BFS
所谓宽度优先,就是每次都尝试访问同一层的节点。 如果同一层都访问完了,再访问下一层。
这样做的结果是,BFS 算法找到的路径是从起点开始的 最短 合法路径。换言之,这条路所包含的边数最小。
在 BFS 结束时,每个节点都是通过从起点到该点的最短路径访问的。
实现
bfs(s) { q = new queue() q.push(s), visited[s] = true while (!q.empty()) { u = q.pop() for each edge(u, v) { if (!visited[v]) { q.push(v) visited[v] = true } } } }
应用场景
- 迷宫图求最短路,求连通性
- 图论
- 树的层序遍历
- 图的最短路,连通性(求图的联通分量,跑多次BFS,例题:flood fill)
- 隐式图搜索 ,找最短路
- 建立显示图
- 通过状态转移找点
- 拓扑排序
- 分层图
0-1 BFS(双端队列BFS)
边权值为可能有,也可能没有(由于 BFS 适用于权值为 1 的图,所以一般是 0 or 1),或者能够转化为这种边权值的最短路问题。
一般情况下,我们把没有权值的边扩展到的点放到队首,有权值的边扩展到的点放到队尾。这样即可保证在整个队列中,像普通 BFS 一样,越靠近队首,权值越小,且权值零一之间有分隔。
while (队列不为空) { int u = 队首; 弹出队首; if (vis[u]) continue; vis[u] = 1; for (枚举 u 的邻居) { 更新数据 if (...) 添加到队首; else 添加到队尾; } }
优先队列BFS
优先队列,相当于一个二叉堆,STL 中提供了 std::priority_queue,可以方便我们使用优先队列。
在基于优先队列的 BFS 中,我们每次从队首取出代价最小的结点进行进一步搜索。容易证明这个贪心思想是正确的,
因为从这个结点开始扩展的搜索,一定不会更新原来那些代价更高的结点。换句话说,其余那些代价更高的结点,我们不回去考虑更新它。
当然,每个结点可能会被入队多次,只是每次入队的代价不同。当该结点第一次从优先队列中取出,以后便无需再在该结点进行搜索,直接忽略即可。
所以,优先队列的 BFS 当中,每个结点只会被处理一次。
相对于普通队列的 BFS,时间复杂度多了一个$log$,毕竟要维护这个优先队列嘛。不过普通 BFS 有可能每个结点入队、出队多次,时间复杂度会达到$O(n^2)$,不是$O(n)$。所以优先队列 BFS 通常还是快的。
诶?这怎么听起来这么像堆优化的 Dijkstra 算法呢?事实上,堆优化 Dijkstra 就是优先队列 BFS。
LC102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
层序遍历二叉树,按层输出
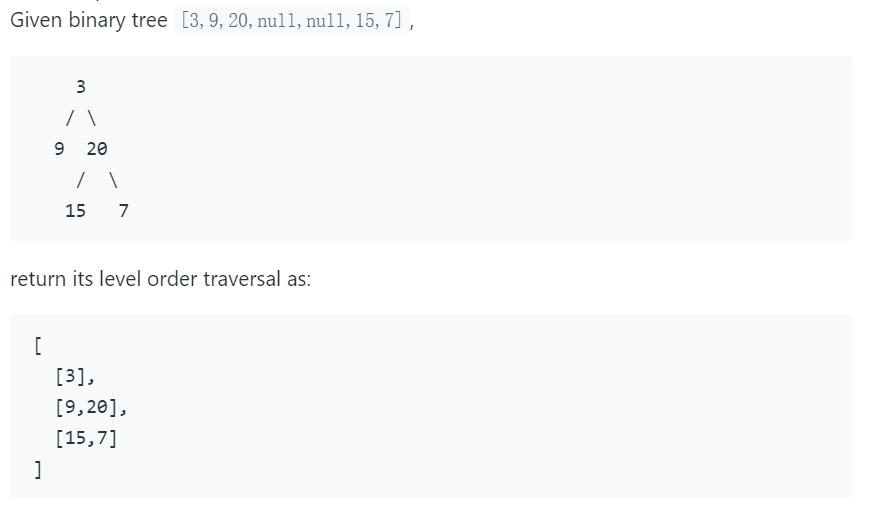
方法一:BFS
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { vector<vector<int>> res; if (!root) return res; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); while (!q.empty()) { int levelNum = q.size(); vector<int> level; for (int i = 0; i < levelNum; ++i) { TreeNode* t = q.front(); q.pop(); level.push_back(t->val); if (t->left) q.push(t->left); if (t->right) q.push(t->right); } res.push_back(level); } return res; } };
方法二:DFS
由于是每一层放入一个vector,因此可以用dfs,用一个参数记录深度信息,将当前节点插入对应深度的结果vector中
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> res; void dfs(TreeNode* u, int dep) { if (!u) return; if (res.size() == dep) res.emplace_back(); res[dep].push_back(u->val); dfs(u->left, dep + 1); dfs(u->right, dep + 1); } vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { dfs(root, 0); return res; } };
本题类似题目
LC429. N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal n叉树层序遍历
LC1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix 迷宫图问题,记住此模板

class Solution { public: typedef pair<int, int> PII; int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int n = grid.size(); if (grid[0][0] || grid[n - 1][n - 1]) return -1; grid[0][0] = 1; queue<PII> q; q.emplace(0, 0); while (!q.empty()) { PII u = q.front(); q.pop(); int x = u.first, y = u.second; for (int i = -1; i <= 1; ++i) { for (int j = -1; j <= 1; ++j) { int nx = x + i; int ny = y + j; if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= n || grid[nx][ny]) continue; grid[nx][ny] = grid[x][y] + 1; q.emplace(nx, ny); } } } return grid[n - 1][n - 1] == 0 ? -1 : grid[n - 1][n - 1]; } };
LC279. Perfect Squares
完美平方数为1,4,9,16,···,给定n,求和为n的完美平方数的最小个数。
这道题可以转换为完全背包问题,也可以用BFS做。从节点0开始,下一层能到的数入队,以此类推,直到遇到节点n,结果就是层数。
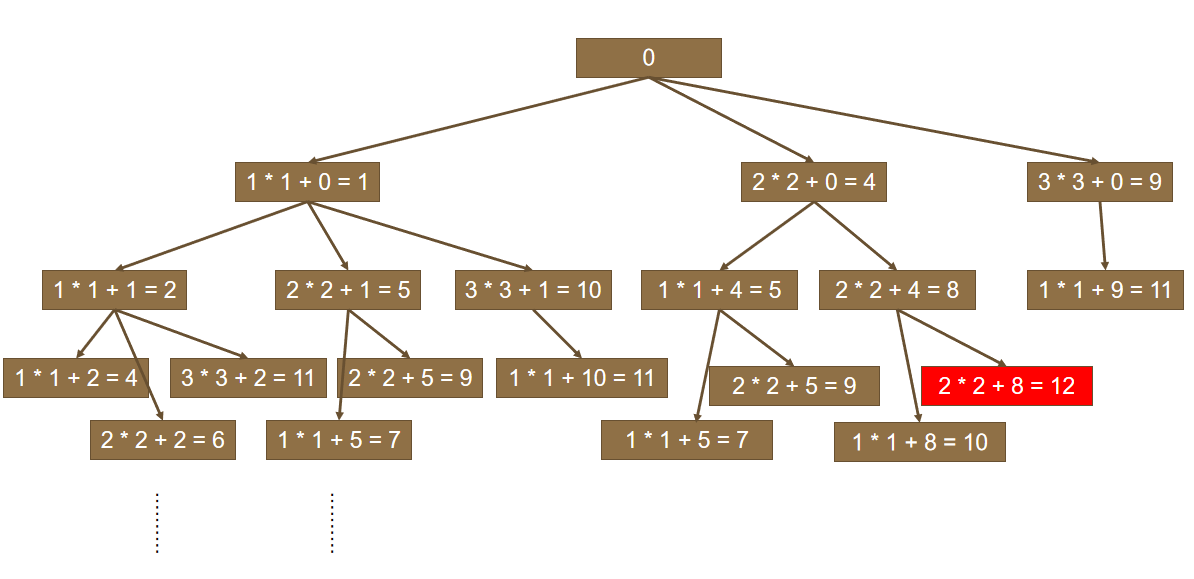
class Solution { public: int numSquares(int n) { queue<int> q; unordered_set<int> vis; q.push(0); vis.insert(0); int d = 0; while (!q.empty()) { d++; int size = q.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { int f = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int j = 1; j * j + f <= n; ++j) { int next = j * j + f; if (next == n) return d; if (!vis.count(next)) { q.push(next); vis.insert(next); } } } } return 0; } };
LC1368. Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid

方法一:Dijkstra算法
Dijkstra算法适合用来求出无负权边图中的单源最短路径。由于所有边的权值均为0或1,并且我们只需要求出从$(0, 0)$到$(m - 1, n - 1)$的最短路,因此可以直接套用Dijkstra算法得到答案。
class Solution { private: static constexpr int dirs[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}; public: int minCost(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int m = grid.size(); int n = grid[0].size(); vector<int> dist(m * n, INT_MAX); vector<int> seen(m * n, 0); dist[0] = 0; priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> q; q.emplace(0, 0); while (!q.empty()) { auto [cur_dis, cur_pos] = q.top(); q.pop(); if (seen[cur_pos]) { continue; } seen[cur_pos] = 1; int x = cur_pos / n; int y = cur_pos % n; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int nx = x + dirs[i][0]; int ny = y + dirs[i][1]; int new_pos = nx * n + ny; int new_dis = cur_dis + (grid[x][y] != i + 1); if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && new_dis < dist[new_pos]) { dist[new_pos] = new_dis; q.emplace(new_dis, new_pos); } } } return dist[m * n - 1]; } };

方法二:0-1 BFS

class Solution { private: static constexpr int dirs[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}; public: int minCost(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int m = grid.size(); int n = grid[0].size(); vector<int> dist(m * n, INT_MAX); vector<int> seen(m * n, 0); dist[0] = 0; deque<int> q; q.push_back(0); while (!q.empty()) { auto cur_pos = q.front(); q.pop_front(); if (seen[cur_pos]) { continue; } seen[cur_pos] = 1; int x = cur_pos / n; int y = cur_pos % n; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int nx = x + dirs[i][0]; int ny = y + dirs[i][1]; int new_pos = nx * n + ny; int new_dis = dist[cur_pos] + (grid[x][y] != i + 1); if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && new_dis < dist[new_pos]) { dist[new_pos] = new_dis; if (grid[x][y] == i + 1) { q.push_front(new_pos); } else { q.push_back(new_pos); } } } } return dist[m * n - 1]; } };

LC407. Trapping Rain Water II
$m imes n$矩阵代表二维高度图中每个单元的高度,计算图中形状最多能接多少体积的雨水。
解法:优先队列BFS
class Solution { public: int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) { if (heightMap.size() == 0) return 0; priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>>q; int row = heightMap.size(), col = heightMap[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> visited(row, vector<int>(col, 0)); int ans = 0, Max = INT_MIN; for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j) { if (!(i == 0 || i == row - 1 || j == 0 || j == col - 1)) continue; q.emplace(heightMap[i][j], i * col + j); visited[i][j] = 1; } } vector<vector<int>> dir{{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}}; while (!q.empty()) { auto val = q.top(); q.pop(); int height = val.first, x = val.second / col, y = val.second % col; Max = max(Max, height); for (auto& d : dir) { int x2 = x + d[0], y2 = y + d[1]; if (x2 >= row || x2 < 0 || y2 >= col || y2 < 0 || visited[x2][y2]) continue; visited[x2][y2] = 1; if (heightMap[x2][y2] < Max) ans += Max - heightMap[x2][y2]; q.emplace(heightMap[x2][y2], x2 * col + y2); } } return ans; } };
LC301. Remove Invalid Parentheses
一个字符串,包含括号和字母,删除最少的括号,使字符串合法,输出所有可能的结果。
分析:用BFS,初始点为原字符串,第一层,从原字符串删去任意一个括号,将所有可能结果加入队列,判断该层是否有有效字符串,如果有,找到所有有效字符串即可,如果没有,取出队首字符串,开始第二层遍历。
class Solution { public: vector<string> removeInvalidParentheses(string s) { vector<string> res; if(s.empty()) return {""}; unordered_set<string> vis; queue<string> q; q.push(s); vis.insert(s); bool found = false; while (!q.empty()) { auto f = q.front(); q.pop(); if (isValid(f)) { res.push_back(f); found = true; } if (found) continue; for (int i = 0; i < f.size(); ++i) { if (f[i] != '(' && f[i] != ')') continue; string t = f.substr(0, i) + f.substr(i + 1); if (!vis.count(t)) { q.push(t); vis.insert(t); } } } return res; } bool isValid(string& s) { int cnt = 0; for (char& c : s) { if (c == '(') cnt++; if (c == ')' && cnt-- == 0) return false; } return cnt == 0; } };