1、在项目开发过程中需要考虑不同的运行环境:开发环境(dev)、测试环境(beta)和生产环境(product)。在以往的开发过程中通常使用Maven构建工具进行控制,但却需要进行大量的配置。SpringBoot考虑到此类问题,专门设计了profile支持。
备注:尤其是项目开发完毕,在正式环境部署的时候出现问题,进行本地调试的时候就头疼了,因为正式环境的参数配置都和本地不一样,所以使用Springboot的profile配置就极大节省了时间,也简化了操作,方便自己使用,避免了搞不清那些配置是正式的,那些是本地环境的。
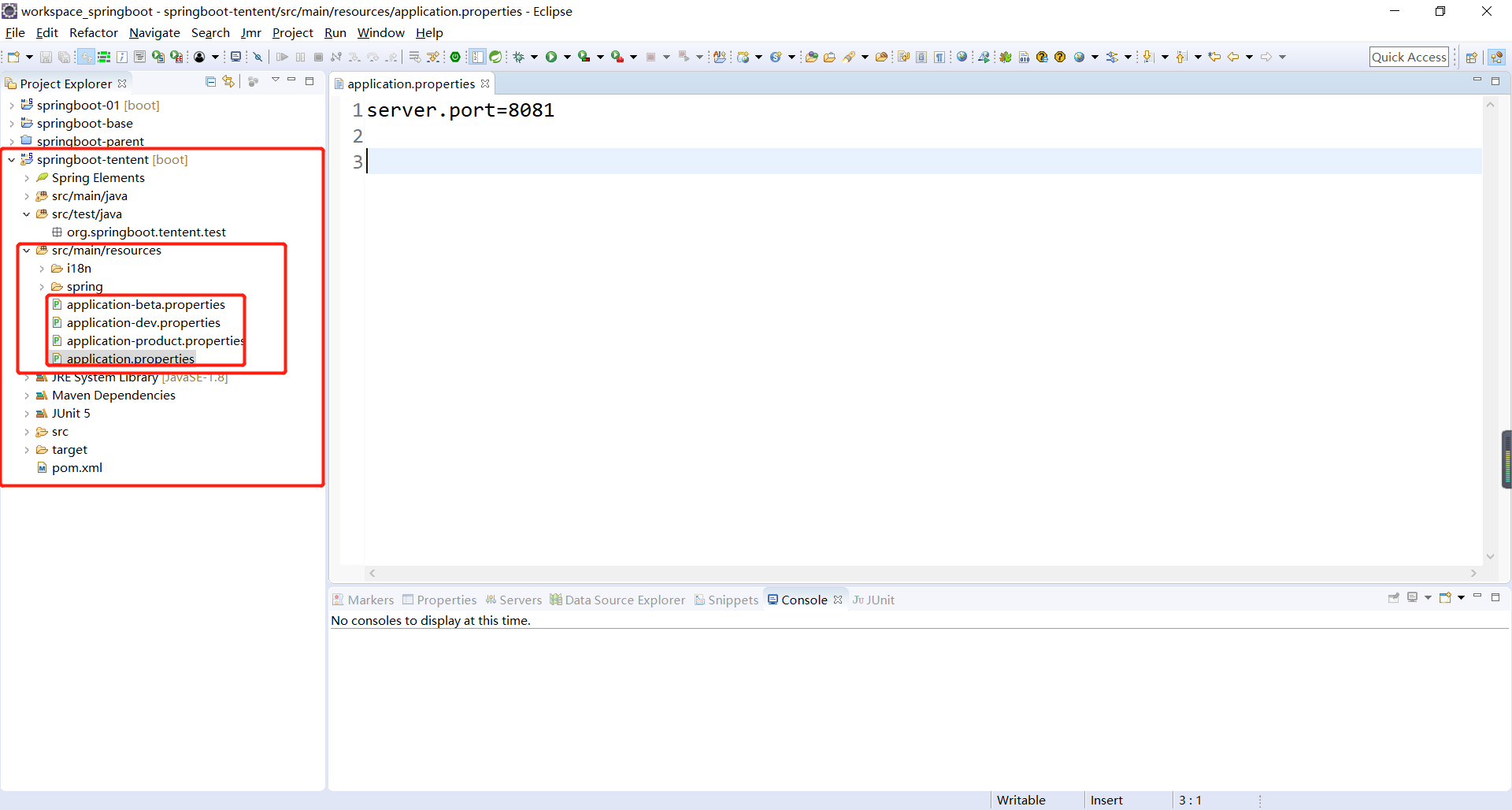
2、首先,创建开发环境,测试环境,生产环境的三种配置文件,外加application.properties配置文件,如下所示:
application-beta.properties、application-dev.properties、application-product.properties三个配置文件分别指定项目的端口号为8082、8083、8084,application.properties配置文件指定激活的环境,如下所示:
1 spring.profiles.active=beta
为了使项目正常进行打包,还需要修改pom.xml文件,追加resource配置,主要的功能是进行源文件夹中内容的打包输出,配置完成后可以将配置文件打包到*.jar文件中。,如下所示:
1 <?xml version="1.0"?> 2 <project 3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 4 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" 5 xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" 6 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"> 7 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 8 9 <parent> 10 <groupId>com.bie</groupId> 11 <artifactId>springboot-base</artifactId> 12 <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 13 </parent> 14 15 <!-- 父项目已经指定,这里可以省略 --> 16 <!-- <groupId>com.bie</groupId> --> 17 <artifactId>springboot-tentent</artifactId> 18 <!-- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> --> 19 <name>springboot-tentent</name> 20 <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> 21 22 <properties> 23 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> 24 </properties> 25 26 <dependencies> 27 <dependency> 28 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 29 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 30 </dependency> 31 <dependency> 32 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 33 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> 34 <scope>test</scope> 35 </dependency> 36 <dependency> 37 <groupId>junit</groupId> 38 <artifactId>junit</artifactId> 39 <scope>test</scope> 40 </dependency> 41 <dependency> 42 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 43 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId> 44 </dependency> 45 </dependencies> 46 47 <build> 48 <plugins> 49 <!-- 该插件的主要功能是进行项目的打包发布处理 --> 50 <plugin> 51 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 52 <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> 53 <!-- 设置程序执行的主类 --> 54 <configuration> 55 <mainClass>org.springboot.tentent.Springboot01Application</mainClass> 56 </configuration> 57 <executions> 58 <execution> 59 <goals> 60 <goal>repackage</goal> 61 </goals> 62 </execution> 63 </executions> 64 </plugin> 65 </plugins> 66 <resources> 67 <resource> 68 <directory>src/main/resources</directory> 69 <includes> 70 <include>**/*.properties</include> 71 <include>**/*.yml</include> 72 <include>**/*.xml</include> 73 <include>**/*.tld</include> 74 </includes> 75 <filtering>false</filtering> 76 </resource> 77 <resource> 78 <directory>src/main/java</directory> 79 <includes> 80 <include>**/*.properties</include> 81 <include>**/*.xml</include> 82 <include>**/*.tld</include> 83 </includes> 84 <filtering>false</filtering> 85 </resource> 86 </resources> 87 </build> 88 89 90 </project>
修改完pom.xml配置文件之后,记得更新项目,Maven -> Update Project。此时开始,为项目打包,这里直接通过Eclipse进行打包配置,如下所示:
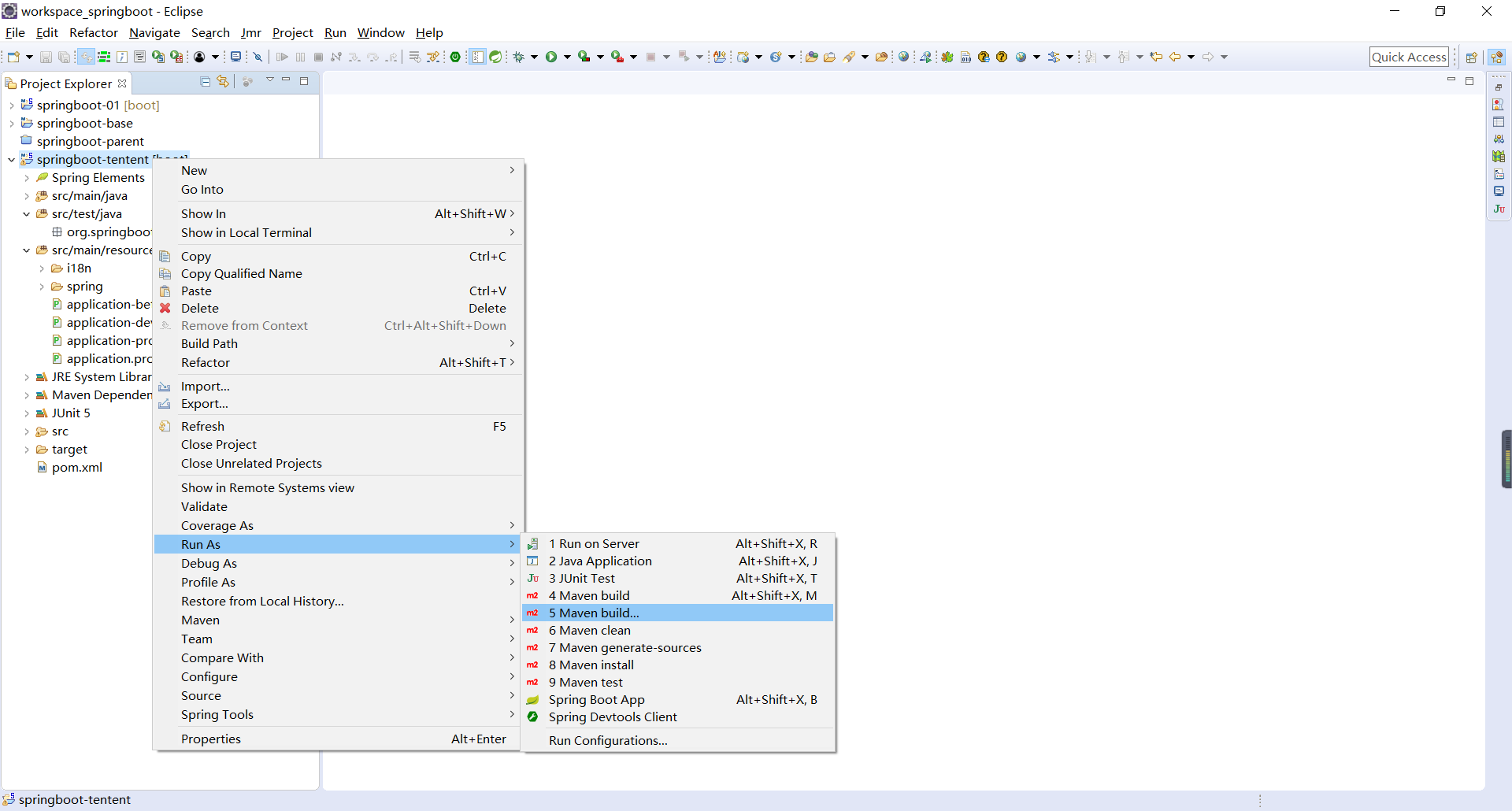
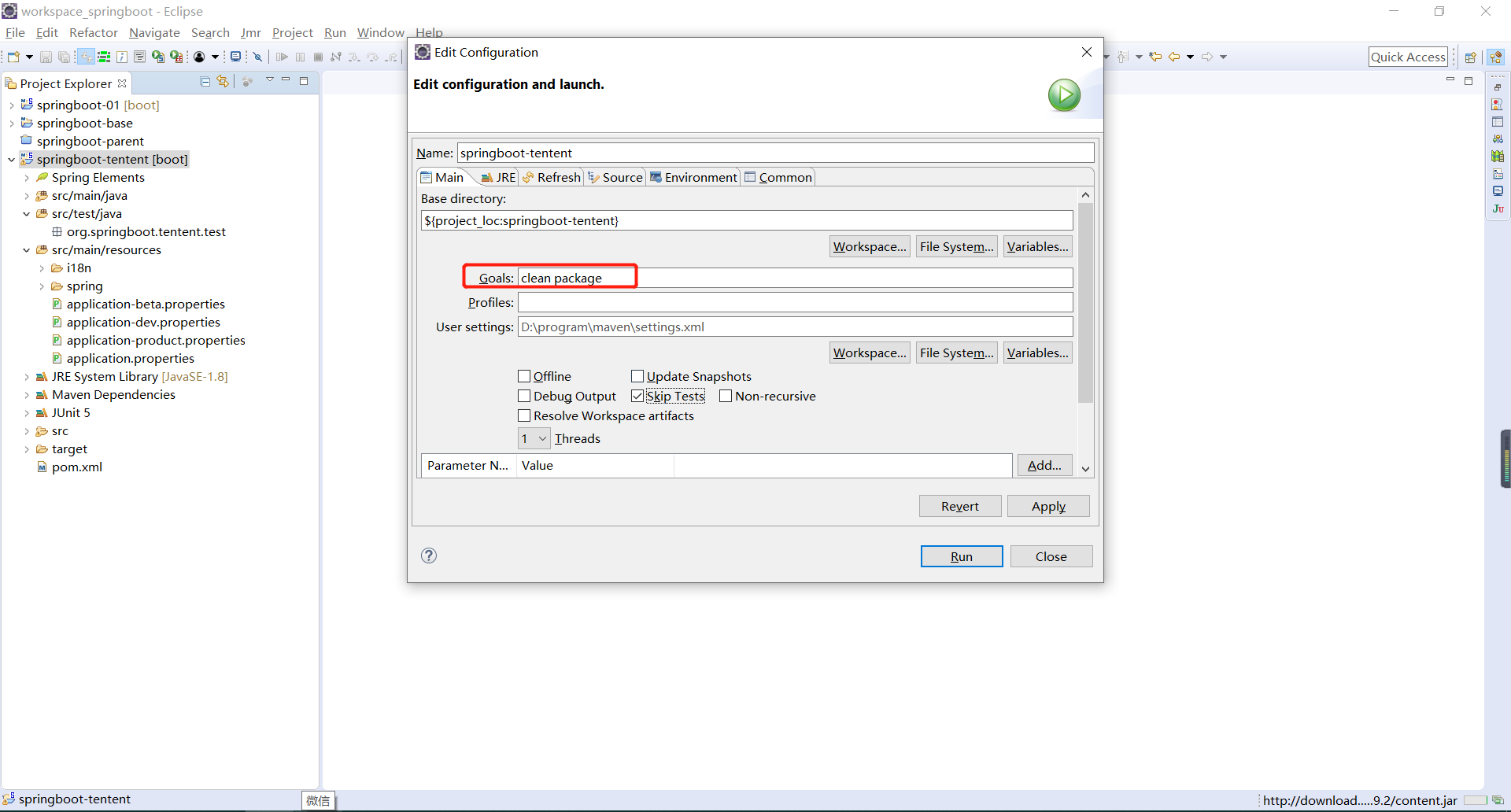
由于在application.properties指定的是spring.profiles.active=beta,所以如果直接运行打好的jar包,那么运行的就是测试环境的端口号,项目打包完成后运行程序,如果不做出任何的指定,那么默认配置的活跃profile(beta)就将直接起作用(java -jar xxx.jar)。
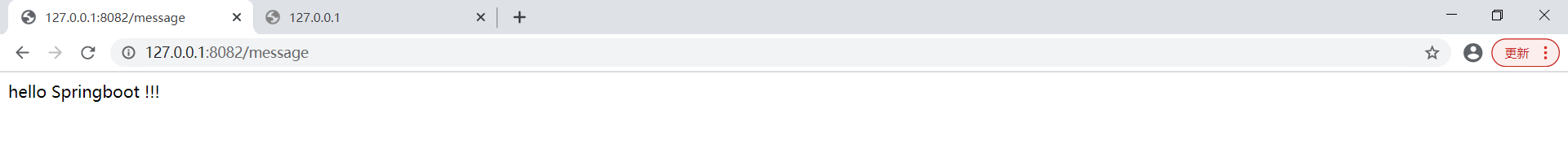
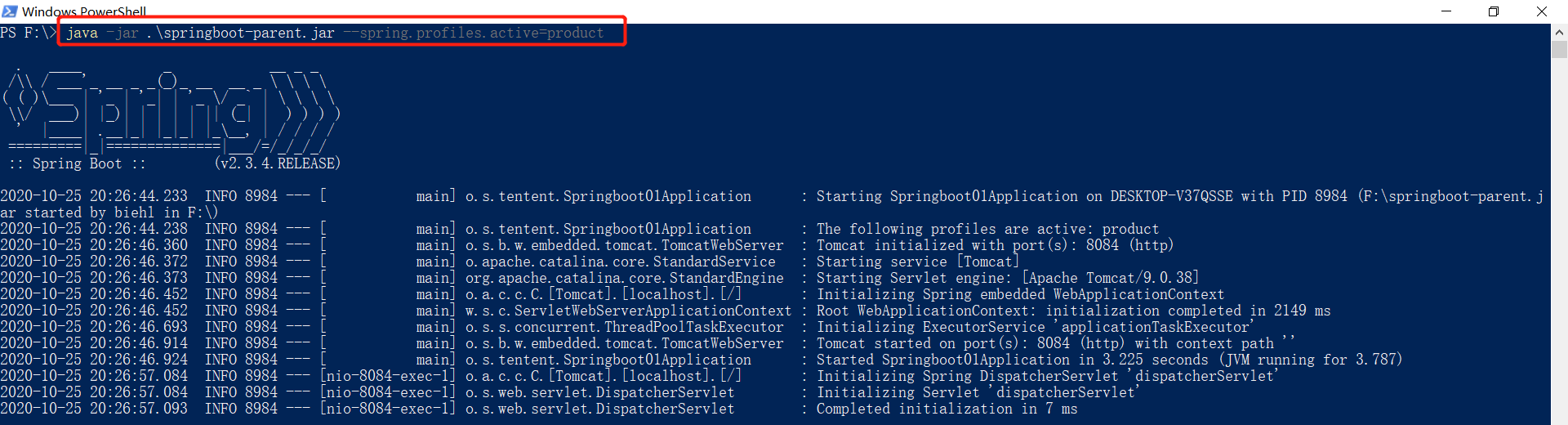
如果想要切换到不同的profile环境,可以在启动时动态配置(java -jar .springboot-parent.jar --spring.profiles.active=product),如下所示:
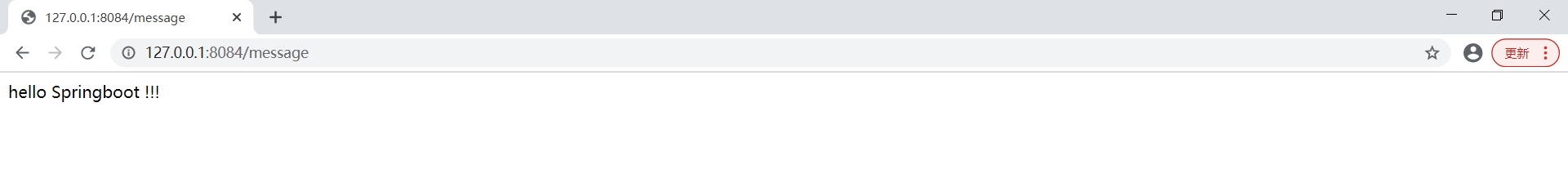
演示效果,如下所示:
注意:*.properties与*.yml配置不同。
使用application.yml进行多profile配置的时候,只需要在一个配置文件中使用“---”分割不同的profile配置。但是此类模式不适合于application.properties配置,此时应该采用不同的*.properties保存不同的配置,才可以实现多profile。