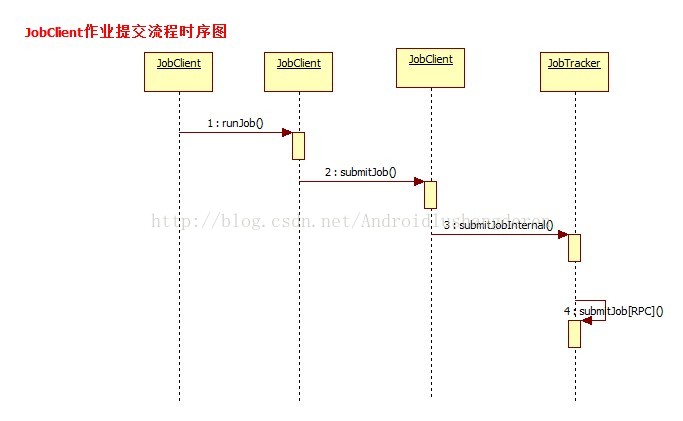
在Hadoop中,启动作业运行的方式有很多,可以用命令行格式把打包好后的作业提交还可以,用Hadoop的插件进行应用开发,在这么多的方式中,都会必经过一个流程,作业会以JobInProgress的形式提交到JobTracker中。什么叫JobTracker呢,也许有些人了解Hadoop只知道他的MapReduce计算模型,那个过程只是其中的Task执行的一个具体过程,比较微观上的流程,而JobTrack是一个比较宏观上的东西。涉及到作业的提交的过程。Hadoop遵循的是Master/Slave的架构,也就是主从关系,对应的就是JobTracker/TaskTracker,前者负责资源管理和作业调度,后者主要负责执行由前者分配过来的作业。这样说的话,简单明了。JobTracker里面的执行的过程很多,那就得从开头开始分析,也就是作业最最开始的提交流程开始。后面的分析我会结合MapReduce的代码穿插式的分析,便于大家理解。
其实在作业的提交状态之前,还不会到达JobTacker阶段的,首先是到了MapReduce中一个叫JobClient的类中。也就是说,比如用户通过bin/hadoop jar xxx.jar把打包的jar包上传到系统中时,首先会触发的就是JobClient.。
public RunningJob submitJob(String jobFile) throws FileNotFoundException,
InvalidJobConfException,
IOException {
// Load in the submitted job details
JobConf job = new JobConf(jobFile);
return submitJob(job);
}
public RunningJob submitJob(JobConf job) throws FileNotFoundException,
IOException {
try {
//又继续调用的是submitJobInternal方法
return submitJobInternal(job);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
throw new IOException("interrupted", ie);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cnfe) {
throw new IOException("class not found", cnfe);
}
}
...
jobCopy = (JobConf)context.getConfiguration();
// Create the splits for the job 为作业创建输入信息
FileSystem fs = submitJobDir.getFileSystem(jobCopy);
LOG.debug("Creating splits at " + fs.makeQualified(submitJobDir));
int maps = writeSplits(context, submitJobDir);
jobCopy.setNumMapTasks(maps);
// write "queue admins of the queue to which job is being submitted"
// to job file.
String queue = jobCopy.getQueueName();
AccessControlList acl = jobSubmitClient.getQueueAdmins(queue);
jobCopy.set(QueueManager.toFullPropertyName(queue,
QueueACL.ADMINISTER_JOBS.getAclName()), acl.getACLString());
// Write job file to JobTracker's fs
FSDataOutputStream out =
FileSystem.create(fs, submitJobFile,
new FsPermission(JobSubmissionFiles.JOB_FILE_PERMISSION));
try {
jobCopy.writeXml(out);
} finally {
out.close();
}
//
// Now, actually submit the job (using the submit name)
//
printTokens(jobId, jobCopy.getCredentials());
//所有信息配置完毕,作业的初始化工作完成,最后将通过RPC方式正式提交作业
status = jobSubmitClient.submitJob(
jobId, submitJobDir.toString(), jobCopy.getCredentials());
JobProfile prof = jobSubmitClient.getJobProfile(jobId);至此我们知道,我们作业已经从本地提交出去了,后面的事情就是JobTracker的事情了,这个时候我们直接会触发的是JobTacker的addJob()方法。
private synchronized JobStatus addJob(JobID jobId, JobInProgress job)
throws IOException {
totalSubmissions++;
synchronized (jobs) {
synchronized (taskScheduler) {
jobs.put(job.getProfile().getJobID(), job);
//观察者模式,会触发每个监听器的方法
for (JobInProgressListener listener : jobInProgressListeners) {
listener.jobAdded(job);
}
}
}
myInstrumentation.submitJob(job.getJobConf(), jobId);
job.getQueueMetrics().submitJob(job.getJobConf(), jobId);
LOG.info("Job " + jobId + " added successfully for user '"
+ job.getJobConf().getUser() + "' to queue '"
+ job.getJobConf().getQueueName() + "'");
AuditLogger.logSuccess(job.getUser(),
Operation.SUBMIT_JOB.name(), jobId.toString());
return job.getStatus();
}
/**
* Start the JobTracker process. This is used only for debugging. As a rule,
* JobTracker should be run as part of the DFS Namenode process.
* JobTracker也是一个后台进程,伴随NameNode进程启动进行,main方法是他的执行入口地址
*/
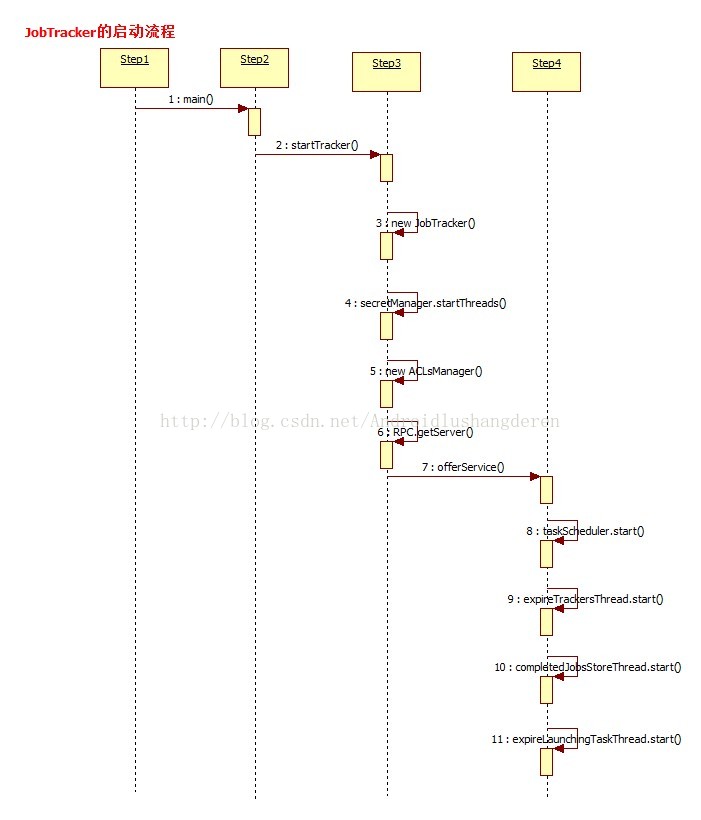
public static void main(String argv[]
) throws IOException, InterruptedException
public static void main(String argv[]
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringUtils.startupShutdownMessage(JobTracker.class, argv, LOG);
try {
if(argv.length == 0) {
//调用startTracker方法开始启动JobTracker
JobTracker tracker = startTracker(new JobConf());
//JobTracker初始化完毕,开启里面的各项线程服务
tracker.offerService();
}
else {
if ("-dumpConfiguration".equals(argv[0]) && argv.length == 1) {
dumpConfiguration(new PrintWriter(System.out));
}
else {
System.out.println("usage: JobTracker [-dumpConfiguration]");
System.exit(-1);
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOG.fatal(StringUtils.stringifyException(e));
System.exit(-1);
}
}
JobTracker(final JobConf conf, String identifier, Clock clock, QueueManager qm)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
.....
//初始化安全相关操作
secretManager =
new DelegationTokenSecretManager(secretKeyInterval,
tokenMaxLifetime,
tokenRenewInterval,
DELEGATION_TOKEN_GC_INTERVAL);
secretManager.startThreads();
......
// Read the hosts/exclude files to restrict access to the jobtracker.
this.hostsReader = new HostsFileReader(conf.get("mapred.hosts", ""),
conf.get("mapred.hosts.exclude", ""));
//初始化ACL访问控制列表
aclsManager = new ACLsManager(conf, new JobACLsManager(conf), queueManager);
LOG.info("Starting jobtracker with owner as " +
getMROwner().getShortUserName());
// Create the scheduler
Class<? extends TaskScheduler> schedulerClass
= conf.getClass("mapred.jobtracker.taskScheduler",
JobQueueTaskScheduler.class, TaskScheduler.class);
//初始化Task任务调度器
taskScheduler = (TaskScheduler) ReflectionUtils.newInstance(schedulerClass, conf);
// Set service-level authorization security policy
if (conf.getBoolean(
ServiceAuthorizationManager.SERVICE_AUTHORIZATION_CONFIG, false)) {
ServiceAuthorizationManager.refresh(conf, new MapReducePolicyProvider());
}
int handlerCount = conf.getInt("mapred.job.tracker.handler.count", 10);
this.interTrackerServer =
RPC.getServer(this, addr.getHostName(), addr.getPort(), handlerCount,
false, conf, secretManager);
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
Properties p = System.getProperties();
for (Iterator it = p.keySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
String key = (String) it.next();
String val = p.getProperty(key);
LOG.debug("Property '" + key + "' is " + val);
}
}1.初始化ACL访问控制列表数据
2.创建TaskSchedule任务调度器
3.得到DPC Server。
4.还有其他一些零零碎碎的操作....
然后第2个方法offService(),主要开启了各项服务;
public void offerService() throws InterruptedException, IOException {
// Prepare for recovery. This is done irrespective of the status of restart
// flag.
while (true) {
try {
recoveryManager.updateRestartCount();
break;
} catch (IOException ioe) {
LOG.warn("Failed to initialize recovery manager. ", ioe);
// wait for some time
Thread.sleep(FS_ACCESS_RETRY_PERIOD);
LOG.warn("Retrying...");
}
}
taskScheduler.start();
.....
this.expireTrackersThread = new Thread(this.expireTrackers,
"expireTrackers");
//启动该线程的主要作用是发现和清理死掉的任务
this.expireTrackersThread.start();
this.retireJobsThread = new Thread(this.retireJobs, "retireJobs");
//启动该线程的作用是清理长时间驻留在内存中且已经执行完的任务
this.retireJobsThread.start();
expireLaunchingTaskThread.start();
if (completedJobStatusStore.isActive()) {
completedJobsStoreThread = new Thread(completedJobStatusStore,
"completedjobsStore-housekeeper");
//该线程的作用是把已经运行完成的任务的信息保存到HDFS中,以便后续的查询
completedJobsStoreThread.start();
}
// start the inter-tracker server once the jt is ready
this.interTrackerServer.start();
synchronized (this) {
state = State.RUNNING;
}
LOG.info("Starting RUNNING");
this.interTrackerServer.join();
LOG.info("Stopped interTrackerServer");
}
void close() throws IOException {
//服务停止
if (this.infoServer != null) {
LOG.info("Stopping infoServer");
try {
this.infoServer.stop();
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOG.warn("Exception shutting down JobTracker", ex);
}
}
if (this.interTrackerServer != null) {
LOG.info("Stopping interTrackerServer");
this.interTrackerServer.stop();
}
if (this.expireTrackersThread != null && this.expireTrackersThread.isAlive()) {
LOG.info("Stopping expireTrackers");
//执行线程中断操作
this.expireTrackersThread.interrupt();
try {
//等待线程执行完毕再执行后面的操作
this.expireTrackersThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (this.retireJobsThread != null && this.retireJobsThread.isAlive()) {
LOG.info("Stopping retirer");
this.retireJobsThread.interrupt();
try {
this.retireJobsThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (taskScheduler != null) {
//调度器的方法终止
taskScheduler.terminate();
}
if (this.expireLaunchingTaskThread != null && this.expireLaunchingTaskThread.isAlive()) {
LOG.info("Stopping expireLaunchingTasks");
this.expireLaunchingTaskThread.interrupt();
try {
this.expireLaunchingTaskThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (this.completedJobsStoreThread != null &&
this.completedJobsStoreThread.isAlive()) {
LOG.info("Stopping completedJobsStore thread");
this.completedJobsStoreThread.interrupt();
try {
this.completedJobsStoreThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (jobHistoryServer != null) {
LOG.info("Stopping job history server");
try {
jobHistoryServer.shutdown();
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOG.warn("Exception shutting down Job History server", ex);
}
}
DelegationTokenRenewal.close();
LOG.info("stopped all jobtracker services");
return;
}至此,JobTracker的执行过程总算有了一个了解了吧,不算太难。后面的过程分析。JobTracker是如何把任务进行分解和分配的,从宏观上去理解Hadoop的工作原理。下面是以上过程的一个时序图