈现的矩阵的尺寸,并 Paint 显示它。 类包含类型为的 MatrixPaint 属性 SKPaint ,可将其替换为不同的字号或颜色。
ShowAffineMatrixPage文件实例化 SKCanvasView 并附加一个 TouchEffect 。 ShowAffineMatrixPage.xaml.cs代码隐藏文件创建三个 TouchPoint 对象,然后将其设置为与从嵌入资源加载的位图的三个角相对应的位置:
public partial class ShowAffineMatrixPage : ContentPage
{
SKMatrix matrix;
SKBitmap bitmap;
SKSize bitmapSize;
TouchPoint[] touchPoints = new TouchPoint[3];
MatrixDisplay matrixDisplay = new MatrixDisplay();
public ShowAffineMatrixPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
string resourceID = "SkiaSharpFormsDemos.Media.SeatedMonkey.jpg";
Assembly assembly = GetType().GetTypeInfo().Assembly;
using (Stream stream = assembly.GetManifestResourceStream(resourceID))
{
bitmap = SKBitmap.Decode(stream);
}
touchPoints[0] = new TouchPoint(100, 100); // upper-left corner
touchPoints[1] = new TouchPoint(bitmap.Width + 100, 100); // upper-right corner
touchPoints[2] = new TouchPoint(100, bitmap.Height + 100); // lower-left corner
bitmapSize = new SKSize(bitmap.Width, bitmap.Height);
matrix = ComputeMatrix(bitmapSize, touchPoints[0].Center,
touchPoints[1].Center,
touchPoints[2].Center);
}
...
}
仿射矩阵由三个点唯一定义。 这三个 TouchPoint 对象对应于位图的左上角、右上角和左下角。 由于仿射矩阵只能将矩形转换为平行四边形,因此第四个点将被另三个点所隐含。 构造函数通过调用来结束 ComputeMatrix ,这 SKMatrix 三个点计算对象的单元格。
TouchAction处理程序调用 ProcessTouchEvent 每个的方法 TouchPoint 。 scale值从坐标转换 Xamarin.Forms 为像素:
public partial class ShowAffineMatrixPage : ContentPage
{
...
void OnTouchEffectAction(object sender, TouchActionEventArgs args)
{
bool touchPointMoved = false;
foreach (TouchPoint touchPoint in touchPoints)
{
float scale = canvasView.CanvasSize.Width / (float)canvasView.Width;
SKPoint point = new SKPoint(scale * (float)args.Location.X,
scale * (float)args.Location.Y);
touchPointMoved |= touchPoint.ProcessTouchEvent(args.Id, args.Type, point);
}
if (touchPointMoved)
{
matrix = ComputeMatrix(bitmapSize, touchPoints[0].Center,
touchPoints[1].Center,
touchPoints[2].Center);
canvasView.InvalidateSurface();
}
}
...
}
如果任何 TouchPoint 已移动,则方法将 ComputeMatrix 再次调用并使图面无效。
ComputeMatrix方法确定这三个点隐含的矩阵。 "矩阵" 是指 A 基于三个点将一个象素方形矩形转换为平行四边形,而 "缩放" 转换称为 "将 S 位图缩放为一个像素的矩形"。 复合矩阵为 S × A :
public partial class ShowAffineMatrixPage : ContentPage
{
...
static SKMatrix ComputeMatrix(SKSize size, SKPoint ptUL, SKPoint ptUR, SKPoint ptLL)
{
// Scale transform
SKMatrix S = SKMatrix.MakeScale(1 / size.Width, 1 / size.Height);
// Affine transform
SKMatrix A = new SKMatrix
{
ScaleX = ptUR.X - ptUL.X,
SkewY = ptUR.Y - ptUL.Y,
SkewX = ptLL.X - ptUL.X,
ScaleY = ptLL.Y - ptUL.Y,
TransX = ptUL.X,
TransY = ptUL.Y,
Persp2 = 1
};
SKMatrix result = SKMatrix.MakeIdentity();
SKMatrix.Concat(ref result, A, S);
return result;
}
...
}
最后,该 PaintSurface 方法基于该矩阵呈现位图,在屏幕底部显示矩阵,并在位图的三个角呈现触摸点:
public partial class ShowAffineMatrixPage : ContentPage
{
...
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
// Display the bitmap using the matrix
canvas.Save();
canvas.SetMatrix(matrix);
canvas.DrawBitmap(bitmap, 0, 0);
canvas.Restore();
// Display the matrix in the lower-right corner
SKSize matrixSize = matrixDisplay.Measure(matrix);
matrixDisplay.Paint(canvas, matrix,
new SKPoint(info.Width - matrixSize.Width,
info.Height - matrixSize.Height));
// Display the touchpoints
foreach (TouchPoint touchPoint in touchPoints)
{
touchPoint.Paint(canvas);
}
}
}
下面的 iOS 屏幕显示第一次加载页面时的位图,而另两个屏幕在执行某种操作后显示该位图:
[ ](matrix-images/showaffinematrix-large.png#lightbox ""显示仿射矩阵" 页的三个屏幕截图")
](matrix-images/showaffinematrix-large.png#lightbox ""显示仿射矩阵" 页的三个屏幕截图")
尽管触摸点看起来好像是触摸点,但这只是一种错觉。 从触摸点计算的矩阵会转换位图,使拐角与触摸点重合。
用户对位图进行移动、调整大小和旋转,并不是通过拖动角来实现,但通过直接在对象上使用一个或两个手指进行拖动、缩小和旋转,这种方式更加自然。 下一文 触摸操作中对此进行了介绍。
3 x 3 矩阵的原因
可能需要二维图形系统只需要 2 x 2 的转换矩阵:
│ ScaleX SkewY │
| x y | × │ │ = | x' y' |
│ SkewX ScaleY │
这适用于缩放、旋转甚至扭曲,但它不能是转换的最基本转换。
问题在于,2 x 2 的矩阵表示两个维度中的 线性 转换。 线性转换保留一些基本算术运算,但其中一个含义是线性转换永远不会改变点 (0,0) 。 线性转换无法进行转换。
在三个维度中,线性变换矩阵如下所示:
│ ScaleX SkewYX SkewZX │
| x y z | × │ SkewXY ScaleY SkewZY │ = | x' y' z' |
│ SkewXZ SkewYZ ScaleZ │
标有标签的单元格 SkewXY 表示该值基于 Y 的值倾斜 x 坐标; 单元 SkewXZ 表示该值基于 Z 的值来倾斜 x 坐标; 对于其他单元格,值会倾斜 Skew 。
可以通过将和设置为0,将此3D 变换矩阵限制为二维平面 SkewZX SkewZY ,并将设置 ScaleZ 为1:
│ ScaleX SkewYX 0 │
| x y z | × │ SkewXY ScaleY 0 │ = | x' y' z' |
│ SkewXZ SkewYZ 1 │
如果二维图形完全在3D 空间(其中 Z 等于1)上绘制,则转换乘法如下所示:
│ ScaleX SkewYX 0 │
| x y 1 | × │ SkewXY ScaleY 0 │ = | x' y' 1 |
│ SkewXZ SkewYZ 1 │
所有内容保持在二维平面上,其中 Z 等于1,但 SkewXZ 和 SkewYZ 单元格实际上变成了二维转换因素。
这就是三维线性转换如何作为二维非线性转换的方式。 按照类比 (,3D 图形中的变换基于4个 4 x 4 的矩阵。 )
SKMatrixSkiaSharp 中的结构定义该第三行的属性:
│ ScaleX SkewY Persp0 │
| x y 1 | × │ SkewX ScaleY Persp1 │ = | x' y' z` |
│ TransX TransY Persp2 │
和的非零值 Persp0 会 Persp1 导致在 Z 等于1的情况下将对象移出二维平面的变换。 在 非仿射转换一文中介绍了将这些对象移回该平面时会发生什么情况。
相关链接
对应3d绘制,需要4维矩阵:SkM44
坐标体系:左上角开始,往右下走:
* Skia assumes a right-handed coordinate system:
* +X goes to the right
* +Y goes down
* +Z goes into the screen (away from the viewer)
初始化用二维或者1维数组(按行优先RowMajor,列优先方式ColMajor)
默认时列优先模式存储:
/* Stored in column-major. * Indices * 0 4 8 12 1 0 0 trans_x * 1 5 9 13 e.g. 0 1 0 trans_y * 2 6 10 14 0 0 1 trans_z * 3 7 11 15 0 0 0 1 */
平移:坐标在列上
SkM44& setTranslate(SkScalar x, SkScalar y, SkScalar z = 0) { *this = { 1, 0, 0, x, 0, 1, 0, y, 0, 0, 1, z, 0, 0, 0, 1 }; return *this; } SkM44& setScale(SkScalar x, SkScalar y, SkScalar z = 1) { *this = { x, 0, 0, 0, 0, y, 0, 0, 0, 0, z, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 }; return *this; }
x不等于0时做拉伸:
/** * A matrix is categorized as 'perspective' if the bottom row is not [0, 0, 0, 1]. * For most uses, a bottom row of [0, 0, 0, X] behaves like a non-perspective matrix, though * it will be categorized as perspective. Calling normalizePerspective() will change the * matrix such that, if its bottom row was [0, 0, 0, X], it will be changed to [0, 0, 0, 1] * by scaling the rest of the matrix by 1/X. * * | A B C D | | A/X B/X C/X D/X | * | E F G H | -> | E/X F/X G/X H/X | for X != 0 * | I J K L | | I/X J/X K/X L/X | * | 0 0 0 X | | 0 0 0 1 | */ void normalizePerspective();
与2d的相互转换,去掉了第三行,第三列:
/* When converting from SkM44 to SkMatrix, the third row and * column is dropped. When converting from SkMatrix to SkM44 * the third row and column remain as identity: * [ a b c ] [ a b 0 c ] * [ d e f ] -> [ d e 0 f ] * [ g h i ] [ 0 0 1 0 ] * [ g h 0 i ] */
 下载示例
下载示例