1.盒子边框的线条动画:

.gif)
<div class="cont"> <div class="bb"></div> </div> .bb{ position: relative; width: 200px; height: 200px; background: #666666; border: 1px solid #5EF75E; } .bb:before,.bb:after{ content: " "; display: block; position: absolute; width:220px; height:220px; top: -10px; left: -10px; border:2px solid #00FF00; z-index:10; box-sizing: border-box; -webkit-animation: clipAni 4s infinite linear; } .bb:before{ -webkit-animation-delay: 2s; } @keyframes clipAni{ 0%,100%{ clip:rect(0px,220px,220px,217px); } 25%{ clip:rect(0px,220px,3px,0px); } 50%{ clip:rect(0px,3px,220px,0px); } 75%{ clip:rect(217px,220px,220px,0px); } }
用到的知识点:
clip 属性用来设置元素的形状。用来剪裁绝对定位元素。
当一幅图像的尺寸大于包含它的元素时,"clip" 属性允许规定一个元素的可见尺寸,这样此元素就会被修剪并显示在这个元素中。
用这个属性需要注意以下三点:
1.clip属性只能用于绝对定位元素,position:absolute或fixed。
2.clip属性有三种取值:auto 默认的
inherit继承父级的
一个定义好的形状,但现在只能是方形的 rect()
clip: { shape | auto | inherit } ;
3.shape rect(<top>, <right>, <bottom>, <left>)中的四个元素不可省略。
下面看下clip属性的rect()函数
clip: rect(<top>, <right>, <bottom>, <left>);
具体四个数值表示什么呢?看下张图即可理解。
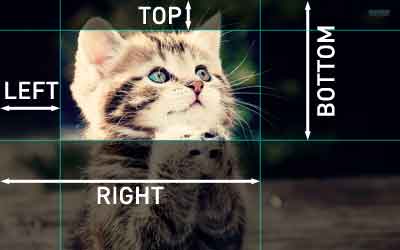

简单的理解就是:图片飞高就是bottom-top,宽就是right-left.当然图片不会是负数。
clip属性对于多数浏览器都可以用,写法会有点不同
.my-element { position: absolute; clip: rect(10px 350px 170px 0); /* IE4 to IE7 */ clip: rect(10px, 350px, 170px, 0); /* IE8+ & other browsers */ }
2

用到的知识点::focus-within
:focus-within 是一个CSS 伪类 ,表示一个元素获得焦点,或,该元素的后代元素获得焦点。换句话说,元素自身或者它的某个后代匹配:focus伪类。
元素的子元素或者自身元素的文本框获取焦点后执行的样式
.gif)
源码:
<div class="g-container"> <div class="g-section"> <input type="button"> <p> :focus-within 是一个CSS 伪类 ,表示一个元素获得焦点,或,该元素的后代元素获得焦点。换句话说,元素自身或者它的某个后代匹配:focus伪类。 </p> </div> <div class="g-section"> <input type="button"> <p> :focus-within 是一个CSS 伪类 ,表示一个元素获得焦点,或,该元素的后代元素获得焦点。换句话说,元素自身或者它的某个后代匹配:focus伪类。 </p> </div> <div class="g-section"> <input type="button"> <p> :focus-within 是一个CSS 伪类 ,表示一个元素获得焦点,或,该元素的后代元素获得焦点。换句话说,元素自身或者它的某个后代匹配:focus伪类。 </p> </div> </div> .g-container { width: 300px; margin: 50px auto; } .g-container p { line-height: 1.4; padding-left: 40px; } .g-container input { position: absolute; border: none; outline: none; background: none; width: 20px; height: 20px; border-radius: 50%; border: 1px solid #aaa; box-sizing: border-box; top: 50%; left: 10px; -webkit-transform: translate(0, -50%); transform: translate(0, -50%); cursor: pointer; } .g-container .g-section { position: relative; padding: 10px; box-sizing: border-box; border: 1px solid transparent; } .g-container .g-section:focus-within { background: linear-gradient(90deg, #03a9f4 50%, transparent 0) repeat-x, linear-gradient(90deg, #03a9f4 50%, transparent 0) repeat-x, linear-gradient(0deg, #03a9f4 50%, transparent 0) repeat-y, linear-gradient(0deg, #03a9f4 50%, transparent 0) repeat-y; background-size: 8px 1px, 8px 1px, 1px 8px, 1px 8px; background-position: 0 0, 0 100%, 0 0, 100% 0; -webkit-animation: linearGradientMove .5s infinite linear; animation: linearGradientMove .5s infinite linear; } .g-container .g-section:focus-within input { background: #03a9f4; } @-webkit-keyframes linearGradientMove { 100% { background-position: 6% 0, -6% 100%, 0 -6%, 100% 6%; } } @keyframes linearGradientMove { 100% { background-position: 6% 0, -6% 100%, 0 -6%, 100% 6%; } }
仅支持在pc端运行在移动端是不支持的
3:focus-within

.gif)
源码:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> * { margin: 0 ; padding: 0; } .container { width: 300px; margin: 50px auto; padding: 10px; boder: 1px solid #ddd; } .nav-box { font-size: 0; } button { width: 150px; height: 64px; box-sizing: border-box; outline: none; background: #fff; border: 1px solid #ddd; font-size: 18px; cursor: pointer; } button:focus-within { color: #fff; background: #ffcc00; } .content-box { font-size: 24px; border: 1px solid #ddd; height: 100px; } .content-box div { display: none; } .nav-box:not(:focus-within) .nav-A { color: #fff; background: #ffcc00; } .nav-box:not(:focus-within) .content-A { display: block; } .nav-A:focus-within ~ .content-box .content-A { display: block; } .nav-B:focus-within ~ .content-box .content-B { display: block; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="nav-box"> <button class="nav-A">Tab-A</button> <button class="nav-B">Tab-B</button> <div class="content-box"> <div class="content-A"> content-A </div> <div class="content-B"> content-B </div> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
4.
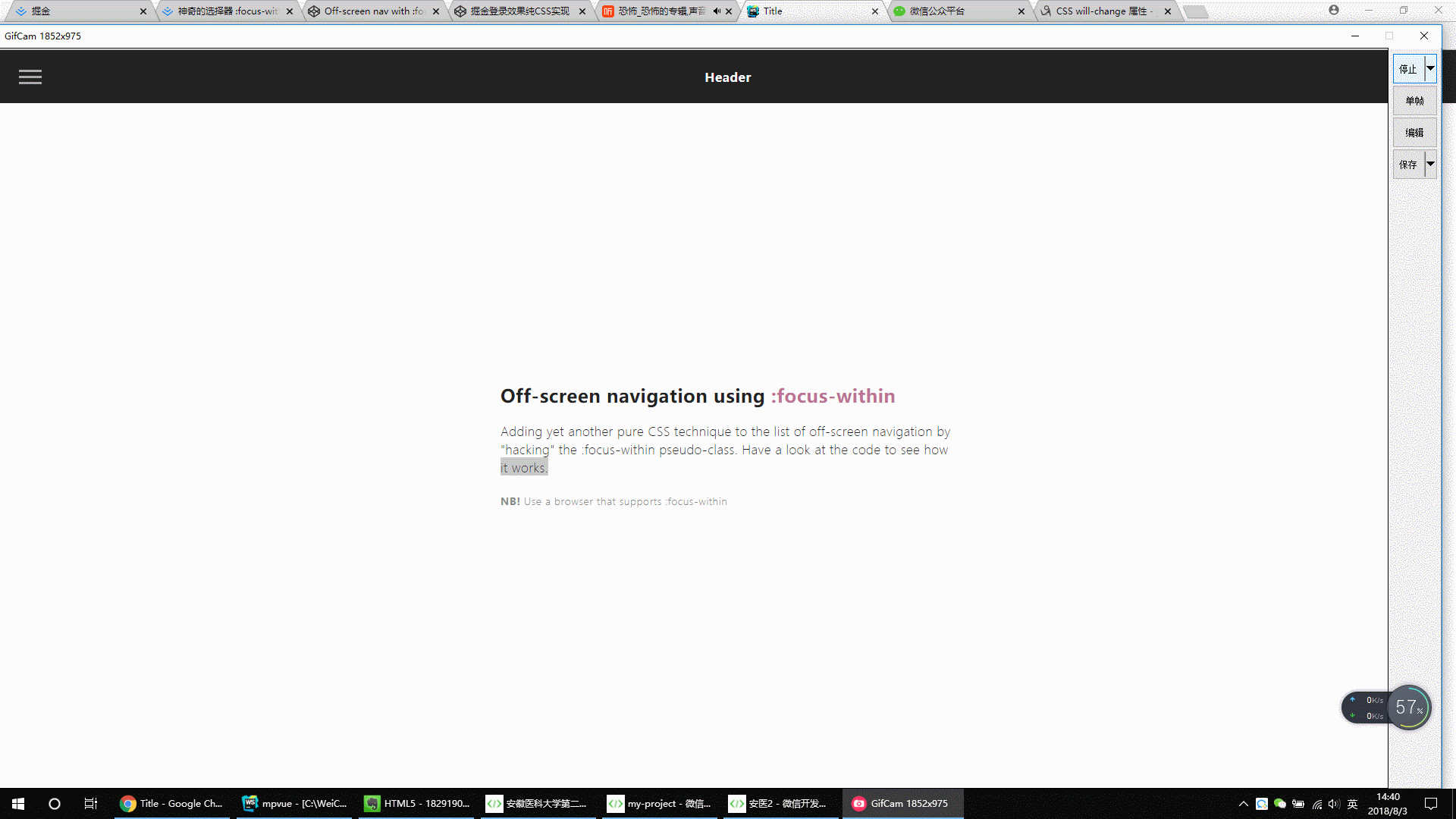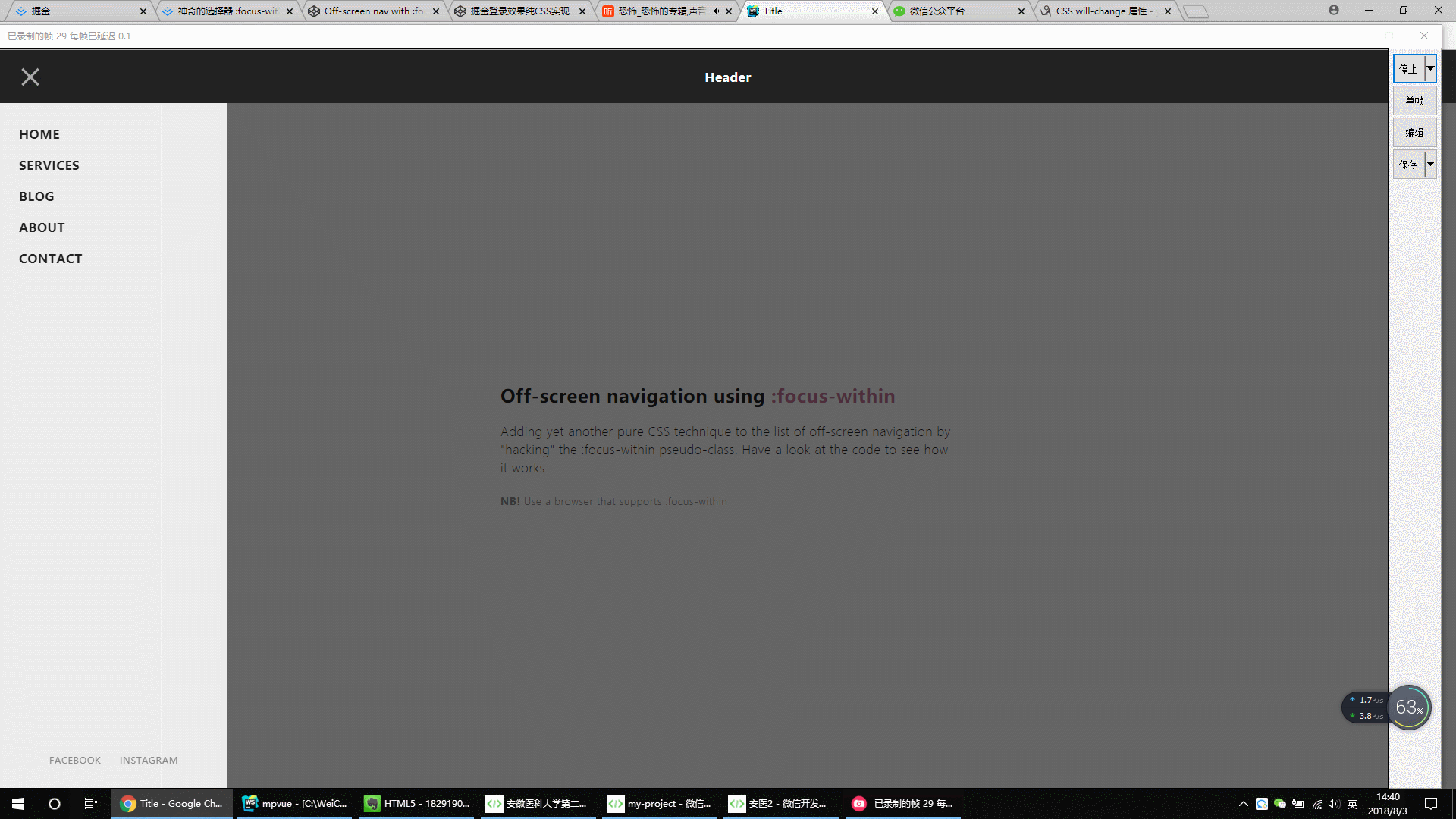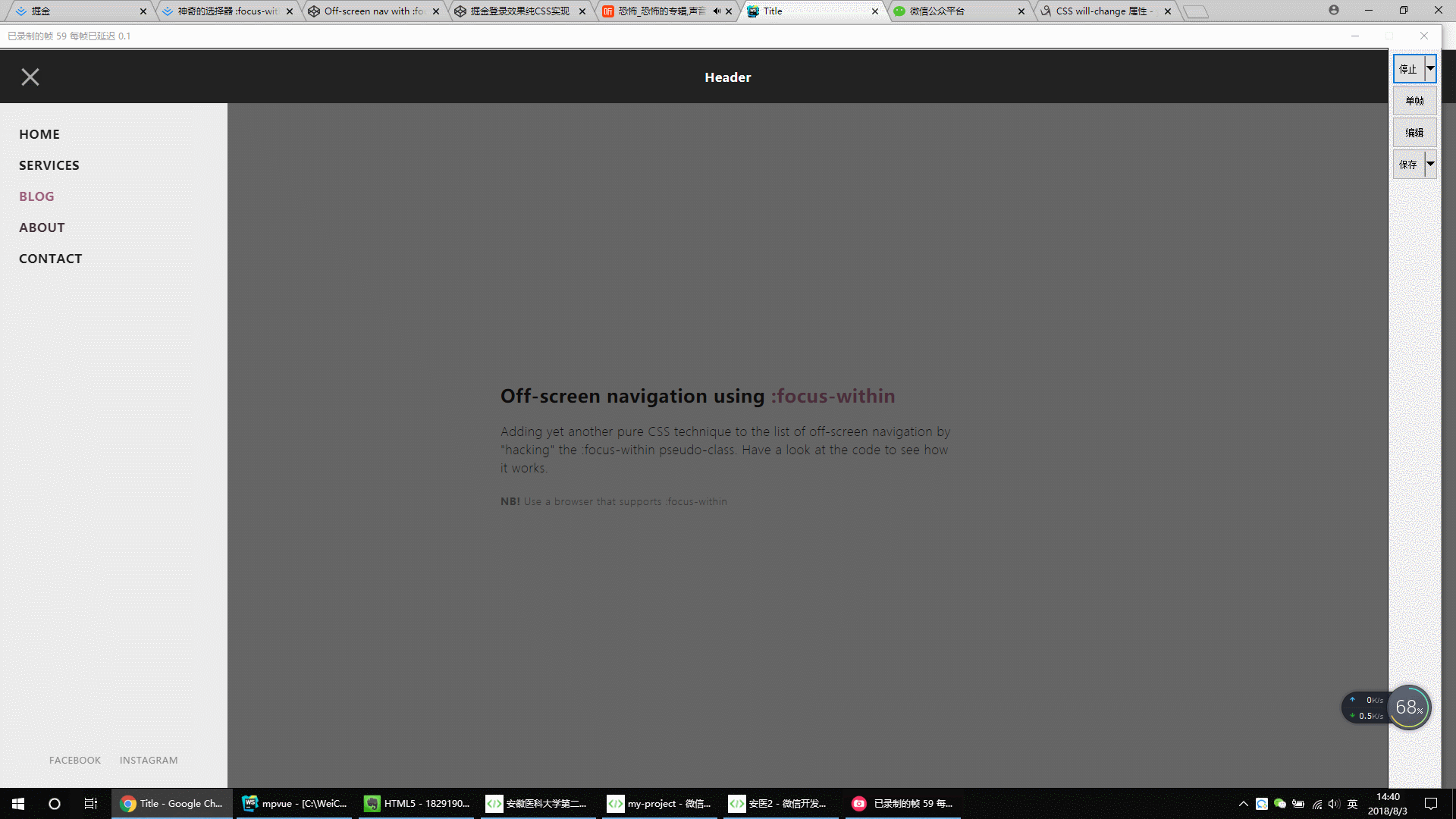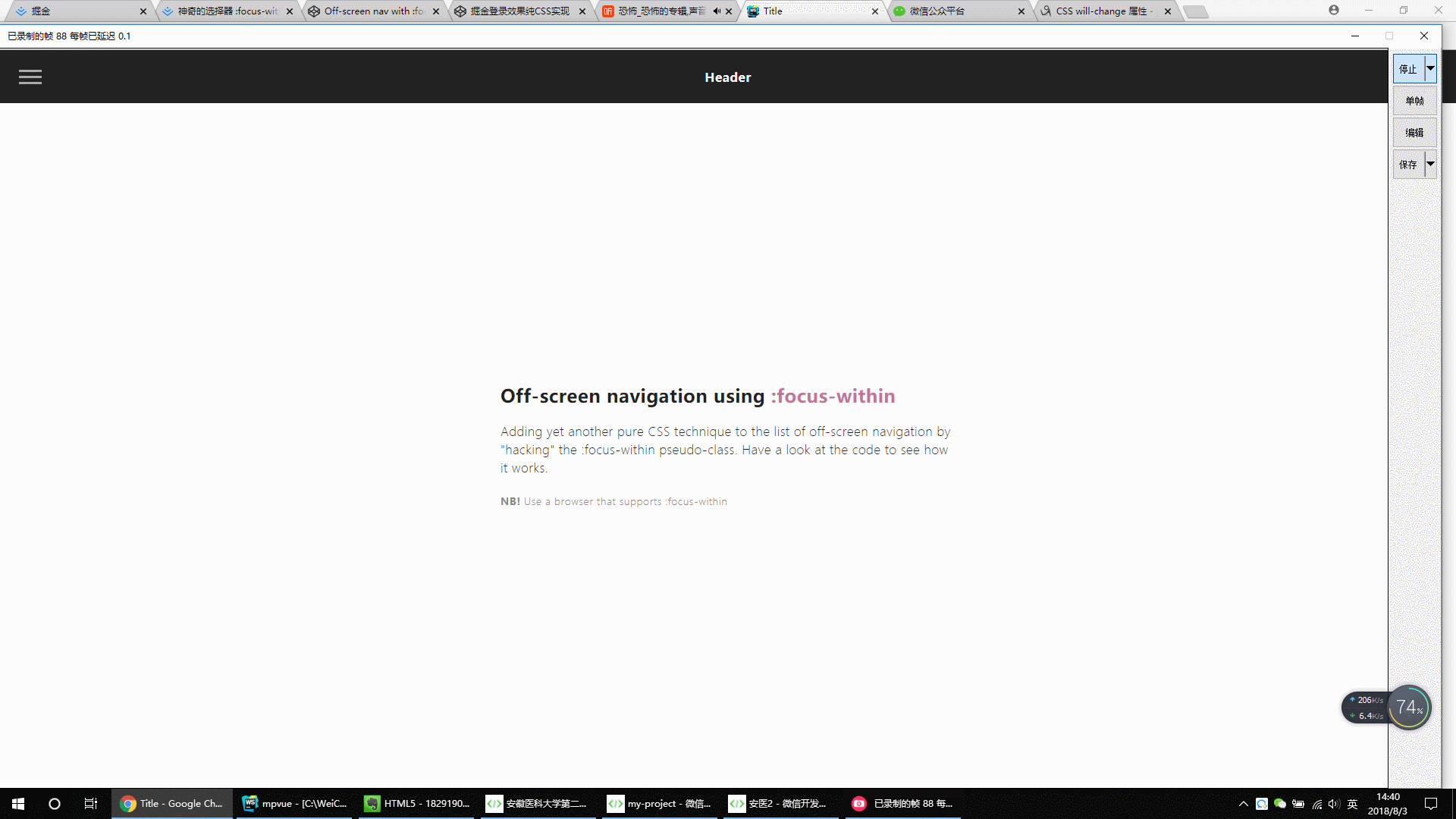
.gif)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> * { outline: none; } strong { font-weight: 600; } .page { width: 100%; height: 100vh; background: #fdfdfd; font-family: 'Encode Sans Condensed', sans-serif; font-weight: 600; letter-spacing: .03em; color: #212121; } header { display: flex; position: fixed; width: 100%; height: 70px; background: #212121; color: #fff; justify-content: center; align-items: center; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0,0,0,0); } main { padding: 70px 20px 0; display: flex; flex-direction: column; height: 100%; } main > div { margin: auto; max-width: 600px; } main h2 span { color: #BF7497; } main p { line-height: 1.5; font-weight: 200; margin: 20px 0; } main small { font-weight: 300; color: #888; } #nav-container { position: fixed; height: 100vh; width: 100%; pointer-events: none; } #nav-container .bg { position: absolute; top: 70px; left: 0; width: 100%; height: calc(100% - 70px); visibility: hidden; opacity: 0; transition: .3s; background: #000; } #nav-container:focus-within .bg { visibility: visible; opacity: .6; } #nav-container * { visibility: visible; } .button { position: relative; display: flex; flex-direction: column; justify-content: center; z-index: 1; -webkit-appearance: none; border: 0; background: transparent; border-radius: 0; height: 70px; width: 30px; cursor: pointer; pointer-events: auto; margin-left: 25px; touch-action: manipulation; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0,0,0,0); } .icon-bar { display: block; width: 100%; height: 3px; background: #aaa; transition: .3s; } .icon-bar + .icon-bar { margin-top: 5px; } #nav-container:focus-within .button { pointer-events: none; } #nav-container:focus-within .icon-bar:nth-of-type(1) { transform: translate3d(0,8px,0) rotate(45deg); } #nav-container:focus-within .icon-bar:nth-of-type(2) { opacity: 0; } #nav-container:focus-within .icon-bar:nth-of-type(3) { transform: translate3d(0,-8px,0) rotate(-45deg); } #nav-content { margin-top: 70px; padding: 20px; width: 90%; max-width: 300px; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; height: calc(100% - 70px); background: #ececec; pointer-events: auto; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0,0,0,0); transform: translateX(-100%); transition: transform .3s; will-change: transform; contain: paint; } #nav-content ul { height: 100%; display: flex; flex-direction: column; } #nav-content li a { padding: 10px 5px; display: block; text-transform: uppercase; transition: color .1s; } #nav-content li a:hover { color: #BF7497; } #nav-content li:not(.small) + .small { margin-top: auto; } .small { display: flex; align-self: center; } .small a { font-size: 12px; font-weight: 400; color: #888; } .small a + a { margin-left: 15px; } #nav-container:focus-within #nav-content { transform: none; } * { box-sizing: border-box; margin: 0; padding: 0; } html, body { height: 100%; } a,a:visited,a:focus,a:active,a:link { text-decoration: none; outline: 0; } a { color: currentColor; transition: .2s ease-in-out; } h1, h2, h3, h4 { margin: 0; } ul { padding: 0; list-style: none; } img { vertical-align: middle; height: auto; width: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="page"> <header tabindex="0">Header</header> <div id="nav-container"> <div class="bg"></div> <div class="button" tabindex="0"> <span class="icon-bar"></span> <span class="icon-bar"></span> <span class="icon-bar"></span> </div> <div id="nav-content" tabindex="0"> <ul> <li><a href="#0">Home</a></li> <li><a href="#0">Services</a></li> <li><a href="#0">Blog</a></li> <li><a href="#0">About</a></li> <li><a href="#0">Contact</a></li> <li class="small"><a href="#0">Facebook</a><a href="#0">Instagram</a></li> </ul> </div> </div> <main> <div class="content"> <h2>Off-screen navigation using <span>:focus-within</span></h2> <p>Adding yet another pure CSS technique to the list of off-screen navigation by "hacking" the :focus-within pseudo-class. Have a look at the code to see how it works.</p> <small><strong>NB!</strong> Use a browser that supports :focus-within</small> </div> </main> </div> </body> </html>
5.
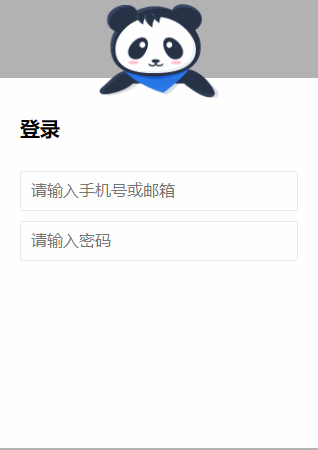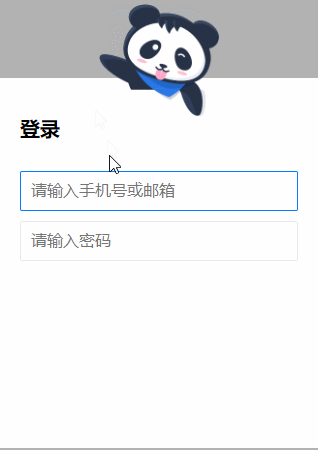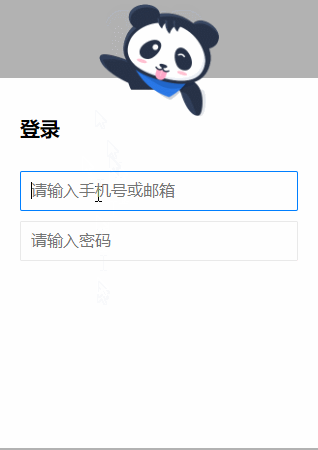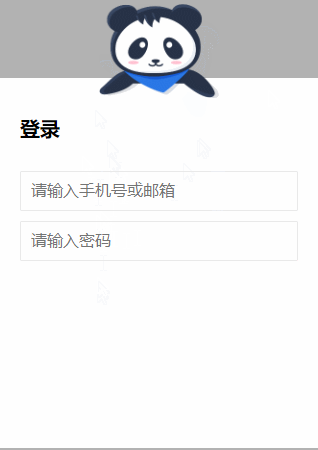

源码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .g-wrap { position: fixed; top: 0; left: 0; bottom: 0; right: 0; background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3); } .g-container { position: relative; width: 318px; margin: 100px auto; height: 370px; padding: 20px; box-sizing: border-box; background: #fff; z-index: 10; } .g-container h2 { font-size: 20px; font-weight: bold; margin-bottom: 30px; } .g-container input { outline: none; padding: 10px; width: 100%; border: 1px solid #e9e9e9; border-radius: 2px; outline: none; box-sizing: border-box; font-size: 16px; } img { position: absolute; top: -20%; left: 50%; width: 120px; height: 95px; -webkit-transform: translate(-50%, 0); transform: translate(-50%, 0); } .g-username { margin-bottom: 10px; } .g-username img { display: none; width: 120px; height: 113px; } .g-username:focus-within ~ img { display: none; } .g-username:focus-within input { border-color: #007fff; } .g-username:focus-within img { display: block; } .g-password { margin-bottom: 10px; } .g-password img { display: none; width: 103px; height: 84px; top: -15%; } .g-password:focus-within ~ img { display: none; } .g-password:focus-within input { border-color: #007fff; } .g-password:focus-within img { display: block; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="g-wrap"></div> <div class="g-container"> <h2>登录</h2> <div class="g-username"> <input name="loginPhoneOrEmail" maxlength="64" placeholder="请输入手机号或邮箱" class="input"> <img src="https://b-gold-cdn.xitu.io/v3/static/img/greeting.1415c1c.png" class="g-username"> </div> <div class="g-password"> <input name="loginPassword" type="password" maxlength="64" placeholder="请输入密码" class="input"> <img src="https://b-gold-cdn.xitu.io/v3/static/img/blindfold.58ce423.png" class="g-password"> </div> <img src="https://b-gold-cdn.xitu.io/v3/static/img/normal.0447fe9.png" class="g-normal"> </div> </body> </html>