前言
在HDFS中,数据的存储是以Block块的形式进行组织的.而每个块的默认副本数是3个,所以一般每个在HDFS中会存在3个相同的block块分布在不同的DataNode节点之上.所以在每个DataNode上,会存储着大量的block,那么这些块是如何被组织,联系起来的的呢,HDFS在添加块,移除块时是如何操作这些block块以及对应的关联信息呢,链表?数组?HashMap?答案就在BlockInfoContiguous这个类中.
BlockInfoContiguous邻近信息块
这个类不是在所有的Hadoop版本中都有,在最新的hadoop-trunk代码中这个类已经不怎么使用了,所以这里我要说明一下我学习使用的版本是hadoop-2.7.1.在此版本中,BlockInfoContiguous就是用来联系寻找block块的直接信息类.在官方的源码中对BlockInfoContiguous的注释为:
/**
* BlockInfo class maintains for a given block
* the {@link INodeFile} it is part of and datanodes where the replicas of
* the block are stored.
* BlockInfo class maintains for a given block
* the {@link BlockCollection} it is part of and datanodes where the replicas of
* the block are stored.
*/
@InterfaceAudience.Private
public class BlockInfoContiguous extends Block
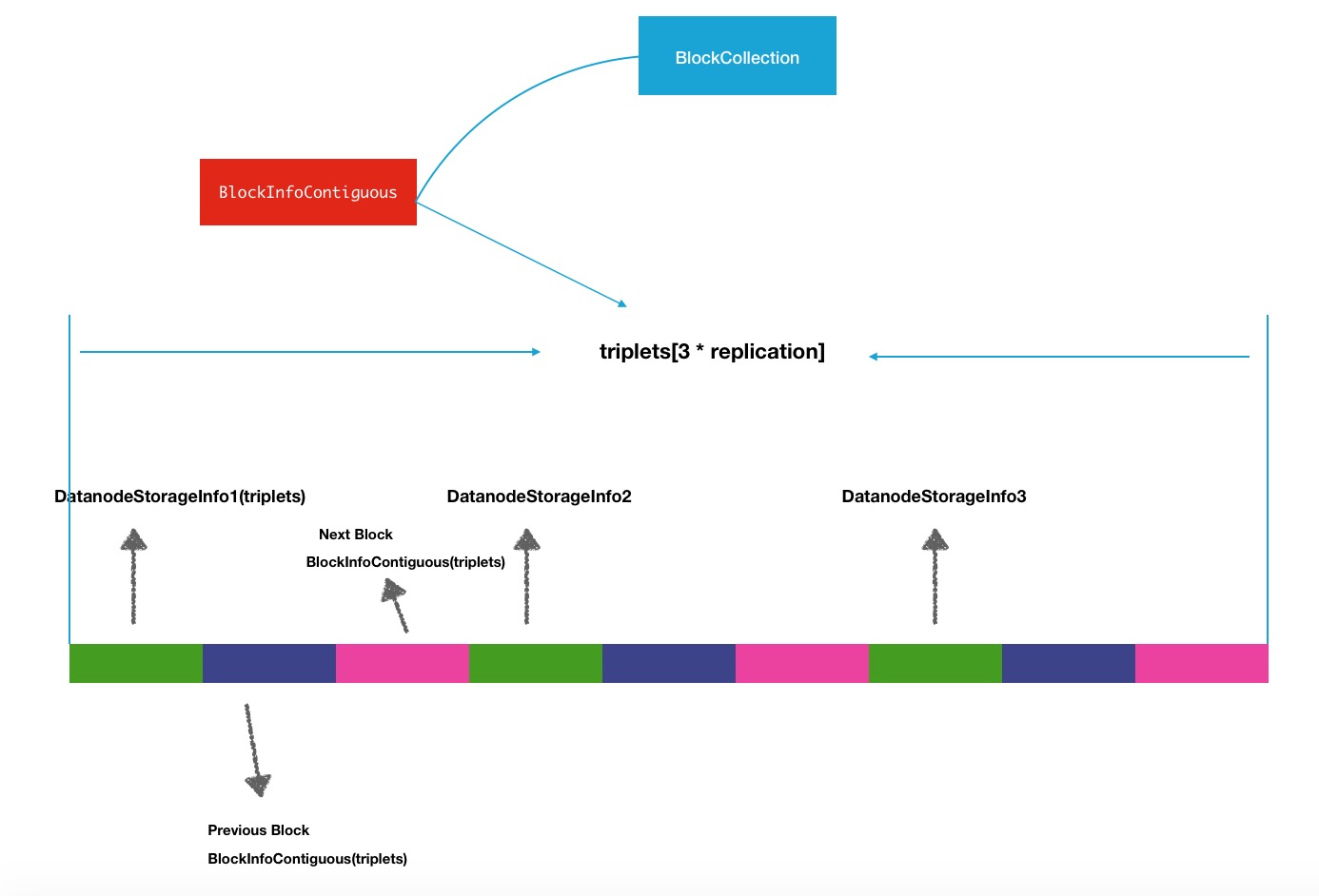
implements LightWeightGSet.LinkedElement {在BlockInfoContiguous类中,有2个内部关键的对象信息BlockCollection和triplets.前者保存了类似副本数,副本位置等的一些信息,而triplets对象数组的设计则是本文的一个重点.所以下面要独立出篇幅来详细的分析triplets的设计结构和思想.
triplets对象数组
triplets对象起始初始化是若干长度的Object对象,但是在赋值的时候,会存储2类的对象.此对象的源码注释如下:
/**
* This array contains triplets of references. For each i-th storage, the
* block belongs to triplets[3*i] is the reference to the
* {@link DatanodeStorageInfo} and triplets[3*i+1] and triplets[3*i+2] are
* references to the previous and the next blocks, respectively, in the list
* of blocks belonging to this storage.
*
* Using previous and next in Object triplets is done instead of a
* {@link LinkedList} list to efficiently use memory. With LinkedList the cost
* per replica is 42 bytes (LinkedList#Entry object per replica) versus 16
* bytes using the triplets.
*/
private Object[] triplets;1.对于当前block块的信息,block存在于哪些data-storage中,假如存储于i个节点,则triplets对象数组大小就是3 * i个,一般存储的节点数视副本系数而定.
2.对triplets每3个为一单位的数组来说,triplets[3 * i]保存的是data-storage信息,triplets[3 * i + 1]保存的是此data-storage中previous前一个block对象的信息,triplets[3 * i + 2]保存的则是后一块的block的信息,而保存block信息对象的类同样是BlockInfoContiguous.
所以你可以稍稍的想象一下,这其实是一个"巨大的链表".但是他为了更高效的使用内存没有用jdk自带的LinkList这样的链表结构.介绍triplets的结构重新再来看看BlockInfoContiguous的结构组成,下面是一张结构图:
DatanodeStorageInfo1,2,3是当前block存储的节点,所以triplets的长度根据副本数进行初始化:
/**
* Construct an entry for blocksmap
* @param replication the block's replication factor
*/
public BlockInfoContiguous(short replication) {
this.triplets = new Object[3*replication];
this.bc = null;
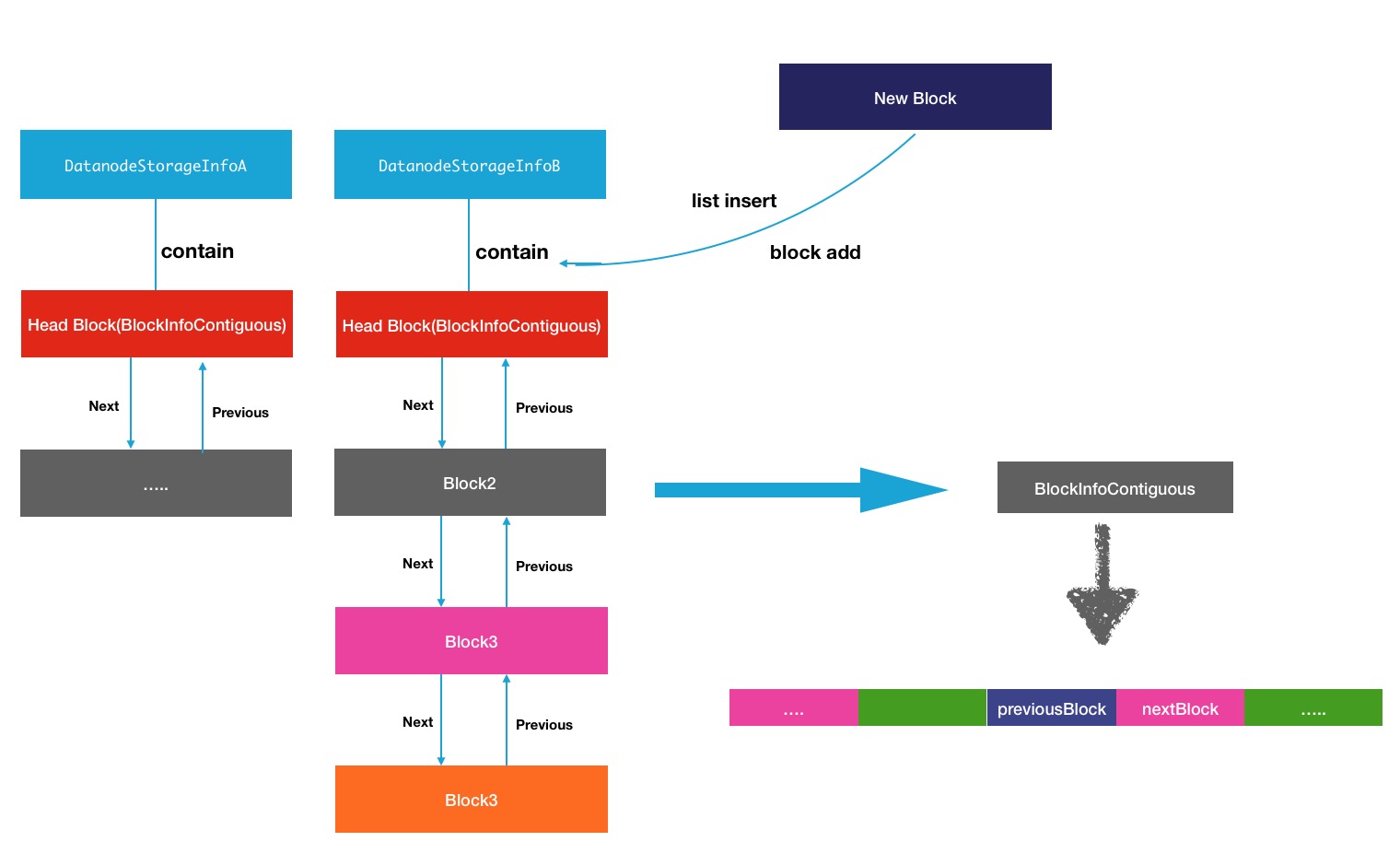
}每个data-storage上会存储大量的block块,于是通过块的next块或previous块,可以遍历完整个节点上的所有块.所有在每个DataNodeStorageInfo中,所持有的block块的结构可以用下图进行展示:
这里的head头block块,对应的是DataNodeStorage中的blacklist对象:
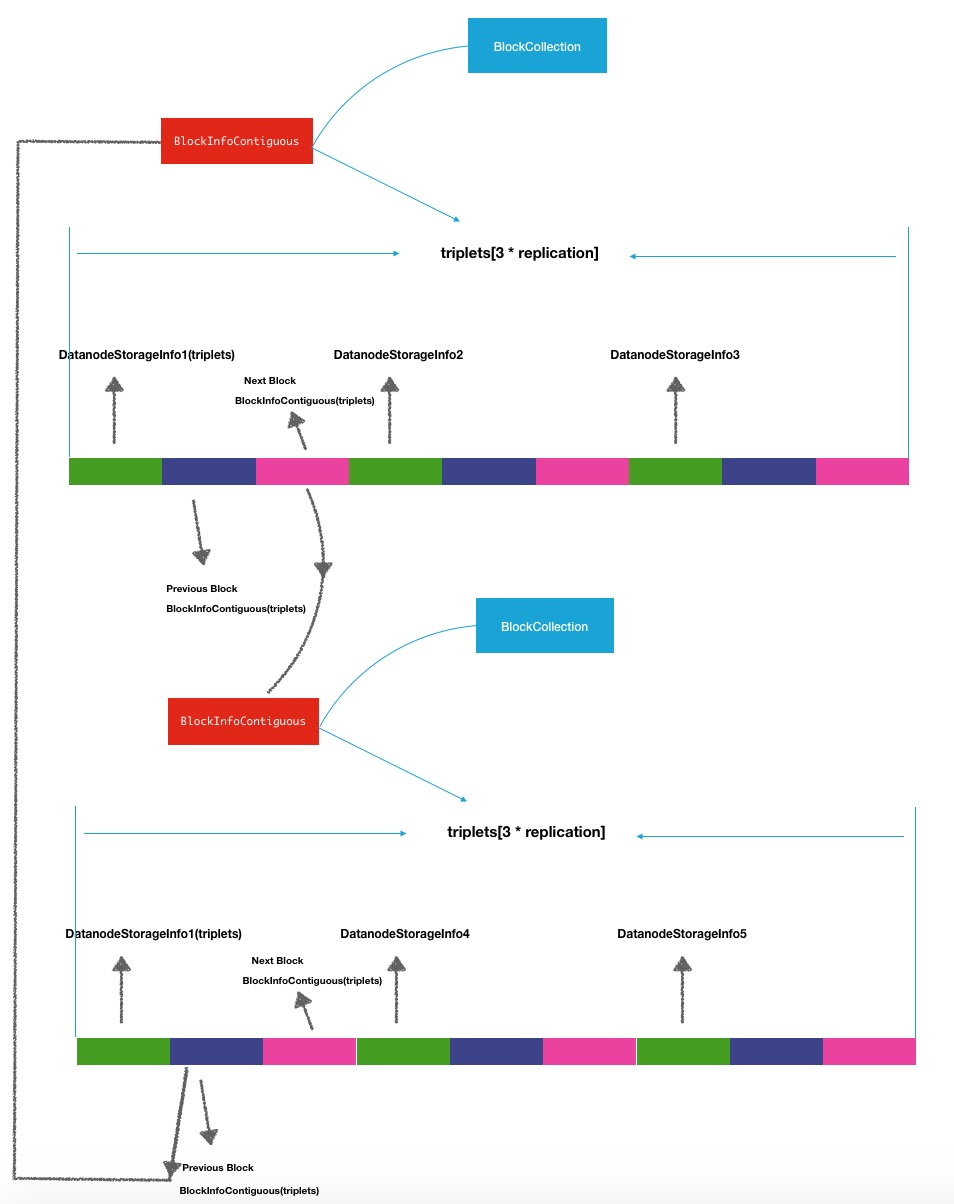
private volatile BlockInfoContiguous blockList = null;上面的同一个节点中的block块与block块之间的关系放大了的表示如下图所示:
data-node上的关于block块的操作都会在他所维护的block列表中进行操作.
BlockInfoContiguous的链表操作
data-node上的block块的添加删除动作对照过来就是BlockInfoContiguous的链表操作.其中的操作主要分为2类,addBlock块的添加,还有一个就是removeBlock操作.这2个方法都是定义在DataNodeStorageInfo中,最终映射到的block的链表操作方法是listInsert和listRemove,下面主要详细分析一下这2个方法:
listInsert
listInsert的操作效果是往对应节点链表中添加一个block块,触发此操作的原始方法是DataNodeStorage的addBlock方法,如下:
public AddBlockResult addBlock(BlockInfoContiguous b) {
// First check whether the block belongs to a different storage
// on the same DN.
AddBlockResult result = AddBlockResult.ADDED;
DatanodeStorageInfo otherStorage =
b.findStorageInfo(getDatanodeDescriptor());
if (otherStorage != null) {
if (otherStorage != this) {
// The block belongs to a different storage. Remove it first.
otherStorage.removeBlock(b);
result = AddBlockResult.REPLACED;
} else {
// The block is already associated with this storage.
return AddBlockResult.ALREADY_EXIST;
}
}
// add to the head of the data-node list
b.addStorage(this); /**
* Add a {@link DatanodeStorageInfo} location for a block
*/
boolean addStorage(DatanodeStorageInfo storage) {
// find the last null node
//triplets数组扩容1个单位的data-storage,相当于扩充3个数组
int lastNode = ensureCapacity(1);
//设置datanode信息对象到triplets[3 * lastNode]中
setStorageInfo(lastNode, storage);
//设置下一block块为null到triplets[3 * lastNode + 2]
setNext(lastNode, null);
//设置前一block块为null到triplets[3 * lastNode + 1]
setPrevious(lastNode, null);
return true;
} private void setStorageInfo(int index, DatanodeStorageInfo storage) {
assert this.triplets != null : "BlockInfo is not initialized";
assert index >= 0 && index*3 < triplets.length : "Index is out of bound";
triplets[index*3] = storage;
}
/**
* Return the previous block on the block list for the datanode at
* position index. Set the previous block on the list to "to".
*
* @param index - the datanode index
* @param to - block to be set to previous on the list of blocks
* @return current previous block on the list of blocks
*/
private BlockInfoContiguous setPrevious(int index, BlockInfoContiguous to) {
assert this.triplets != null : "BlockInfo is not initialized";
assert index >= 0 && index*3+1 < triplets.length : "Index is out of bound";
BlockInfoContiguous info = (BlockInfoContiguous)triplets[index*3+1];
triplets[index*3+1] = to;
return info;
}
blockList = b.listInsert(blockList, this); /**
* Insert this block into the head of the list of blocks
* related to the specified DatanodeStorageInfo.
* If the head is null then form a new list.
* @return current block as the new head of the list.
*/
BlockInfoContiguous listInsert(BlockInfoContiguous head,
DatanodeStorageInfo storage) {
//在当前block中寻找对应data-storage的下标
int dnIndex = this.findStorageInfo(storage);
assert dnIndex >= 0 : "Data node is not found: current";
assert getPrevious(dnIndex) == null && getNext(dnIndex) == null :
"Block is already in the list and cannot be inserted.";
this.setPrevious(dnIndex, null);
//将当前的下一节点指向head头节点
this.setNext(dnIndex, head);
if(head != null)
//将头节点的前一节点指向当前节点
head.setPrevious(head.findStorageInfo(storage), this);
//返回当前节点为新的头节点
return this;
}listRemove
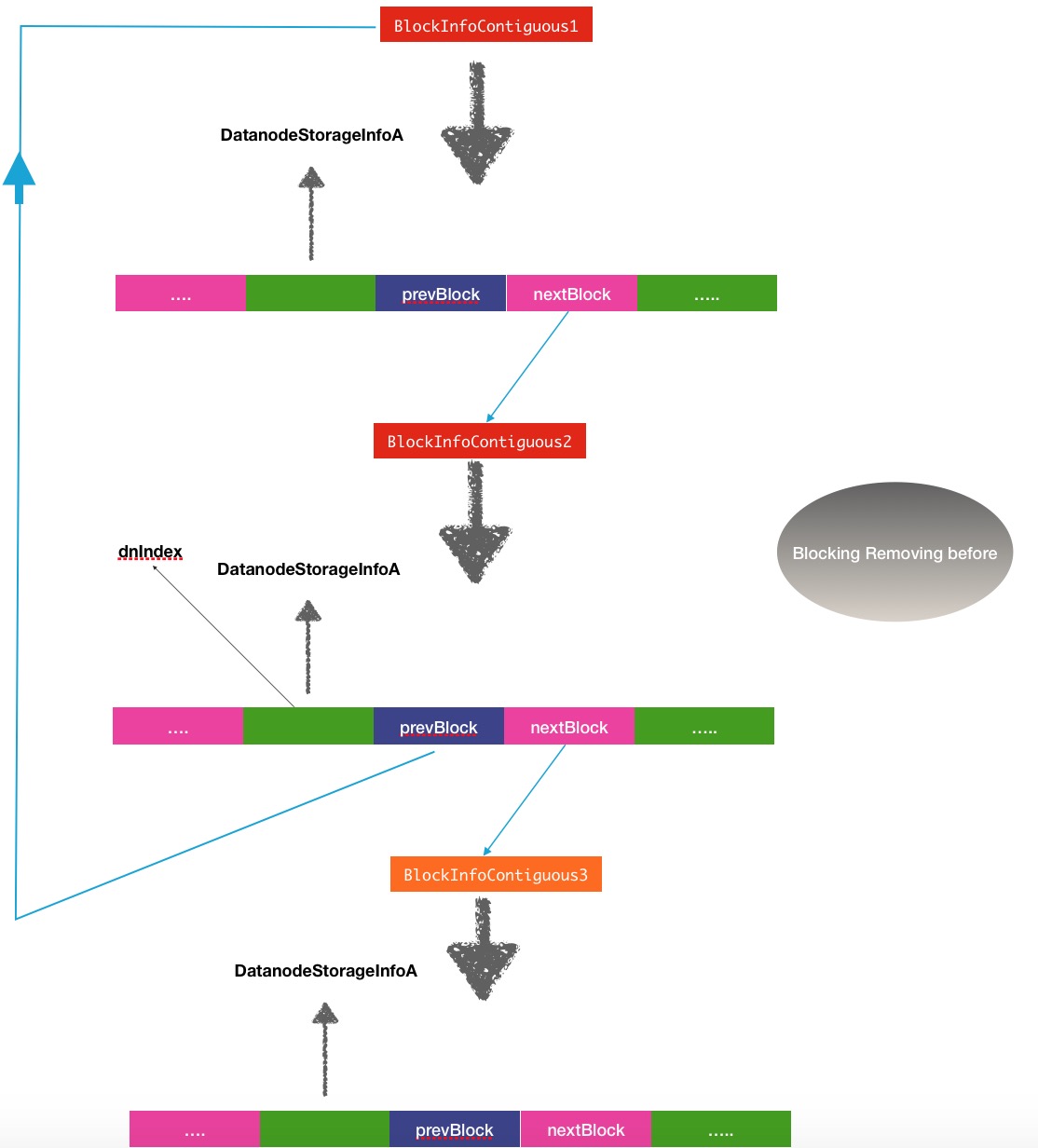
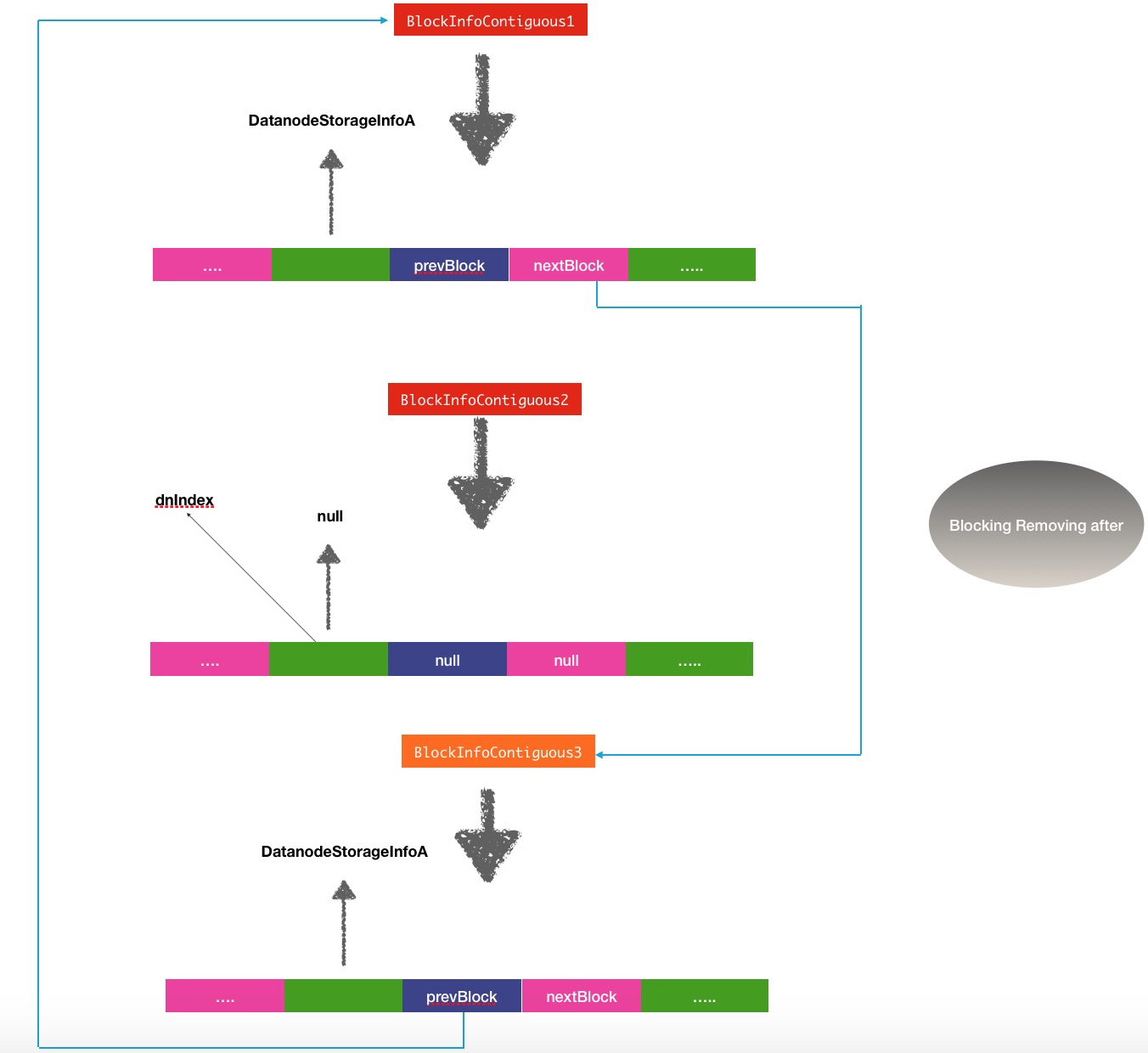
另外一个对应的操作就是data-storage节点的removeBlock动作.在节点上执行了删除block动作之后,会触发这个链表操作.
public boolean removeBlock(BlockInfoContiguous b) {
blockList = b.listRemove(blockList, this);
if (b.removeStorage(this)) {
numBlocks--;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
} /**
* Remove this block from the list of blocks
* related to the specified DatanodeStorageInfo.
* If this block is the head of the list then return the next block as
* the new head.
* @return the new head of the list or null if the list becomes
* empy after deletion.
*/
BlockInfoContiguous listRemove(BlockInfoContiguous head,
DatanodeStorageInfo storage) {
if(head == null)
return null;
int dnIndex = this.findStorageInfo(storage);
if(dnIndex < 0) // this block is not on the data-node list
return head;
//将对应的当前节点信息置为空
BlockInfoContiguous next = this.getNext(dnIndex);
BlockInfoContiguous prev = this.getPrevious(dnIndex);
this.setNext(dnIndex, null);
this.setPrevious(dnIndex, null);
//将前后节点联系关联
if(prev != null)
prev.setNext(prev.findStorageInfo(storage), next);
if(next != null)
next.setPrevious(next.findStorageInfo(storage), prev);
if(this == head) // removing the head
head = next;
return head;
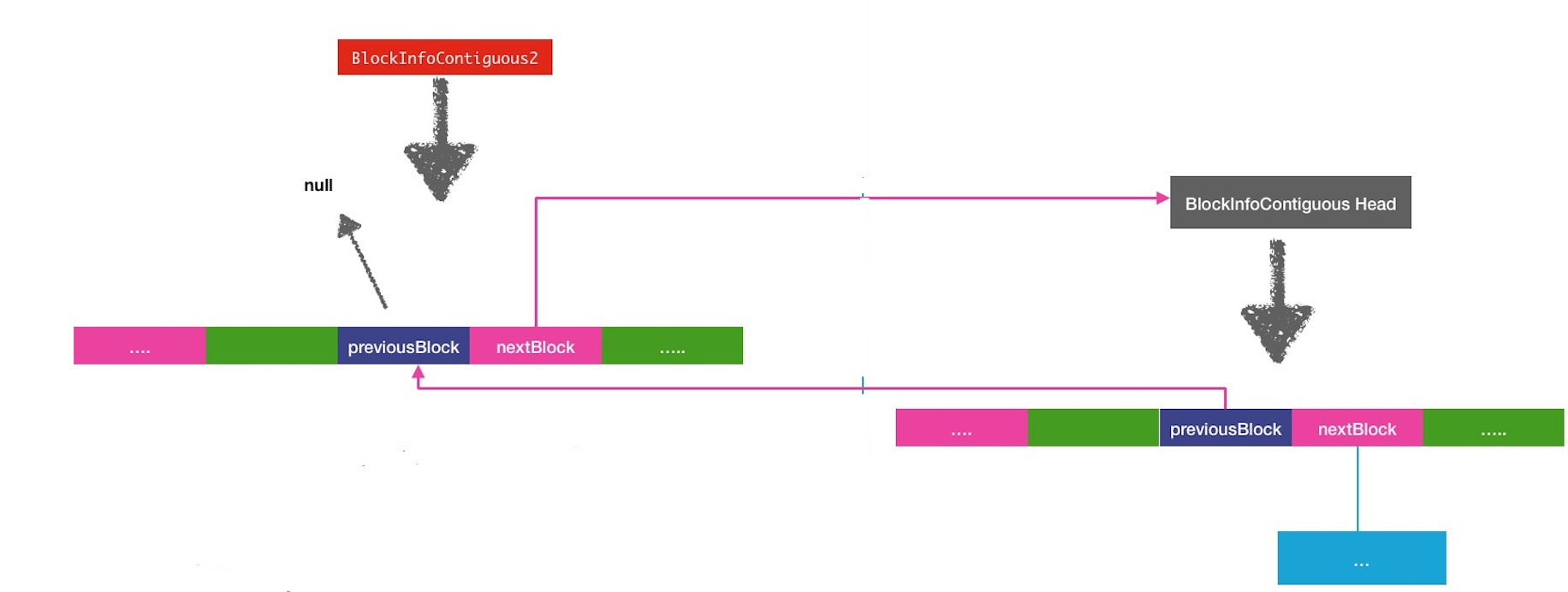
}removeBlock之前:
removeBlock之后:
还有一个操作是将目标block块中的相关data-storage的信息设置为null.
/**
* Remove {@link DatanodeStorageInfo} location for a block
*/
boolean removeStorage(DatanodeStorageInfo storage) {
int dnIndex = findStorageInfo(storage);
if(dnIndex < 0) // the node is not found
return false;
assert getPrevious(dnIndex) == null && getNext(dnIndex) == null :
"Block is still in the list and must be removed first.";
// find the last not null node
int lastNode = numNodes()-1;
// replace current node triplet by the lastNode one
setStorageInfo(dnIndex, getStorageInfo(lastNode));
setNext(dnIndex, getNext(lastNode));
setPrevious(dnIndex, getPrevious(lastNode));
// set the last triplet to null
setStorageInfo(lastNode, null);
setNext(lastNode, null);
setPrevious(lastNode, null);
return true;
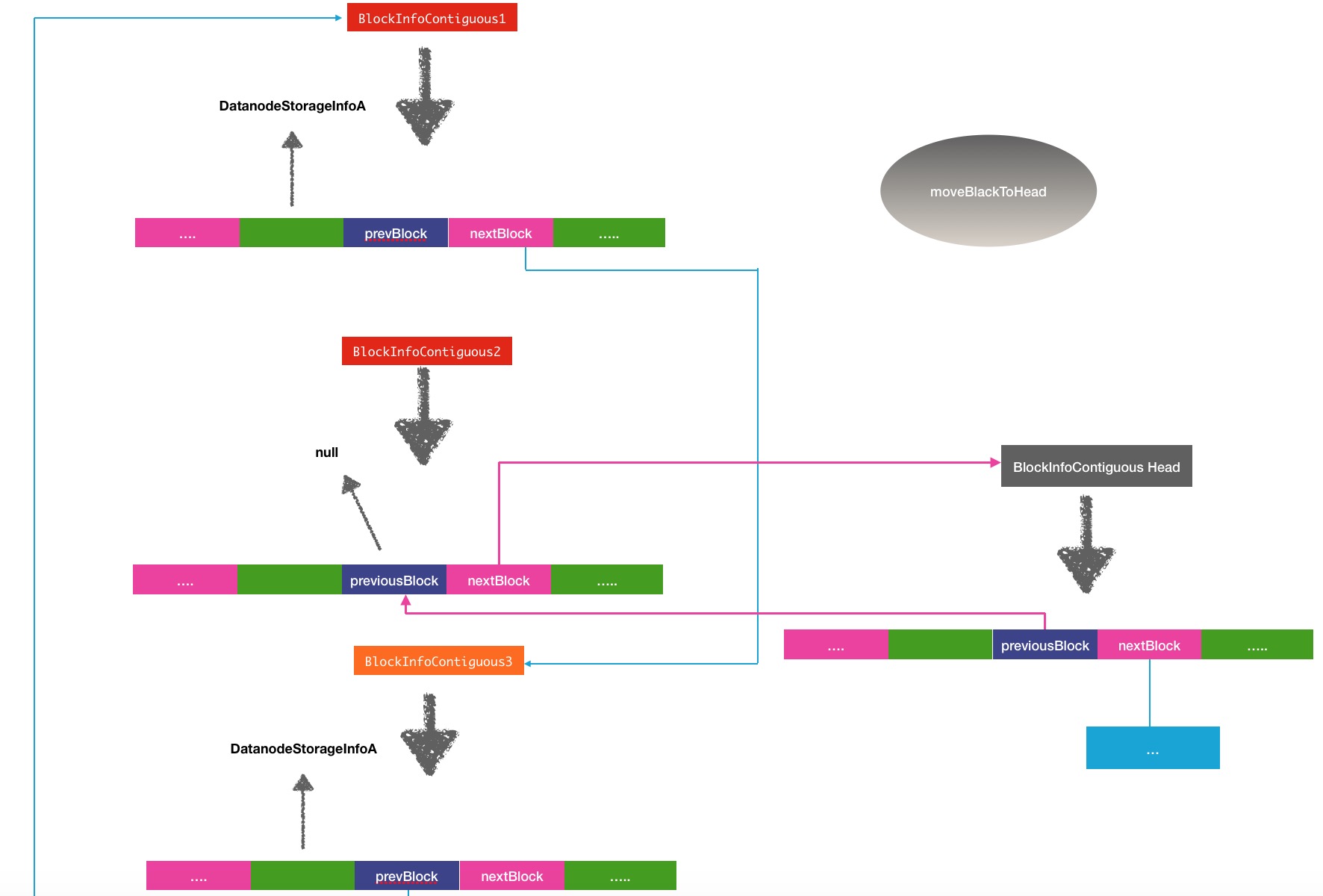
}moveBlockToHead
moveBlockToHead操作也是BlockInfoContiguous经常会被调用的方法,而且这个方法在之前的一篇文章中NameNode处理上报block块逻辑分析有被提到过.在reportDiff方法中被调用到了.
private void reportDiff(DatanodeStorageInfo storageInfo,
BlockListAsLongs newReport,
Collection<BlockInfoContiguous> toAdd, // add to DatanodeDescriptor
Collection<Block> toRemove, // remove from DatanodeDescriptor
Collection<Block> toInvalidate, // should be removed from DN
Collection<BlockToMarkCorrupt> toCorrupt, // add to corrupt replicas list
Collection<StatefulBlockInfo> toUC) { // add to under-construction list
// place a delimiter in the list which separates blocks
// that have been reported from those that have not
BlockInfoContiguous delimiter = new BlockInfoContiguous(new Block(), (short) 1);
AddBlockResult result = storageInfo.addBlock(delimiter);
assert result == AddBlockResult.ADDED
: "Delimiting block cannot be present in the node";
int headIndex = 0; //currently the delimiter is in the head of the list
int curIndex;
//...
// scan the report and process newly reported blocks
for (BlockReportReplica iblk : newReport) {
...
// move block to the head of the list
if (storedBlock != null &&
(curIndex = storedBlock.findStorageInfo(storageInfo)) >= 0) {
headIndex = storageInfo.moveBlockToHead(storedBlock, curIndex, headIndex);
}
}
... /**
* Remove this block from the list of blocks related to the specified
* DatanodeDescriptor. Insert it into the head of the list of blocks.
*
* @return the new head of the list.
*/
public BlockInfoContiguous moveBlockToHead(BlockInfoContiguous head,
DatanodeStorageInfo storage, int curIndex, int headIndex) {
if (head == this) {
return this;
}
//将当前block的下一节点指向头节点
BlockInfoContiguous next = this.setNext(curIndex, head);
//置空前一节点
BlockInfoContiguous prev = this.setPrevious(curIndex, null);
//设置头节点的前一节点为空
head.setPrevious(headIndex, this);
//将当前节点原来的前后节点相连
prev.setNext(prev.findStorageInfo(storage), next);
if (next != null) {
next.setPrevious(next.findStorageInfo(storage), prev);
}
return this;
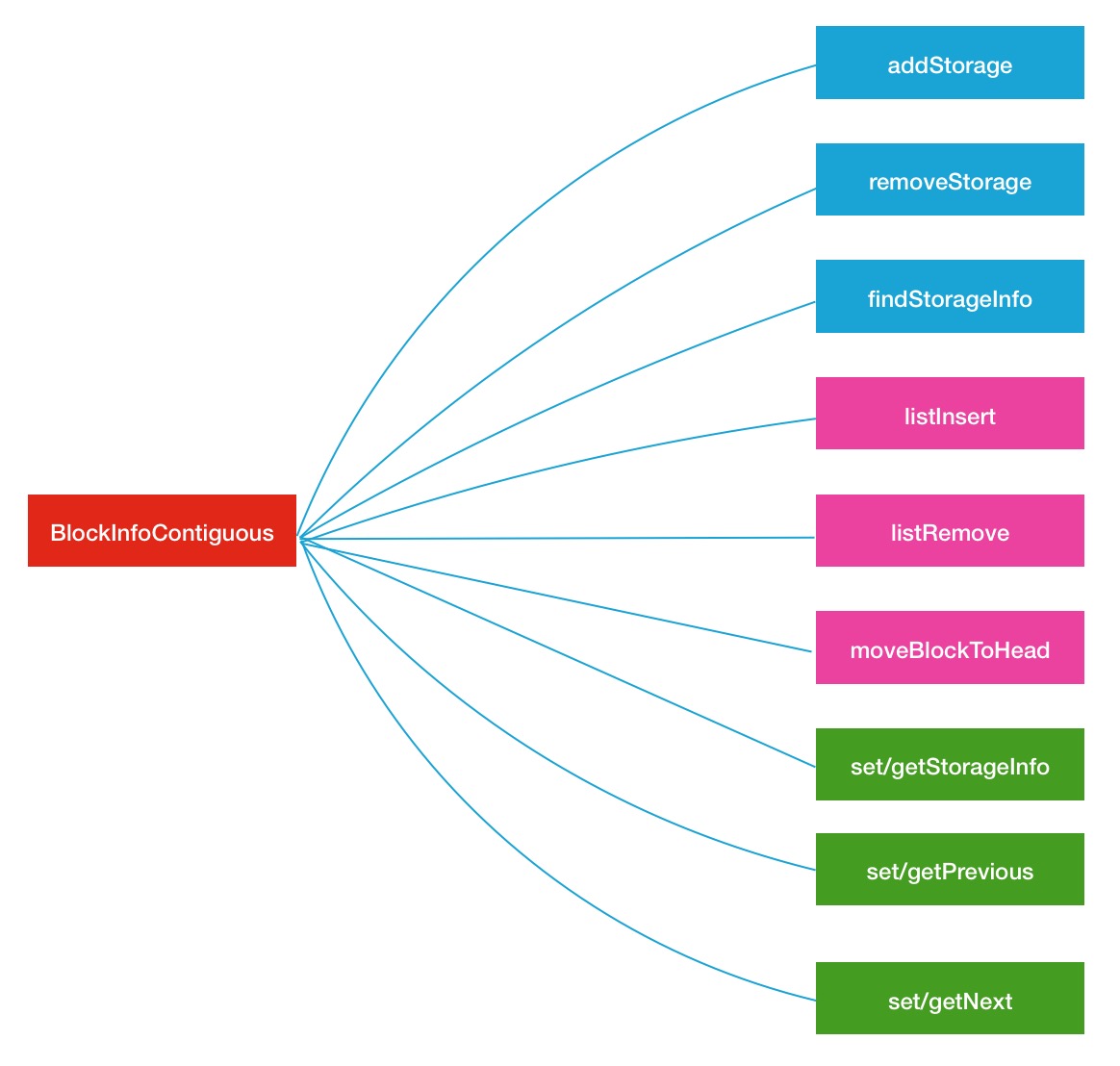
}在BlockInfoContiguous类中,其实还有一些其他的辅助方法,这里主要分析其中的3种也是经常被调用的3种方法,下图是其中主要的方法分类,同种颜色表明是同类型的操作
Block迭代器BlockIterator
对于一个节点上来说,我们想要遍历其上的block,就需要一个迭代器,能够通过next()类似的方法获取其中的block块,在jdk自带的链表中是有直接获取的方法的,但是对于HDFS中如此设计的链表,HDFS的内部也同样设计了对应的迭代器.
private static class BlockIterator implements Iterator<BlockInfoContiguous> {
private int index = 0;
private final List<Iterator<BlockInfoContiguous>> iterators;
private BlockIterator(final DatanodeStorageInfo... storages) {
List<Iterator<BlockInfoContiguous>> iterators = new ArrayList<Iterator<BlockInfoContiguous>>();
for (DatanodeStorageInfo e : storages) {
iterators.add(e.getBlockIterator());
}
this.iterators = Collections.unmodifiableList(iterators);
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
update();
return !iterators.isEmpty() && iterators.get(index).hasNext();
}
@Override
public BlockInfoContiguous next() {
update();
return iterators.get(index).next();
}
@Override
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Remove unsupported.");
}
private void update() {
while(index < iterators.size() - 1 && !iterators.get(index).hasNext()) {
index++;
}
}
}DatanodeStorageInfo[] getStorageInfos() {
synchronized (storageMap) {
final Collection<DatanodeStorageInfo> storages = storageMap.values();
return storages.toArray(new DatanodeStorageInfo[storages.size()]);
}
} /**
* Iterates over the list of blocks belonging to the data-node.
*/
class BlockIterator implements Iterator<BlockInfoContiguous> {
private BlockInfoContiguous current;
BlockIterator(BlockInfoContiguous head) {
this.current = head;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return current != null;
}
public BlockInfoContiguous next() {
BlockInfoContiguous res = current;
current = current.getNext(current.findStorageInfo(DatanodeStorageInfo.this));
return res;
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Sorry. can't remove.");
}
}在DecommisionManager的processForDecomInternal中就用到了这个迭代器:
/**
* Returns a list of blocks on a datanode that are insufficiently
* replicated, i.e. are under-replicated enough to prevent decommission.
* <p/>
* As part of this, it also schedules replication work for
* any under-replicated blocks.
*
* @param datanode
* @return List of insufficiently replicated blocks
*/
private AbstractList<BlockInfoContiguous> handleInsufficientlyReplicated(
final DatanodeDescriptor datanode) {
AbstractList<BlockInfoContiguous> insufficient = new ChunkedArrayList<>();
processBlocksForDecomInternal(datanode, datanode.getBlockIterator(),
insufficient, false);
return insufficient;
}总结
以上就是HDFS中关系着大量block块的链表,也帮大家复习复习了数据结构中的链表操作了.但是这里需要提醒一点,一旦集群中的block块数达到千万级别,BlokcInfoContiguous同样会消耗掉大量的存储空间,也就是说会有同时会有千万个INodeFile和BlockInfoContiguous对象.