参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/big-devil/p/8590007.html
Linux 块设备驱动程序
概念补充:
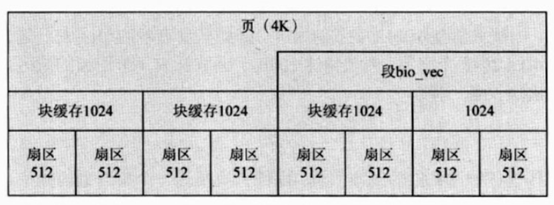
块
扇区是硬件数据传输的基本单元,块则是虚拟文件系统传输数据的基本单位。Linux内核中,块的大小必须是2的次幂,但不能超过一个页(4K)的大小。
段
同一物理页面中的硬盘存储介质上连续的多个块组成一个段。段的大小与块的个数有关,段包含多个块,块包含多个扇区。段在内核中由bio_vec结构体描述,多个段的信息存放于结构体bio中的biz_io_vec数组中,段数组在后续的块设备处理流程中被合并成物理段。bio_vec段结构体定义如下:
-
struct bio_vec {
-
struct page *bv_page;//数据段所在的页,即bh->b_page
-
unsigned int bv_len;//数据段的长度 ,即bh->b_size
-
unsigned int bv_offset;//数据段页内偏移 ,即bh->b_data
-
};
总结:
扇区由磁盘的物理特性决定,快缓冲区大小由内核决定,段由块缓冲区个数决定,但不能超过页的大小。三者关系如下:
Linux内核中,块设备将数据存储在固定大小的块中,每个块具有固定的地址。内核中块设备与其他模块之间的关系如下:
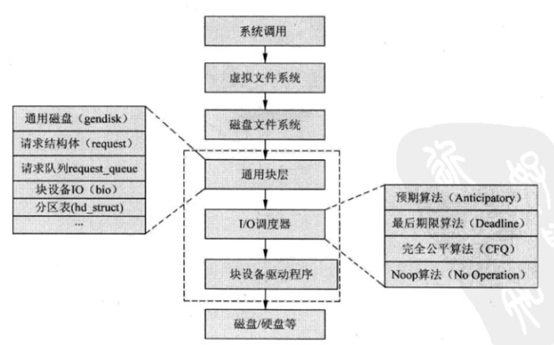
块设备的操作流程简述如下:
(1)、用户程序向磁盘中写入数据时,会发出write()系统调用给内核;
(2)、内核调用虚拟文件系统相应的函数,将需要写入的文件描述符和文件内容指针传递给该函数;
(3)、内核需要确定写入磁盘的位置,通过映射层知道需要写入磁盘的哪一块。
(4)、根据磁盘文件系统的类型,调用对应文件格式的写入函数,将数据发送给通用块层;
(5)、到达通用块层后,对设备发出写请求。内核利用通用块层的启动I/O调度器,对数据进行排序,调度器会将物理上相邻的读写合并在一起,加快访问速度;
(6)、最后块设备驱动向磁盘发送指令和数据,将数据写入磁盘。
Linux块设备驱动程序框架图如下:
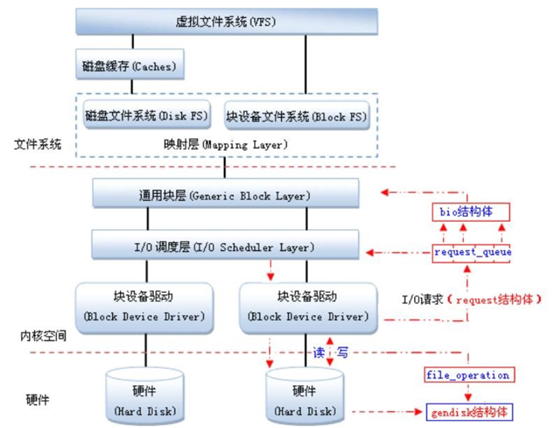
架构分析
bio结构体
当一个进行被read时,首先会去cache中查看是否有相关文件,若没有,系统会利用块设备驱动去磁盘中读取数据。于是read()函数将被初始化成一个bio结构体,提交给通用块层。一个bio对应一个i/o请求。在include/linux/bio.h文件中定义。
-
struct bio {
-
sector_t bi_sector; //该bio结构体所要传输的第一个扇区(512字节),磁盘的位置
-
struct bio *bi_next; //请求链表
-
struct block_device *bi_bdev;//相关的块设备
-
unsigned long bi_flags; //状态和命令标志
-
unsigned long bi_rw; //读写
-
unsigned short bi_vcnt; //bio_vec偏移的个数
-
unsigned short bi_idx; //bvl_vec的当前索引
-
unsigned short bi_phys_segments;//结合后片段数目
-
unsigned short bi_hw_segments;//重映射后的片段数目
-
unsigned int bi_size; //I/O计数
-
unsigned int bi_hw_front_size;//第一个可合并的段大小
-
unsigned int bi_hw_back_size;//最后一个可合并的段大小
-
-
unsigned int bi_max_vecs; //bvl_vecs数目上线
-
struct bio_vec *bi_io_vec; //bio_vec链表:内存的位置
-
-
bio_end_io_t *bi_end_io;//bio_vec完成方法
-
atomic_t bi_cnt; //使用计数
-
-
void *bi_private;//拥有者的私有方法
-
-
bio_destructor_t *bi_destructor; //销毁方法
-
};
bio结构的核心是biz_io_vec数组,表示整个完整的缓冲区,由bio_vec组成,在内核中的定义如下:
-
struct bio_vec {
-
struct page *bv_page;//数据段所在的页
-
unsigned int bv_len;//数据段的长度
-
unsigned int bv_offset;//数据段页内偏移
-
};
当一个块被调用到内存中时,要存储在一个缓冲区中。每一个缓冲区对应一个块,并拥有一个对应的描述符。该描述符使用buffer_head结构体表示,其定义如下:
-
struct buffer_head {
-
unsigned long b_state; /* buffer state bitmap (see above) */
-
struct buffer_head *b_this_page;/* circular list of page's buffers */
-
struct page *b_page; /* the page this bh is mapped to */
-
-
sector_t b_blocknr; /* start block number */
-
size_t b_size; /* size of mapping */
-
char *b_data; /* pointer to data within the page */
-
-
struct block_device *b_bdev;
-
bh_end_io_t *b_end_io; /* I/O completion */
-
void *b_private; /* reserved for b_end_io */
-
struct list_head b_assoc_buffers; /* associated with another mapping */
-
struct address_space *b_assoc_map; /* mapping this buffer is
-
associated with */
-
atomic_t b_count; /* users using this buffer_head */
-
};
bio与bufferhead之间的关系
核心函数ll_rw_block
-
void ll_rw_block(int rw, int nr, struct buffer_head *bhs[])
-
{
-
int i;
-
-
for (i = 0; i < nr; i++) {
-
struct buffer_head *bh = bhs[i];
-
-
if (rw == SWRITE)
-
lock_buffer(bh);
-
else if (test_set_buffer_locked(bh))
-
continue;
-
-
if (rw == WRITE || rw == SWRITE) {
-
if (test_clear_buffer_dirty(bh)) {
-
bh->b_end_io = end_buffer_write_sync;
-
get_bh(bh);
-
submit_bh(WRITE, bh);
-
continue;
-
}
-
} else {
-
if (!buffer_uptodate(bh)) {
-
bh->b_end_io = end_buffer_read_sync;
-
get_bh(bh);
-
submit_bh(rw, bh);
-
continue;
-
}
-
}
-
unlock_buffer(bh);
-
}
-
}
核心函数submit_bh
-
int submit_bh(int rw, struct buffer_head * bh)
-
{
-
struct bio *bio;
-
int ret = 0;
-
-
BUG_ON(!buffer_locked(bh));
-
BUG_ON(!buffer_mapped(bh));
-
BUG_ON(!bh->b_end_io);
-
-
if (buffer_ordered(bh) && (rw == WRITE))
-
rw = WRITE_BARRIER;
-
-
/*
-
* Only clear out a write error when rewriting, should this
-
* include WRITE_SYNC as well?
-
*/
-
if (test_set_buffer_req(bh) && (rw == WRITE || rw == WRITE_BARRIER))
-
clear_buffer_write_io_error(bh);
-
-
/*
-
* from here on down, it's all bio -- do the initial mapping,
-
* submit_bio -> generic_make_request may further map this bio around
-
*/
-
bio = bio_alloc(GFP_NOIO, 1);
-
-
bio->bi_sector = bh->b_blocknr * (bh->b_size >> 9);
-
bio->bi_bdev = bh->b_bdev;
-
bio->bi_io_vec[0].bv_page = bh->b_page;
-
bio->bi_io_vec[0].bv_len = bh->b_size;
-
bio->bi_io_vec[0].bv_offset = bh_offset(bh);
-
-
bio->bi_vcnt = 1;
-
bio->bi_idx = 0;
-
bio->bi_size = bh->b_size;
-
-
bio->bi_end_io = end_bio_bh_io_sync;
-
bio->bi_private = bh;
-
-
bio_get(bio);
-
submit_bio(rw, bio);
-
-
if (bio_flagged(bio, BIO_EOPNOTSUPP))
-
ret = -EOPNOTSUPP;
-
-
bio_put(bio);
-
return ret;
-
}
核心函数submit_bio
-
void submit_bio(int rw, struct bio *bio)
-
{
-
int count = bio_sectors(bio);
-
-
BIO_BUG_ON(!bio->bi_size);
-
BIO_BUG_ON(!bio->bi_io_vec);
-
bio->bi_rw |= rw;
-
if (rw & WRITE) {
-
count_vm_events(PGPGOUT, count);
-
} else {
-
task_io_account_read(bio->bi_size);
-
count_vm_events(PGPGIN, count);
-
}
-
-
if (unlikely(block_dump)) {
-
char b[BDEVNAME_SIZE];
-
printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s(%d): %s block %Lu on %s ",
-
current->comm, current->pid,
-
(rw & WRITE) ? "WRITE" : "READ",
-
(unsigned long long)bio->bi_sector,
-
bdevname(bio->bi_bdev,b));
-
}
-
-
generic_make_request(bio);
-
}
核心函数generic_make_request
-
void generic_make_request(struct bio *bio)
-
{
-
if (current->bio_tail) {
-
/* make_request is active */
-
*(current->bio_tail) = bio;
-
bio->bi_next = NULL;
-
current->bio_tail = &bio->bi_next;
-
return;
-
}
-
-
BUG_ON(bio->bi_next);
-
do {
-
current->bio_list = bio->bi_next;
-
if (bio->bi_next == NULL)
-
current->bio_tail = ¤t->bio_list;
-
else
-
bio->bi_next = NULL;
-
__generic_make_request(bio);
-
bio = current->bio_list;
-
} while (bio);
-
current->bio_tail = NULL; /* deactivate */
-
}
该函数中主要实现取出每个bio,并执行__generic_make_request函数。
通用层在调用相应的IO调度器时,会将bio合并到已经存在的request中,或创建一个新的request,并将创建的插入到请求队列中,最后由块设备驱动层来完成。Linux内核中,对块设备的IO请求,会向块设备驱动发出一个请求,由结构体request 表示,其定义如下:
-
struct request {
-
struct list_head queuelist;//挂在请求队列链表的节点
-
struct list_head donelist;//挂在已完成请求链表的节点
-
-
request_queue_t *q; //指向请求队列的指针
-
-
unsigned int cmd_flags;//命令标识
-
enum rq_cmd_type_bits cmd_type;//命令标志
-
-
/* Maintain bio traversal state for part by part I/O submission.
-
* hard_* are block layer internals, no driver should touch them!
-
*/
-
-
sector_t sector; //下一个需要提交的扇区的偏移位置
-
sector_t hard_sector; //要完成的下一个扇区的偏移位置
-
unsigned long nr_sectors; //需要提交的扇区数目
-
unsigned long hard_nr_sectors; //剩余需要完成的扇区数目
-
unsigned int current_nr_sectors;//当前segment中剩余需要提交的扇区数目
-
unsigned int hard_cur_sectors;//当前segment中剩余需要完成的扇区数目
-
-
struct bio *bio; //请求中第一个未完成的bio
-
struct bio *biotail;
-
-
...
-
};
请求队列结构体request_queue定义如下:
-
struct request_queue
-
{
-
/*
-
* Together with queue_head for cacheline sharing
-
*/
-
struct list_head queue_head;
-
struct request *last_merge;
-
elevator_t *elevator;
-
struct request_list rq;
-
-
request_fn_proc *request_fn;
-
make_request_fn *make_request_fn;
-
prep_rq_fn *prep_rq_fn;
-
unplug_fn *unplug_fn;
-
merge_bvec_fn *merge_bvec_fn;
-
issue_flush_fn *issue_flush_fn;
-
prepare_flush_fn *prepare_flush_fn;
-
softirq_done_fn *softirq_done_fn;
-
......
-
-
};
blk_init_queue函数
request_queue_t *blk_init_queue(request_fn_proc *rfn, spinlock_t *lock)
第一个参数rfn,指向"请求处理函数",请求处理函数"用于处理和硬盘之间的数据传输。
第二个参数lock,队列访问权限的自旋锁spinlock_t,通过DEFINE_SPINLOCK定义。
__generic_make_request函数中最终会调用make_request_fn函数,这里会分成两种情况。
第一种是执行请求队列中自定义的make_request_fn函数,这里使用blk_queue_make_request函数实现对请求队列和自定义请求处理函数之间的绑定。

第二种使用系统默认的使用系统默认的__make_request。该函数中会启动I/O调度器,对bio进行处理,将其合并到请求队列中的一个请求结构中。最后调用request_fn_proc将数据写入或读出块设备。
对bio结构体的处理可以使用I/O调度器,也可以不使用I/O调度器。blk_init_queue函数使用I/O调度器,通过该函数完成对队列的初始化。blk_alloc_queue函数不使用I/O调度器,通过该函数申请请求队列。
块设备驱动程序的框架:
-
块设备驱动加载
-
使用alloc_disk函数申请一个gendisk结构体;
-
根据是否需要I/O调度,将情况分为两种情况,一种是使用请求队列进行数据传输,一种是不使用请求队列进行数据传输。
-
初始化gendisk结构体;
-
使用register_blkdev函数注册一个块设备,可选;
-
使用add_disk激活磁盘设备。
-
-
块设备驱动卸载
-
使用del_gendisk函数删除一个gendisk结构体;
-
使用blk_cleanup_queue函数删除请求队列;
-
使用blk_unregister_region函数卸载块设备,可选。
-
代码如下:
-
#include <linux/module.h>
-
#include <linux/errno.h>
-
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
-
#include <linux/mm.h>
-
#include <linux/fs.h>
-
#include <linux/kernel.h>
-
#include <linux/timer.h>
-
#include <linux/genhd.h>
-
#include <linux/hdreg.h>
-
#include <linux/ioport.h>
-
#include <linux/init.h>
-
#include <linux/wait.h>
-
#include <linux/blkdev.h>
-
#include <linux/blkpg.h>
-
#include <linux/delay.h>
-
#include <linux/io.h>
-
-
#include <asm/system.h>
-
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
-
#include <asm/dma.h>
-
-
#define RAMBLOCK_SIZE 1024*1024
-
-
static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(ramblock_lock);
-
static struct gendisk *ramblock_gendisk;
-
static struct request_queue *ramblock_queue;
-
static int major;
-
static struct block_device_operations ramblock_fops = {
-
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
-
};
-
-
-
static void do_ramblock_request (request_queue_t * q)
-
{
-
struct request *req;
-
static int cnt = 0;
-
//printk("do_ramblock_request %d", ++cnt);
-
-
while ((req = elv_next_request(q)) != NULL) {
-
end_request(req, 1);
-
}
-
}__generic_make_request
-
-
static int ramblock_init(void)
-
{
-
/*1、分配gendisk结构体*/
-
ramblock_gendisk = alloc_disk(16); /*次设备号个数:分区个数+1*/
-
-
/*2 设置*/
-
/*2.1、分配/设置队列,提供读写能力*/
-
ramblock_queue = blk_init_queue(do_ramblock_request, &ramblock_lock);
-
ramblock_gendisk->queue = ramblock_queue;
-
-
/*2.2 设置gendisk其他信息,比如:容量*/
-
major = register_blkdev(0, "ramblock");
-
ramblock_gendisk->major = major;
-
ramblock_gendisk->first_minor = 0;
-
sprintf(ramblock_gendisk->disk_name, "ramblock");
-
ramblock_gendisk->fops = &ramblock_fops;
-
set_capacity(ramblock_gendisk, RAMBLOCK_SIZE/512);
-
-
/*3、注册*/
-
add_disk(ramblock_gendisk);
-
-
return 0;
-
}
-
-
static void ramblock_exit(void)
-
{
-
blk_unregister_region(major, 256);
-
del_gendisk(ramblock_gendisk);
-
put_disk(ramblock_gendisk);
-
blk_cleanup_queue(ramblock_queue);
-
}
-
-
-
module_init(ramblock_init);
-
module_exit(ramblock_exit);
-
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
驱动程序测试:
1、insmod ramblock
2、格式化 mkdosfs /dev/ramblock
3、挂接 mount /dev/ramblock /tmp/
4、读写文件 cd /tmp/ 在里面vi文件
5、cat /dev/ramblock > ramblock.bin 将ramblock中的内容拷贝到ramblock.bin文件中,做一个磁盘映像
6、在PC桌面系统上查看
mount -o loop ramblock.bin /mnt

对磁盘进行分区
磁盘分区
驱动中需要设置好磁头、柱面、扇区等参数
1、insmod ramblock
2、ls /dev/ramblock*
3、fdisk /dev/ramblock