bash shell如何获取命令行参数(添加到命令后的数据)、命令行选项(确定命令行为的英文字母)、键盘输入数据?
操作命令行参数
1 读取参数
bash shell用位置参数变量(positional parameter)存储命令行输入的所有参数,包括程序名。其中,$0表示程序名,$1表示第1个参数,$2表示第2个参数,...,$9表示第9个参数。如果参数个数多于9个,必须如下表示变量:${10},${11},...
for((count = 1; count <= $1; count++)) do echo The number is $count. done
echo $1, $2, $10, $15
2 读取程序名
首先想到的是利用$0,但是$0获取的文件名包括./以及路径等前缀信息,如下:
echo The command entered is: $0 # 运行:./ # 输出:The command entered is: ./14.sh
如果想仅得到文件名,而不包含./,可以使用basename命令:
name=`basename $0` echo The command entered is: $name # 运行:./ # 输出:The command entered is: 14.sh
3 特殊变量
$#表示命令行参数的个数:
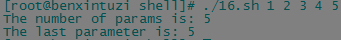
params=$# echo The number of params is: $params for((i = 1; i <= params; i++)) do echo The param is: $i done
那么很自然地,${$#}表示最后一个变量的值,如下程序:
params=$# echo The number of params is: $params echo The last parameter is: ${$#}

这是怎么回事呢?原来在花括号内不能使用$符号,而是以!来代替$工作:
params=$# echo The number of params is: $params echo The last parameter is: ${!#}
如果想获取所有的参数,当然可以利用$#和循环逐个遍历。也可以利用如下两个特殊变量:$*将所有的命令行参数看作一个整体存储,而$@将命令行中以空格间隔的参数单独存储,如下:
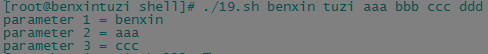
count=1 for param in "$*" do echo "$* parameter $count = $param" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done count=1 for param in "$@" do echo "$@ parameter $count = $param" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done
4 移动变量命令shift
shift命令用于将后一个变量的值移到前一个变量上,即$3的值移到$2,$2的值移到$1,$1的值被删除。 注:变量$0的值不会被替换。该命令可以使得在不需要知道有多少个参数的情况下即可遍历所有参数:
count=1 while [ -n "$1" ] do echo "parameter $count = $1" count=$[ $count + 1 ] shift done
注:使用shift命令移除的参数值是无法恢复的,也可以使用shift移到多位,如:shift 2。
操作命令行选项
1 查找选项
可以判断命令行参数是否存在有效选项:
#! /bin/bash # extracting command line options as parameters while [ -n "$1" ] do case "$1" in -a) echo "found the -a option";; -b) echo "found the -b option";; -c) echo "found the -c option";; *) echo "$1 is not an option";; esac shift done
在Linux中,命令行选项和参数的分离使用--符号,shell将--前边的参数作为选项来处理。如下脚本可以有效地分离出选项和参数:
#! /bin/bash # extracting command line options as parameters while [ -n "$1" ] do case "$1" in -a) echo "found the -a option";; -b) echo "found the -b option";; -c) echo "found the -c option";; --) break;; *) echo "$1 is not an option";; esac shift done shift # 确保跳出while循环后,将--符号移除掉 count=1 for param in $@ do echo "parameter $count: $param" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done
如何处理带有参数值的选项呢?比如,./22.sh -a -b benxin -c -d
#! /bin/bash # extracting command line options as parameters while [ -n "$1" ] do case "$1" in -a) echo "found the -a option";; -b) param="$2" echo "found the -b option with parameter value $param" shift 2;; -c) echo "found the -c option";; --) shift break;; *) echo "$1 is not an option";; esac shift done count=1 for param in "$@" do echo "parameter $count: $param" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done
合并选项时可以使用getopt命令,格式如下:
getopt options optstring parameters
options定义了命令行中有效的选项字母以及哪些选项字母需要附加参数值等(在需要附加参数值的选项字母后加一个冒号),如getopt ab:cd -a -b benxin -cd tuzi benxintuzi,optstring定义了4个有效字母:a、b、c、d,并且说明了选项b需要附带参数值。getopt命令自动将-cd拆分成-c和-d两个选项,并且用双破折号--隔开命令行中的额外参数。

2 选项的标准化约定
|
选项 |
说明 |
|
-a |
显示所有对象 |
|
-c |
生成一个计数 |
|
-d |
指定一个目录 |
|
-e |
扩展一个对象 |
|
-f |
指定输入文件 |
|
-h |
显示命令帮助 |
|
-i |
忽略文本大小写 |
|
-l |
产生输出的长格式版本 |
|
-n |
使用非交互模式(批量) |
|
-o |
指定输出文件 |
|
-q |
以安静模式运行 |
|
-r |
递归处理目录或文件 |
|
-s |
以安静模式运行 |
|
-v |
生成详细输出 |
|
-x |
排除某个对象 |
|
-y |
对所有问题回答yes |
操作键盘输入
1 基本的读取
read命令接受从键盘或文件描述符中的输入数据,将其存储到一个指定变量中。使用-p选项可以指定输入提示信息,如下所示:
#! /bin/bash # testing the read option read -p "Please enter your name: " name echo "Hello $name."
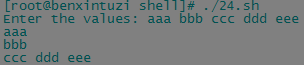
read命令中,可以根据需要将输入的数据保存在多个变量中,如果指定的变量比较少,那么最后一个变量将包含余下的所有输入,如下所示:
#! /bin/bash # testing the read option read -p "Enter the values: " val1 val2 val3 echo "$val1" echo "$val2" echo "$val3"
注:如果使用read命令时不指定变量,那么read将其接收的任何数据都放到环境变量REPLY中。
2 输入超时
使用read命令时,脚本会一直等待用户输入数据,如果想设置等待时间,使用-t选项即可指定一个计时器,当计时器超时后,read命令会返回一个非零状态码。
if read -t 5 -p "Please enter your name: " name then echo "Hello $name." else echo echo "Sorry, too slow" fi
3 隐藏输入显示
当输入敏感信息时,比如密码,不希望显示在屏幕上,那么可以使用read的-s选项,-s选项的功能是将输入文本颜色设置为与背景色一样:
#! /bin/bash # testing the read option read -s -p "Enter your password: " passwd echo echo "Is your password really $passwd?"
4 从文件中读取
read每次从文件中读取一行数据,当文件中没有数据时,read命令返回非零状态码。最常见的方法是将cat命令运行后的结果通过管道传给含有read的while语句,如下:
#! /bin/bash # testing the read option count=1 cat 25.sh | while read line do echo "Line $count: $line" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done echo "Finished processing the file"