一、AOP完成日志输出
1,导入AOP模块
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId> <version>5.3.0</version> </dependency>
2,定义业务逻辑类
public class MathCalculator { public int div(int i,int j) { System.out.println("div....方法被执行"); return i / j; } }
3,定义日志切面类

@Aspect public class LogAspects { /** * 抽取公用的切面表达式 * 1,本类引用直接使用当前方法名就行 * 2,其他切面引用则需要加上全类名和方法 */ @Pointcut("execution(public int com.xcc.annotation.aop.log.MathCalculator.*(..))") public void pointCut() { } /** * 前置处理器 */ @Before("pointCut()") public void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + "运行。。。@Before:参数列表是:{" + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()) + "}"); } /** * 后置处理器 */ @After("com.xcc.annotation.aop.log.LogAspects.pointCut()") public void logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + "运行。。。@After ..." ); } /** * 返回通知 * JoinPoint一定要出现在参数表的第一位 */ @AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()",returning = "result") public void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result) { System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + "运行。。。@AfterReturning:返回值为:{" + result + "}"); } @AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()",throwing = "e") public void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception e) { System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName() +"异常。。。异常信息:{"+e+"}"); } }
在切面类中定义对应的通知方法:
- 前置通知(@Before):logStart:在目标方法(div)运行之前运行
- 后置通知(@After):logEnd:在目标方法(div)运行结束之后运行(无论方法正常结束还是异常结束)
- 返回通知(@AfterReturning):logReturn:在目标方法(div)正常返回之后运行
- 异常通知(@AfterThrowing):logException:在目标方法(div)出现异常以后运行
- 环绕通知(@Around):动态代理,手动推进目标方法运行(joinPoint.procced())
注意:切面类上必须定义@Aspect注解,告知Spring哪个类是切面类
4,将切面类和业务类加入到Spring容器
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class Demo01_Aspect { @Bean public LogAspects logAspects() { return new LogAspects(); } @Bean public MathCalculator mathCalculator() { return new MathCalculator(); } }
注意:必须加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy用于开启基于注解的AOP模式
5,测试
@Test public void testAspect() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Demo01_Aspect.class); MathCalculator bean = applicationContext.getBean(MathCalculator.class); bean.div(11, 1); }
输出为:
div运行。。。@Before:参数列表是:{[11, 1]}
div....方法被执行
div运行。。。@After ...
div运行。。。@AfterReturning:返回值为:{11}
二、AOP的原理解析
1,查看注解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
/** * @Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class):给容器中导入AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar * 利用AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar自定义给容器中注册bean; * RootBeanDefinition ..internalAutoProxyCreator = AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator * 说白了就是:给容器中注册一个 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator; */
2,查看AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的构建关系
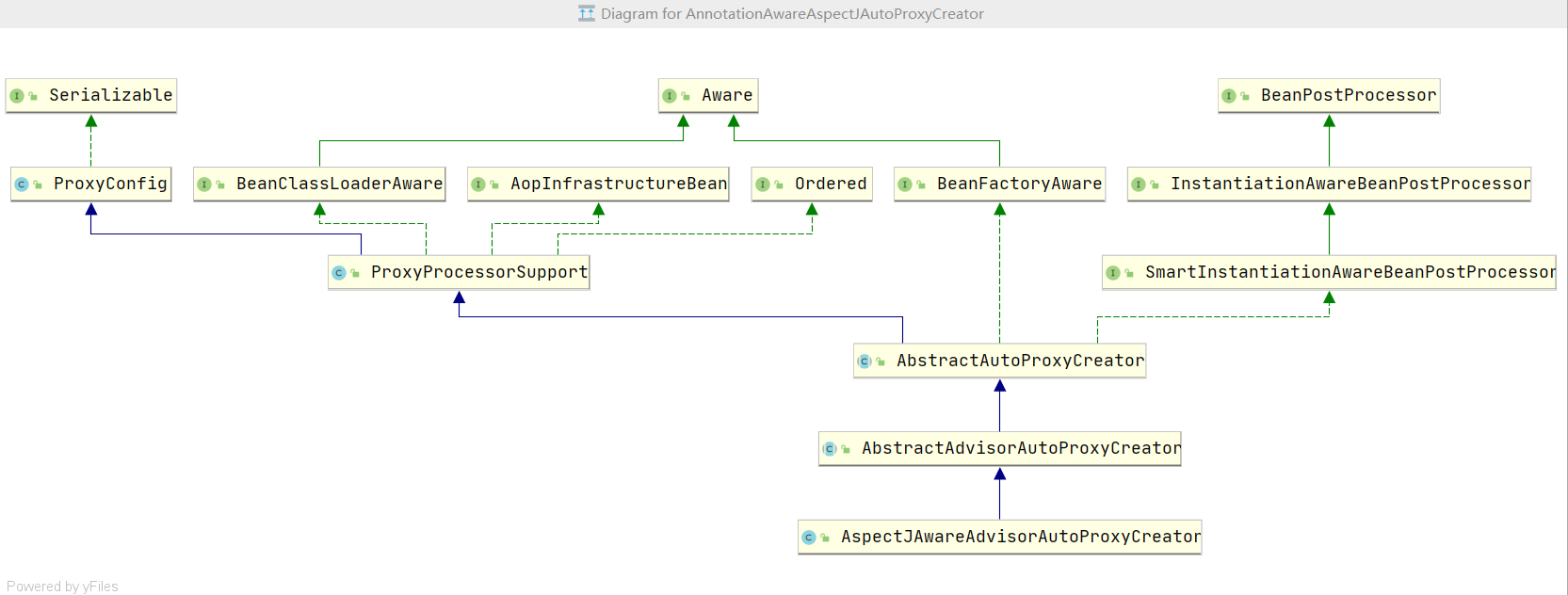
3,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的创建流程
a)AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的创建
/** * 1)、传入配置类,创建ioc容器 * 2)、注册配置类,调用refresh()刷新容器; * 3)、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);注册bean的后置处理器来方便拦截bean的创建; * 1)、先获取ioc容器已经定义了的需要创建对象的所有BeanPostProcessor * 2)、给容器中加别的BeanPostProcessor * 3)、优先注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor; * 4)、再给容器中注册实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor; * 5)、注册没实现优先级接口的BeanPostProcessor; * 6)、注册BeanPostProcessor,实际上就是创建BeanPostProcessor对象,保存在容器中; * 创建internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanPostProcessor【AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator】 * 1)、创建Bean的实例 * 2)、populateBean;给bean的各种属性赋值 * 3)、initializeBean:初始化bean; * 1)、invokeAwareMethods():处理Aware接口的方法回调 * 2)、applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization():应用后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization() * 3)、invokeInitMethods();执行自定义的初始化方法 * 4)、applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization();执行后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization(); * 4)、BeanPostProcessor(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator)创建成功;--》aspectJAdvisorsBuilder * 7)、把BeanPostProcessor注册到BeanFactory中; * beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor); */
b)初始化实例BeanFactory,创建剩余bean
/** * AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator => InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor * 4)、finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);完成BeanFactory初始化工作;创建剩下的单实例bean * 1)、遍历获取容器中所有的Bean,依次创建对象getBean(beanName); * getBean->doGetBean()->getSingleton()-> * 2)、创建bean * 【AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator在所有bean创建之前会有一个拦截,InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,会调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation()】 * 1)、先从缓存中获取当前bean,如果能获取到,说明bean是之前被创建过的,直接使用,否则再创建; * 只要创建好的Bean都会被缓存起来 * 2)、createBean();创建bean; * AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 会在任何bean创建之前先尝试返回bean的实例 * 【BeanPostProcessor是在Bean对象创建完成初始化前后调用的】 * 【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是在创建Bean实例之前先尝试用后置处理器返回对象的】 * 1)、resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);解析BeforeInstantiation * 希望后置处理器在此能返回一个代理对象;如果能返回代理对象就使用,如果不能就继续 * 1)、后置处理器先尝试返回对象; * bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(): * 拿到所有后置处理器,如果是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor; * 就执行postProcessBeforeInstantiation * if (bean != null) { * bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName); * } * 2)、doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);真正的去创建一个bean实例;和3.6流程一样; */
4,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor】 的作用
/** * 1)、每一个bean创建之前,调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation(); * 关心MathCalculator和LogAspect的创建 * 1)、判断当前bean是否在advisedBeans中(保存了所有需要增强bean) * 2)、判断当前bean是否是基础类型的Advice、Pointcut、Advisor、AopInfrastructureBean, * 或者是否是切面(@Aspect) * 3)、是否需要跳过 * 1)、获取候选的增强器(切面里面的通知方法)【List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors】 * 每一个封装的通知方法的增强器是 InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor; * 判断每一个增强器是否是 AspectJPointcutAdvisor 类型的;返回true * 2)、永远返回false * * 2)、创建对象postProcessAfterInitialization; * return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);//包装如果需要的情况下 * 1)、获取当前bean的所有增强器(通知方法) Object[] specificInterceptors * 1、找到候选的所有的增强器(找哪些通知方法是需要切入当前bean方法的) * 2、获取到能在bean使用的增强器。 * 3、给增强器排序 * 2)、保存当前bean在advisedBeans中; * 3)、如果当前bean需要增强,创建当前bean的代理对象; * 1)、获取所有增强器(通知方法) * 2)、保存到proxyFactory * 3)、创建代理对象:Spring自动决定 * JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);jdk动态代理; * ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);cglib的动态代理; * 4)、给容器中返回当前组件使用cglib增强了的代理对象; * 5)、以后容器中获取到的就是这个组件的代理对象,执行目标方法的时候,代理对象就会执行通知方法的流程; * * 3)、目标方法执行 ; * 容器中保存了组件的代理对象(cglib增强后的对象),这个对象里面保存了详细信息(比如增强器,目标对象,xxx); * 1)、CglibAopProxy.intercept();拦截目标方法的执行 * 2)、根据ProxyFactory对象获取将要执行的目标方法拦截器链; * List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); * 1)、List<Object> interceptorList保存所有拦截器 5 * 一个默认的ExposeInvocationInterceptor 和 4个增强器; * 2)、遍历所有的增强器,将其转为Interceptor; * registry.getInterceptors(advisor); * 3)、将增强器转为List<MethodInterceptor>; * 如果是MethodInterceptor,直接加入到集合中 * 如果不是,使用AdvisorAdapter将增强器转为MethodInterceptor; * 转换完成返回MethodInterceptor数组; * 3)、如果没有拦截器链,直接执行目标方法; * 拦截器链(每一个通知方法又被包装为方法拦截器,利用MethodInterceptor机制) * 4)、如果有拦截器链,把需要执行的目标对象,目标方法, * 拦截器链等信息传入创建一个 CglibMethodInvocation 对象, * 并调用 Object retVal = mi.proceed(); * 5)、拦截器链的触发过程; * 1)、如果没有拦截器执行执行目标方法,或者拦截器的索引和拦截器数组-1大小一样(指定到了最后一个拦截器)执行目标方法; * 2)、链式获取每一个拦截器,拦截器执行invoke方法,每一个拦截器等待下一个拦截器执行完成返回以后再来执行; * 拦截器链的机制,保证通知方法与目标方法的执行顺序; */
三、SpringAOP总结
- @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 开启AOP功能
- @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 会给容器中注册一个组件 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
- AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是一个后置处理器;
- 容器的创建流程:
- registerBeanPostProcessors()注册后置处理器;创建AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator对象
- finishBeanFactoryInitialization()初始化剩下的单实例bean
- 创建业务逻辑组件和切面组件
- AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator拦截组件的创建过程
- 组件创建完之后,判断组件是否需要增强。是:切面的通知方法,包装成增强器(Advisor);给业务逻辑组件创建一个代理对象(cglib);
- 执行目标方法:
- 代理对象执行目标方法
- CglibAopProxy.intercept();
-
-
- 得到目标方法的拦截器链(增强器包装成拦截器MethodInterceptor)
- 利用拦截器的链式机制,依次进入每一个拦截器进行执行;
- 效果:
-
正常执行:前置通知-》目标方法-》后置通知-》返回通知
出现异常:前置通知-》目标方法-》后置通知-》异常通知
四、Spring注解事务开启案例
1,添加依赖
spring-tx
2,加注解
@Transactional
3,配置开启事务
@EnableTransactionManagement
五、Spring注解事务的源码分析
1,@EnableTransactionManagement
利用TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector给容器中会导入组件。导入两个组件为AutoProxyRegistrar和ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration。
2,AutoProxyRegistrar:
1)、为容器中注册一个 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 组件;
2)、利用后置处理器机制在对象创建以后,包装对象,返回一个代理对象(增强器),代理对象执行方法利用拦截器链进行调用。
其源码类同于SpringAOP。
3,ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration的分析:
主要是给容器中注册事务增强器(BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor):
1)、事务增强器要用事务注解的信息,AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource解析事务注解
SpringTransactionAnnotationParser解析各种@Transactional的属性等...
2)、事务拦截器TransactionInterceptor
保存了事务属性信息,事务管理器;
实际就是一个MethodInterceptor;在目标方法执行的时候invoke()->invokeWithinTransaction(..);
执行拦截器链;事务拦截器:
1)、先获取事务相关的属性TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute ..)
2)、再获取PlatformTransactionManager,如果事先没有添加指定任何transactionmanger,最终会从容器中按照类型获取一个PlatformTransactionManager;
3)、执行目标方法 invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
如果异常,获取到事务管理器,利用事务管理回滚操作;completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex)。
如果正常,利用事务管理器,提交事务。commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo)。
