前言
之前的文章中谈论了几个最近几年HDFS中比较重要的特性(比如异构存储),本文继续探讨另一重大特性-Snapshot.Snapshot就是快照的意思.Snapshot是一个非常好的东西,一个形象的比喻,快照就好像拍风景照时的那一个瞬间的投影,过了那个时间点之后,又会有新的一个瞬间投影.所以其实Snapshot快照用一个更好的词来形容就是”瞬间映像“.
Snapshot快照概念
在进一步分析HDFS内部的快照管理之前,需要先了解Snapshot快照的概念.首先一个很根本的原则:
快照不是数据的简单拷贝,只做差异的复制这一原则在其他很多系统快照概念中都是遵守的,比如磁盘快照,也是不保存真实数据的.因为不保存实际的数据,所以快照的生成往往非常的迅速.在HDFS中,如果对其中一个目录比如/A下创建一个快照,则快照文件中将会有与/A目录下完全一样的子目录文件结构以及相应的属性信息,通过fs -cat也能看到里面的具体的文件内容,但是这并不意着snapshot对此数据进行完全拷贝,这里遵循一原则,对于大多不变的数据,你所看到的数据其实是当前物理路径所指的内容,而发生变更的INode才是会被snapshot额外拷贝,其实是一个差异拷贝.
HDFS中的快照相关命令
我们首先从hdfs暴露给客户端使用的命令为一个切入点,看看在HDFS中,至少存在以下所列的快照操作:
$ hadoop fs
Usage: hadoop fs [generic options]
[-createSnapshot <snapshotDir> [<snapshotName>]]
[-deleteSnapshot <snapshotDir> <snapshotName>]
[-renameSnapshot <snapshotDir> <oldName> <newName>]还有hdfs命令下的几个:
$ hdfs
Usage: hdfs [--config confdir] [--loglevel loglevel] COMMAND
where COMMAND is one of:
snapshotDiff diff two snapshots of a directory or diff the
current directory contents with a snapshot
lsSnapshottableDir list all snapshottable dirs owned by the current user
Use -help to see options以上2部分总共包含了6个客户端命令,通过命令的名称以及对应的解释,我们也能大概明白其作用.这些命令的具体使用方法不是本文的重点,具体用法可点此HDFS Snapshots.
如果读者仔细观察上述的6个命令,可以看出其中主要围绕着2个概念:
- 1.Snapshottable Directories, 快照目录
- 2.Snapshot: 具体快照
在逻辑上的对应关系如下:
一个快照目录下可以有多个快照文件,快照目录可以创建,删除自身目录下的快照文件,同时快照目录本身又被快照目录管理器所管理.这里面就引出了更深层次的内容:HDFS内部的快照管理机制.
HDFS内部的快照管理机制
Snapshot结构关系
针对上一小节中提到的对应关系,在源码层面是如何表现的呢?
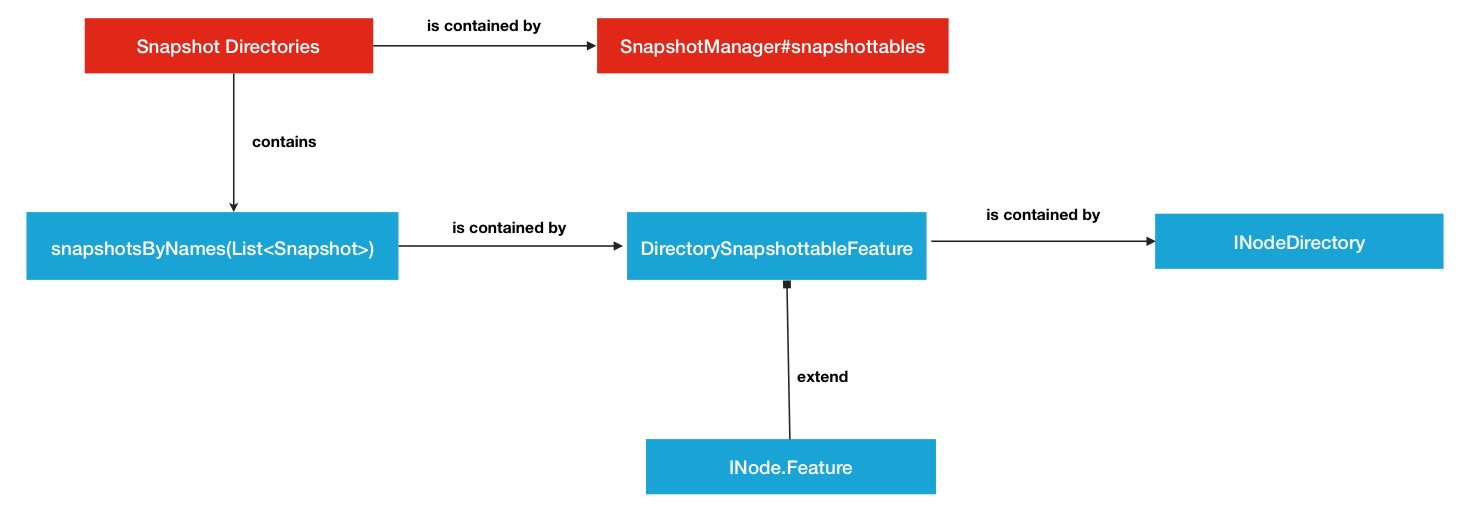
1.快照管理器管理多个快照目录.
public class SnapshotManager implements SnapshotStatsMXBean { //... /** All snapshottable directories in the namesystem. */ private final Map<Long, INodeDirectory> snapshottables = new HashMap<Long, INodeDirectory>(); ...所以其实每个快照目录就是我们非常熟悉的INodeDirectory类.
2.一个快照目录拥有多个快照文件. Snapshot快照在快照目录中的存放就不是很明显了.他是作为一个Feature特性存在于INodeDirectory的父类INodeWithAdditionalFields中(INodeWithAdditionalFields存放的基本是最基本的一些变量,例如name,permission,modificationTime等等),代码中定义如下:
public abstract class INodeWithAdditionalFields extends INode implements LinkedElement { ... /** An array {@link Feature}s. */ private static final Feature[] EMPTY_FEATURE = new Feature[0]; protected Feature[] features = EMPTY_FEATURE; ...而snapshot列表是存在于其中一个叫DirectorySnapshottableFeature的Feature继承子类中,源码中定义如下:
public class DirectorySnapshottableFeature extends DirectoryWithSnapshotFeature { ... /** * Snapshots of this directory in ascending order of snapshot names. * Note that snapshots in ascending order of snapshot id are stored in * {@link DirectoryWithSnapshotFeature}.diffs (a private field). */ private final List<Snapshot> snapshotsByNames = new ArrayList<Snapshot>(); ...
下面用一张结构关系图来复述一下前面 提到的2大存放关系,这相当于是所有关系的一个大背景.
Snapshot调用流程
下面我们来学习一下snapshot快照的调用过程,整个过程我们以SnapshotManager为一个处理中心.
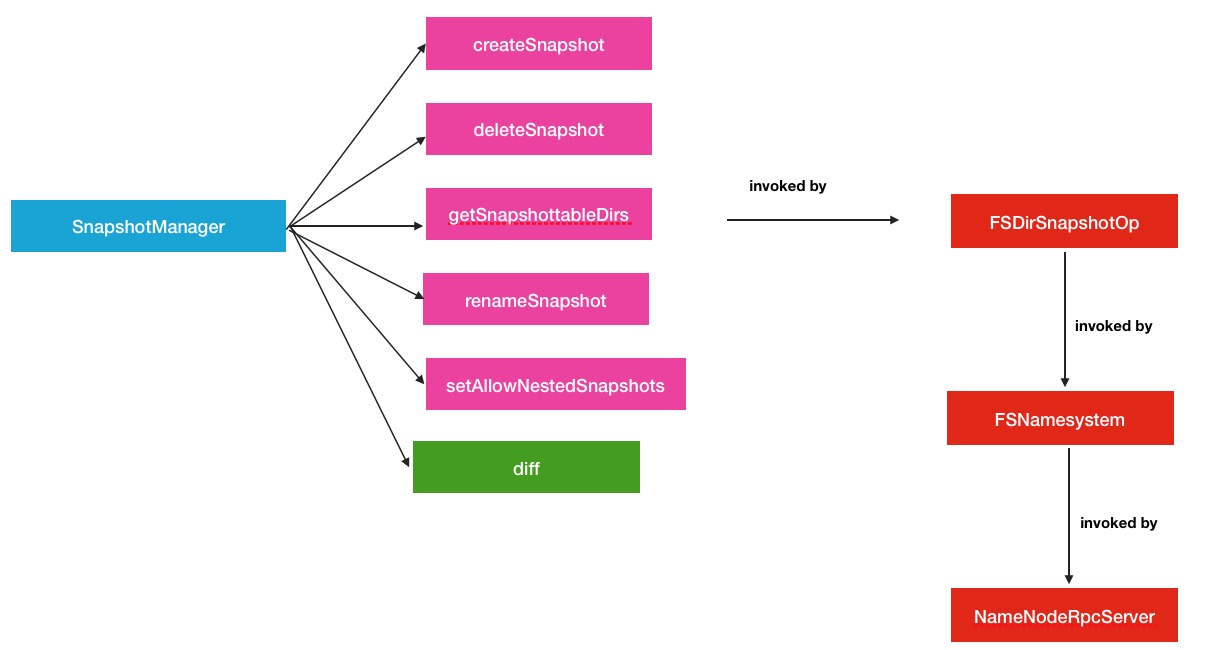
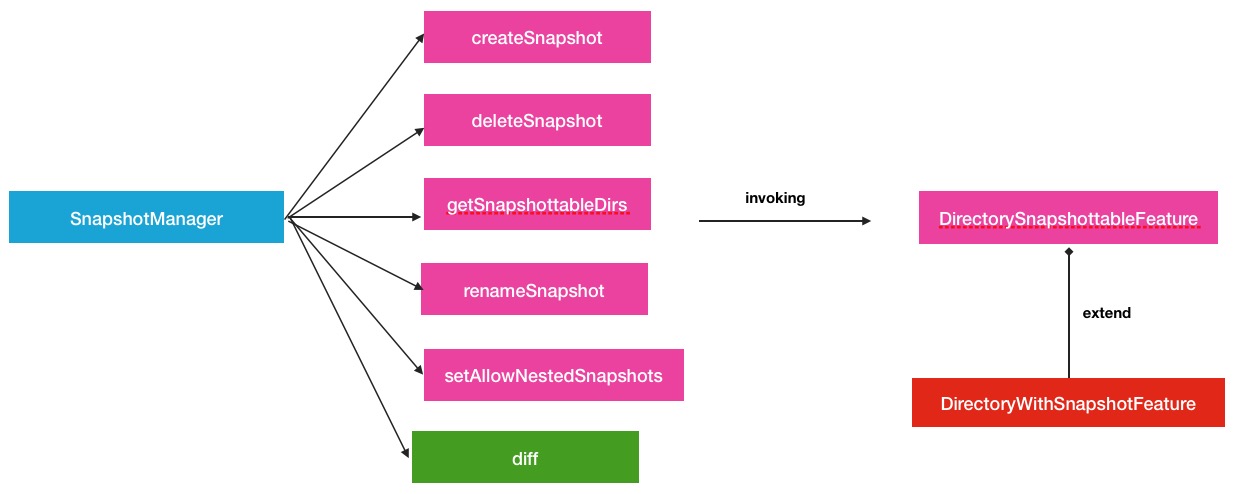
SnapshotManager负责接收snapshot操作请求,继而调用相关类进行处理这里的相关类就是INodeDirectory中的Feature继承类了.所以全部过程分为如下2部分:
- 1.上游请求的接收.如图:
- 1.请求的下游处理.如图:
其中,在上游的请求接收阶段中,与以往直接接收NameNode RPC请求方式略有不同,中间还经过了一层FSDirSnapshotOp,在这个类中,才调用了SnapshotManager的操作方法.这样做还是有益处的,可以在FSNamesystem的众多操作里很好的辨别和区分操作的类型.
Snapshot原理实现分析
前面篇幅的部分主要从大的角度来讲HDFS的快照管理,相反地,这一小节将要探讨的内容是Snapshot的内部原理实现,将会从更细粒度的层面去分析其中的原理实现,这其中的部分逻辑还是有些复杂的.Snapshot快照的实现,我们关系的主要有2点:
- 1.Snapshot快照如何生成的,如何能够做到元数据的完全一致的?
- 2.Snapshot快照之间是如何做diff比较出不同的?
这2个问题中的每个问题实现起来都不是那么的简单,大家阅读完下面的分析,只要理解就行了.
Snapshot的生成
Snapshot的创建操作是基于hadoop fs的-createSnapshot命令触发的,需要传入2个参数,快照所在父目录名和快照名称.所以在创建快照之前,需要先有快照目录,就是要让哪些目录下能够有创建快照的权利.这就需要对目标目录执行allowSnapshot操作.在此操作执行的时候,记住一个原则:
不允许创建出网状关系的快照目录这个用标准英文的术语说就是NestedSnapshots,通俗的讲,就是你目标允许的快照目录的子目录和父目录不能够已经是快照目录.这个操作常常是容易被忽略的.
在进入最终的createSnapshot之前,会做一个系统中全局Snapshot数的判断:
public String createSnapshot(final INodesInPath iip, String snapshotRoot,
String snapshotName) throws IOException {
INodeDirectory srcRoot = getSnapshottableRoot(iip);
if (snapshotCounter == getMaxSnapshotID()) {
// We have reached the maximum allowable snapshot ID and since we don't
// handle rollover we will fail all subsequent snapshot creation
// requests.
//
throw new SnapshotException(
"Failed to create the snapshot. The FileSystem has run out of " +
"snapshot IDs and ID rollover is not supported.");
}
srcRoot.addSnapshot(snapshotCounter, snapshotName);
...每次新增snapshot快照,Counter就会加1,然后做计数判断,这里的MaxSnapshotID就是一个上限值
public int getMaxSnapshotID() {
return ((1 << SNAPSHOT_ID_BIT_WIDTH) - 1);
}这里的SNAPSHOT_ID_BIT_WIDTH值是24,所以最大的快照数是2的24次方减1,基本可以认为是用不完的.
继续进入最终createSnapshot方法内部:
/** Add a snapshot. */
public Snapshot addSnapshot(INodeDirectory snapshotRoot, int id, String name)
throws SnapshotException, QuotaExceededException {
//check snapshot quota
final int n = getNumSnapshots();
if (n + 1 > snapshotQuota) {
throw new SnapshotException("Failed to add snapshot: there are already "
+ n + " snapshot(s) and the snapshot quota is "
+ snapshotQuota);
}
...可以看到,这里首先会有snapshotQuota的限制,也就是说,在每个目录下,又会有快照总数的限制.默认的snapshotQuota是2的16次方.
/** Limit the number of snapshot per snapshottable directory. */
static final int SNAPSHOT_LIMIT = 1 << 16;
...
/** Number of snapshots allowed. */
private int snapshotQuota = SNAPSHOT_LIMIT;然后是接下来的判断处理:
...
// 新建Snapshot对象类
final Snapshot s = new Snapshot(id, name, snapshotRoot);
final byte[] nameBytes = s.getRoot().getLocalNameBytes();
// 检查是否已经存在同名的快照,如果有则抛异常
final int i = searchSnapshot(nameBytes);
if (i >= 0) {
throw new SnapshotException("Failed to add snapshot: there is already a "
+ "snapshot with the same name "" + Snapshot.getSnapshotName(s) + "".");
}
// 将此目录的改动记录加入到diff列表中
final DirectoryDiff d = getDiffs().addDiff(id, snapshotRoot);
d.setSnapshotRoot(s.getRoot());
snapshotsByNames.add(-i - 1, s);
// set modification time
// 更新快照目录的最近修改时间
final long now = Time.now();
snapshotRoot.updateModificationTime(now, Snapshot.CURRENT_STATE_ID);
s.getRoot().setModificationTime(now, Snapshot.CURRENT_STATE_ID);
return s;
}以下这行操作,就会在快照目录下的隐藏目录./snapshot下创建目标快照
final Snapshot s = new Snapshot(id, name, snapshotRoot);目标快照是创建好了,但是另外一个问题来了,快照是如何完全一致的反映出那一时刻的文件目录信息呢?而且更重要的是,随着时间的推移,文件目录早已发生了改动,快照还是能够保存当时时刻的元信息数据.
一种很自然联想到的想法就是HDFS对当时的文件目录的原信息做了一份拷贝,尽管这能解释的通前面的说法,但是按照这种理论成立的话,会衍生出一个很大的问题.当快照目录下的数据文件都没有做任何变动的情况下,过多的快照创建无疑是毫无意义并且是浪费巨大空间的.所以显然在HDFS中不会这么做.所以Snapshot是文件目录元信息的简单拷贝是不完全正确的.
那么HDFS到底是怎么做的呢,给出下面官方的一段注释:
If it is not {@link Snapshot#CURRENT_STATE_ID}, get the result from the corresponding snapshot;
otherwise, get the result from the current directory.CURRENT_STATE_ID表示的意思是当前的snapshot的状态与当前目录完全一致,没有发生过文件目录信息变动.所以在这种情况下,完全返回当前目录信息即可,否则从snapshotId对应的snapshot快照中获取结果.从这段注释中可以提取出以下关键信息:
每个snapshot都有对应自身目录下的INode信息列表,以snapshotId作为区分标识.我们可以从其中的获取子目录节点的方法中一探究竟
/**
* @param snapshotId
* if it is not {@link Snapshot#CURRENT_STATE_ID}, get the result
* from the corresponding snapshot; otherwise, get the result from
* the current directory.
* @return the current children list if the specified snapshot is null;
* otherwise, return the children list corresponding to the snapshot.
* Note that the returned list is never null.
*/
public ReadOnlyList<INode> getChildrenList(final int snapshotId) {
DirectoryWithSnapshotFeature sf;
// 如果当前快照Id是当前状态I获当前目录的snapshot特性为空,则直接返回当前目录的子节点信息
if (snapshotId == Snapshot.CURRENT_STATE_ID
|| (sf = this.getDirectoryWithSnapshotFeature()) == null) {
return getCurrentChildrenList();
}
// 否则从对应的snapshot中返回信息
return sf.getChildrenList(this, snapshotId);
}进入到sf.getChildrenList方法,
/**
* @return If there is no corresponding directory diff for the given
* snapshot, this means that the current children list should be
* returned for the snapshot. Otherwise we calculate the children list
* for the snapshot and return it.
*/
public ReadOnlyList<INode> getChildrenList(INodeDirectory currentINode,
final int snapshotId) {
// 根据快照Id取出对应的目录变更对象信息
final DirectoryDiff diff = diffs.getDiffById(snapshotId);
// 如果变更目录对象为空则直接返回当前目录的孩子信息,否则从变更对象diff中获取子节点列表
return diff != null ? diff.getChildrenList(currentINode) : currentINode
.getChildrenList(Snapshot.CURRENT_STATE_ID);
}然后进入最后一层通过diff信息获取子节点信息列表的方法
private ReadOnlyList<INode> getChildrenList(final INodeDirectory currentDir) {
return new ReadOnlyList<INode>() {
private List<INode> children = null;
private List<INode> initChildren() {
if (children == null) {
// 获取变更的孩子信息
final ChildrenDiff combined = new ChildrenDiff();
for (DirectoryDiff d = DirectoryDiff.this; d != null;
d = d.getPosterior()) {
combined.combinePosterior(d.diff, null);
}
// 与当前的目录INode信息融合,构成新的子节点列表
children = combined.apply2Current(ReadOnlyList.Util.asList(
currentDir.getChildrenList(Snapshot.CURRENT_STATE_ID)));
}
return children;
}
...所以到这里操作的结束,我们终于知道最终的孩子列表是通过将diff发生过变更的INode信息与原目录节点信息进行结合,然后返回一个新的子节点信息作为最终结果返回的.diff中保留的INode就是当时快照创建时的INode信息.
现在再仔细总结一下整个逻辑:
HDFS中只为每个snapshot快照只保存相对当时快照创建时间点发生过变更的INode信息,只是"存不同".
然后获取快照信息时,根据snapshotId和当前没发生过变更的INode信息,进行对应恢复即可.Snapshot的”比不同”
Snapshot之间的比差异是使用Snapshot功能的人最想要得到的一东西.因为通过比较不同时间的快照,我就可以知道在此期间到底哪些文件目录被修改,新创建,或删除了,甚至还能通过这些差异数据做元数据同步.
这个snapshot”比不同“的命令如下:
hdfs snapshotDiff <path> <fromSnapshot> <toSnapshot>在HDFS的snapshot中,主要有如下4种变更类型:
+: The file/directory has been created.
-: The file/directory has been deleted.
M: The file/directory has been modified.
R: The file/directory has been renamed.举HDFS Snapshot官方介绍的一个例子,如果我们重命名一个目录 “/foo” to “/foo2”, 并且追加新的数据到文件”/foo2/bar”, 则调用命令比较出的结果将会是如下:
R. /foo -> /foo2
M. /foo/bar现在我们直接进入snapshotDiff命令对应的RPC处理代码位置
/**
* Compute the difference between two snapshots of a directory, or between a
* snapshot of the directory and its current tree.
*/
public SnapshotDiffReport diff(final INodesInPath iip,
final String snapshotRootPath, final String from,
final String to) throws IOException {
// Find the source root directory path where the snapshots were taken.
// All the check for path has been included in the valueOf method.
final INodeDirectory snapshotRoot = getSnapshottableRoot(iip);
// 如果源快照,或目标快照为空,则直接构造出SnapshotDiffReport差异快照信息对象
if ((from == null || from.isEmpty())
&& (to == null || to.isEmpty())) {
// both fromSnapshot and toSnapshot indicate the current tree
return new SnapshotDiffReport(snapshotRootPath, from, to,
Collections.<DiffReportEntry> emptyList());
}
// 否则先生成snapshot diff信息对象
final SnapshotDiffInfo diffs = snapshotRoot
.getDirectorySnapshottableFeature().computeDiff(snapshotRoot, from, to);
// 根据diff信息产生report对象
return diffs != null ? diffs.generateReport() : new SnapshotDiffReport(
snapshotRootPath, from, to, Collections.<DiffReportEntry> emptyList());
}以上函数的处理又可以分为2个过程:
- 1.生成SnapshotDiffInfo对象,此对象里面包含了源,目标快照间的发生改变的文件目录信息.
- 2.根据发生改变的文件目录信息生成diff报告,展现出的形式就是上述例子中所示的.
SnapshotDiffIfno对象的构造产生
仔细观察上小节中的2个过程,围绕的核心对象其实就是SnapshotDiffInfo,report报告也是由此对象产生.进入此类,观察里面的变量定义
/**
* A class describing the difference between snapshots of a snapshottable
* directory.
*/
class SnapshotDiffInfo {
...
/**
* A map recording modified INodeFile and INodeDirectory and their relative
* path corresponding to the snapshot root. Sorted based on their names.
*/
private final SortedMap<INode, byte[][]> diffMap =
new TreeMap<INode, byte[][]>(INODE_COMPARATOR);
/**
* A map capturing the detailed difference about file creation/deletion.
* Each key indicates a directory whose children have been changed between
* the two snapshots, while its associated value is a {@link ChildrenDiff}
* storing the changes (creation/deletion) happened to the children (files).
*/
private final Map<INodeDirectory, ChildrenDiff> dirDiffMap =
new HashMap<INodeDirectory, ChildrenDiff>();
private final Map<Long, RenameEntry> renameMap =
new HashMap<Long, RenameEntry>();
...从上述变量及相应的注释中可以了解到这里维护了3大类信息:
- 1.所有被modify过的文件/目录,不包括create,delete
- 2.所有目录下的被create和deleted的子文件
- 3.所有被rename过的文件/目录信息
所以第一个子过程就是如何找出具有这些关系特征的文件目录,并加入到这些变量中,答案就在下面这行代码所执行的操作中:
final SnapshotDiffInfo diffs = snapshotRoot
.getDirectorySnapshottableFeature().computeDiff(snapshotRoot, from, to);进入最终执行的方法computeDiff内.
private void computeDiffRecursively(final INodeDirectory snapshotRoot,
INode node, List<byte[]> parentPath, SnapshotDiffInfo diffReport) {
final Snapshot earlierSnapshot = diffReport.isFromEarlier() ?
diffReport.getFrom() : diffReport.getTo();
final Snapshot laterSnapshot = diffReport.isFromEarlier() ?
diffReport.getTo() : diffReport.getFrom();
byte[][] relativePath = parentPath.toArray(new byte[parentPath.size()][]);
if (node.isDirectory()) {
final ChildrenDiff diff = new ChildrenDiff();
INodeDirectory dir = node.asDirectory();
DirectoryWithSnapshotFeature sf = dir.getDirectoryWithSnapshotFeature();
if (sf != null) {
// 判断2个快照中的指定目录是否发生变化
boolean change = sf.computeDiffBetweenSnapshots(earlierSnapshot,
laterSnapshot, diff, dir);
if (change) {
// 如果发生了改变,就加入到dirDiff中
diffReport.addDirDiff(dir, relativePath, diff);
}
}
...首先是判断目录的变化,在addDirDiff中,就会更新modify列表以及目录对应created/delete子文件的列表.
/** Add a dir-diff pair */
void addDirDiff(INodeDirectory dir, byte[][] relativePath, ChildrenDiff diff) {
// 新增指定目录以及对应的create/delete子文件列表信息
dirDiffMap.put(dir, diff);
// 新增modify的目录
diffMap.put(dir, relativePath);
...然后是rename重命名关系的判断
...
ReadOnlyList<INode> children = dir.getChildrenList(earlierSnapshot
.getId());
for (INode child : children) {
final byte[] name = child.getLocalNameBytes();
boolean toProcess = diff.searchIndex(ListType.DELETED, name) < 0;
if (!toProcess && child instanceof INodeReference.WithName) {
byte[][] renameTargetPath = findRenameTargetPath(
snapshotRoot, (WithName) child,
laterSnapshot == null ? Snapshot.CURRENT_STATE_ID :
laterSnapshot.getId());
// 如果找到重命名对象,则进行重命名实体更新
if (renameTargetPath != null) {
toProcess = true;
diffReport.setRenameTarget(child.getId(), renameTargetPath);
}
}
...最后是纯文件的变更判断
...
} else if (node.isFile() && node.asFile().isWithSnapshot()) {
INodeFile file = node.asFile();
// 判断快照中的指定INode文件发生变化
boolean change = file.getFileWithSnapshotFeature()
.changedBetweenSnapshots(file, earlierSnapshot, laterSnapshot);
// 则加入到文件变更的对象变量中
if (change) {
diffReport.addFileDiff(file, relativePath);
}
}在addFileDiff中也会进行相关存储对象的更新
//新增modify对象
/** Add a modified file */
void addFileDiff(INodeFile file, byte[][] relativePath) {
diffMap.put(file, relativePath);
}上述过程会涉及到自身方法的递归调用.那么不同快照之间是如何判断同名的目录或文件发生了变更呢,这里举文件变更判断为例子.
boolean changedBetweenSnapshots(INodeFile file, Snapshot from, Snapshot to) {
// 首先根据快照从此文件所属的diff列表中取出对应快照的FileDiff下标
int[] diffIndexPair = diffs.changedBetweenSnapshots(from, to);
if (diffIndexPair == null) {
return false;
}
int earlierDiffIndex = diffIndexPair[0];
int laterDiffIndex = diffIndexPair[1];
final List<FileDiff> diffList = diffs.asList();
// 然后根据对应快照的FileDiff下标取出,然后进行相关属性判断
final long earlierLength = diffList.get(earlierDiffIndex).getFileSize();
final long laterLength = laterDiffIndex == diffList.size() ? file
.computeFileSize(true, false) : diffList.get(laterDiffIndex)
.getFileSize();
if (earlierLength != laterLength) { // file length has been changed
return true;
}
...这里的意思可能有些人不太理解,之前提到过HDFS只是让每个snapshot”存不同“,然后以为snapshotId做区分.也就是说,对于同一目录,会有多个dirDiff(dirDiff指的是相对此snapshot发生改变的INode),这些dirDiff被加入到了DirDiffList列表对象中,然后根据snapshotId作为下标索引进行获取.同样的在File文件中,也存在单个snapshot的FileDiff对象,以及FileDiffList列表项.
整个过程可以用下面的结构图来展现
SnapshotDiffIfno的report报告生成
上个过程结束之后,SnapshotDiffIfno就基本构造完成了,下面就是generateReport的过程了.这个对象的输出就是上述例子中所输出的信息.进入SnapshotDiffInfo的generateReport方法.
public SnapshotDiffReport generateReport() {
List<DiffReportEntry> diffReportList = new ArrayList<DiffReportEntry>();
// 遍历modify列表对象
for (Map.Entry<INode,byte[][]> drEntry : diffMap.entrySet()) {
INode node = drEntry.getKey();
byte[][] path = drEntry.getValue();
// 在diffReportList中新增MODIFY记录
diffReportList.add(new DiffReportEntry(DiffType.MODIFY, path, null));
if (node.isDirectory()) {
// 如果是目录,则进行递归生成报告处理
List<DiffReportEntry> subList = generateReport(dirDiffMap.get(node),
path, isFromEarlier(), renameMap);
// 将结果加入到diffReportList列表中
diffReportList.addAll(subList);
}
}
// 返回SnapshotDiffReport对象
return new SnapshotDiffReport(snapshotRoot.getFullPathName(),
Snapshot.getSnapshotName(from), Snapshot.getSnapshotName(to),
diffReportList);
}从上面的方法可以看出,主线是从modify修改列表中进行遍历开始,然后如果是目录,则继续处理.
private List<DiffReportEntry> generateReport(ChildrenDiff dirDiff,
byte[][] parentPath, boolean fromEarlier, Map<Long, RenameEntry> renameMap) {
List<DiffReportEntry> list = new ArrayList<DiffReportEntry>();
List<INode> created = dirDiff.getList(ListType.CREATED);
List<INode> deleted = dirDiff.getList(ListType.DELETED);
byte[][] fullPath = new byte[parentPath.length + 1][];
System.arraycopy(parentPath, 0, fullPath, 0, parentPath.length);
for (INode cnode : created) {
RenameEntry entry = renameMap.get(cnode.getId());
// 如果此实体不在renameMap中的
if (entry == null || !entry.isRename()) {
fullPath[fullPath.length - 1] = cnode.getLocalNameBytes();
// 判断比较的顺序是否是later-earlier,如果是晚的快照于早的比
// 则created列表中的都是CRATE类型,否则相反
list.add(new DiffReportEntry(fromEarlier ? DiffType.CREATE
: DiffType.DELETE, fullPath));
}
}
for (INode dnode : deleted) {
RenameEntry entry = renameMap.get(dnode.getId());
if (entry != null && entry.isRename()) {
// 如果是重名对象,则加入RENAME类型的信息记录
list.add(new DiffReportEntry(DiffType.RENAME,
fromEarlier ? entry.getSourcePath() : entry.getTargetPath(),
fromEarlier ? entry.getTargetPath() : entry.getSourcePath()));
} else {
fullPath[fullPath.length - 1] = dnode.getLocalNameBytes();
// 同样进行上述逻辑判断,如果是later-earlier比较的话,deleted的INode都是DELETE类型的
list.add(new DiffReportEntry(fromEarlier ? DiffType.DELETE
: DiffType.CREATE, fullPath));
}
}
return list;
}在这里,就会有其他3种类型的记录的添加.同时在比较的时候,还需要注意先后快照的比较顺序,不同的顺序的比较,所导致的DiffType会是相反的.以上4种所代表的标签符号如下:
public enum DiffType {
CREATE("+"),
MODIFY("M"),
DELETE("-"),
RENAME("R");
...SnapshotDiffReport对象构造完毕之后,此对象的toString输出就是命令返回的结果.GenerateReport的过程相对还是比较简单的.
HDFS的Snapshot的使用
Snapshot快照在很多场景中具有很大的用处,其中最大的好处是元数据变更信息的获取.获取了这个变更信息之后,我们可以进行元数据的同步.下面举出一个之前文章中提到过的一个例子,HDFS数据迁移解决方案之DistCp工具的巧妙使用.
在这篇文章中,介绍了用DistCp中的-diff参数附加2个from,to快照,进行元数据的变更的同步,然后利用distCp的功能,进行真实数据的拷贝,以此实现集群数据间的同步.这就是HDFS的snapshot的一个很好的使用场景.
当然,HDFS的snapshot还可以有别的使用的场景,关键看你怎么去利用这个new feature.
参考链接
1.https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r2.7.2/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-hdfs/HdfsSnapshots.html