知道自己究竟想做什么,知道自己究竟能做什么是成功的两大关键
—— 比尔盖茨
Problem A: 杯子
题面:
main函数:
int main() { Cup c1; int i, j; cin>>i>>j; Cup c2(i), c3(c2); c3.setVolume(j); return 0; }
考点:类的使用
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Cup { public: int vol; Cup(int _v = 0):vol(_v) { printf("A cup of %d ml is created. ",vol); } Cup(const Cup &b):vol(b.vol) { printf("A cup of %d ml is copied. ",vol); } ~Cup() { printf("A cup of %d ml is erased. ",vol); } void setVolume(int _v){vol=_v;} };
Problem B: QQ好友
题面:


main函数:
int main() { int m, n, i, j, id; string str; Friends friends; cin>>m; for (i = 0; i < m; i++) { cin>>str>>n; Group group(str); for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { cin>>id>>str; QQ qq(id, str); group.addQQ(qq); } friends.addGroup(group); } cin>>m; for (i = 0; i < m; i++) { cin>>str; friends.findGroup(str); } cin>>n; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin>>j; friends.findQq(j); } return 0; }
考点:类的组合,vector容器的使用,注意,要是对传进来的值进行排序,则该参数不能加const,注意格式控制,有点坑。
AC代码:
#include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; class QQ { public: int val; string name; QQ(int _val,string _name):val(_val),name(_name){} bool operator <(const QQ&b) { return val<b.val; } }; class Group { public: string n; vector<QQ> QQlist; Group(string _n):n(_n){} void addQQ(const QQ&b) { QQlist.push_back(b); } }; class Friends { public: vector<Group> Glist; void addGroup( Group&b) { sort(b.QQlist.begin(),b.QQlist.end()); Glist.push_back(b); } void findGroup(string name) { for(int i = 0;i<Glist.size();i++) { if(Glist[i].n ==name) { if(Glist[i].QQlist.size()==0) { cout << "Group " << name << " : empty." << endl; } else { cout << "Group " << name << " :"; int len = Glist[i].QQlist.size(); for(int j= 0;j<len-1;j++) { cout << " " << Glist[i].QQlist[j].val << " " << Glist[i].QQlist[j].name << ";"; } cout << " " << Glist[i].QQlist[len-1].val << " " << Glist[i].QQlist[len-1].name << "." << endl; } return ; } } cout << "Group " << name << " : not existing." << endl; return ; } void findQq(int v) { //sort(Glist.begin(),Glist.end()); //bool flag = false; int len = Glist.size(); vector <string> f; cout << "QQ " << v << " in :"; for(int i = 0;i<len;i++) { int len1 = Glist[i].QQlist.size(); for(int j = 0;j<len1;j++) { if(Glist[i].QQlist[j].val==v) { f.push_back(Glist[i].n); } } } sort(f.begin(),f.end()); if(f.size()==0) cout << " empty." << endl; else { for(int i = 0;i<f.size()-1;i++) cout << " " << f[i] << ";"; cout << " " << f[f.size()-1] << "." << endl; } return ; } };
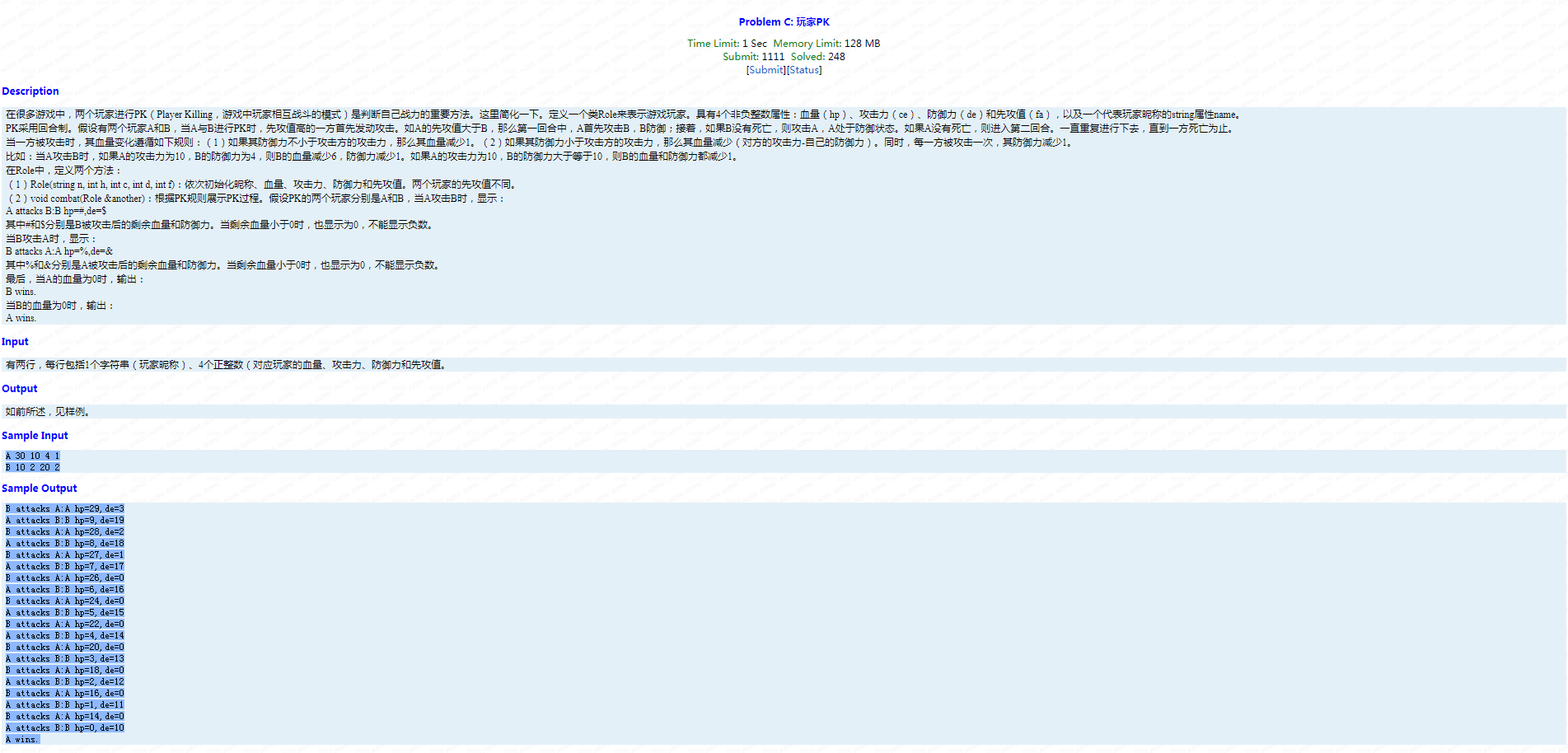
Problem C: 玩家PK
题面:
main函数:
int main() { int a, b, c, d; string name; cin>>name>>a>>b>>c>>d; Role one(name, a, b, c, d); cin>>name>>a>>b>>c>>d; Role two(name, a, b, c, d); one.combat(two); return 0; }
考点:小模拟,注意一下当防御最多只能减到0,含有攻击发起者和被攻击者在输出语句的顺序。
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Role { public: int hp,ce,de,fa; string name; Role(string _name,int _hp,int _ce,int _de,int _fa):hp(_hp),ce(_ce),de(_de),fa(_fa),name(_name) {} void combat(Role &b) { bool flag = false; if(fa>b.fa) flag = true; while(hp>0&&b.hp>0) { if(flag) { if(ce<=b.de) { b.hp--; } else b.hp-=(ce-b.de); b.de--; if(b.hp<0) b.hp=0; if(b.de<0) b.de = 0; cout << name << " attacks " << b.name << ":" << b.name; printf(" hp=%d,de=%d ",b.hp,b.de); } else { if(b.ce<=de) { hp--; } else hp-=(b.ce-de); de--; if(hp<0) hp=0; if(de<0) de = 0; cout << b.name << " attacks " << name << ":" << name; printf(" hp=%d,de=%d ",hp,de); } flag = !flag; } if(hp==0) cout << b.name << " wins." << endl; else cout << name << " wins." << endl; } };
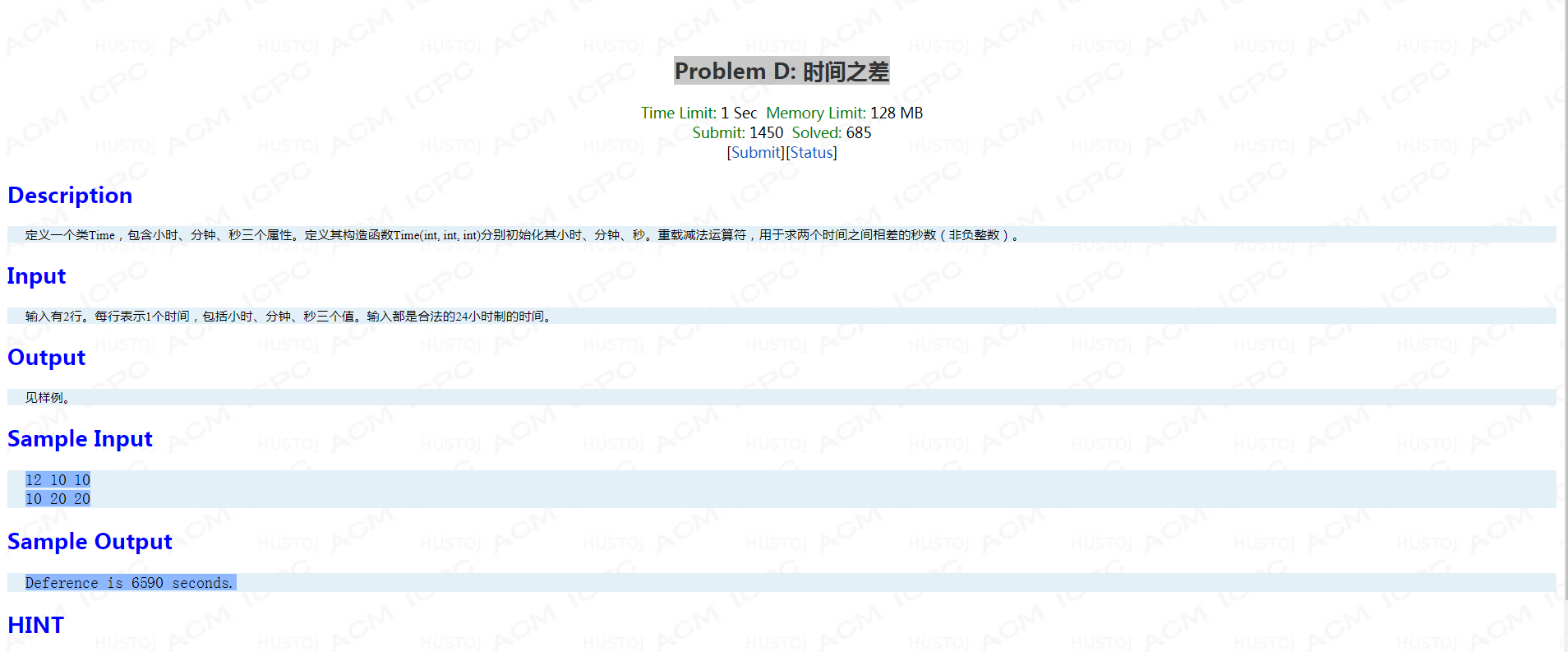
Problem D: 时间之差
题面:
main函数:
int main() { int a, b, c; cin>>a>>b>>c; Time t1(a, b, c); cin>>a>>b>>c; Time t2(a, b, c); cout<<"Deference is "<<(t2 - t1)<<" seconds."<<endl; return 0; }
考点:运算符重载,注意要取秒之差的绝对值
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Time { public: int h, m, s; Time(int _h,int _m,int _s):h(_h),m(_m),s(_s){}; int operator -(const Time& b) { int d = h*3600+m*60+s; int d1 = b.h*3600+b.m*60+b.s; return abs(d-d1); } };
Problem E: 家禽和家畜
题面:
Main函数:
int main() { Animal *animal; char ch; while(cin>>ch) { switch(ch) { case 'c': animal = new Cat(); break; case 'd': animal = new Dog(); break; case 'r': animal = new Rooster(); break; } animal->eat(); animal->fun(); delete animal; } return 0; }
考点:虚基类的使用,记得写虚析构函数
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Animal { public: Animal(){}; virtual void eat()=0; virtual void fun()=0; virtual ~Animal(){}; }; class Cat:public Animal { public: Cat():Animal(){} void eat() { printf("Cat eats fishes. "); } void fun() { printf("Cat catches mouses. "); } ~Cat(){}; }; class Dog:public Animal { public: Dog():Animal(){}; void eat() { printf("Dog eats bones. "); } void fun() { printf("Dog can be housekeeping. "); } ~Dog(){}; }; class Rooster:public Animal { public: Rooster():Animal(){}; void eat() { printf("Rooster eats corns. "); } void fun() { printf("Rooster crows. "); } ~Rooster(){} };
Problem F: 复数类模板
题面:

main函数:
int main() { int a, b; double c, d; cin>>a>>b; Complex<int> c1(a, b); cout<<setiosflags(ios::fixed)<<setprecision(2)<<c1.getModulus()<<endl; cin>>c>>d; Complex<double> c2(c, d); cout<<setiosflags(ios::fixed)<<setprecision(2)<<c2.getModulus()<<endl; return 0; }
考点:类模板
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; template<class T> class Complex { public: T r,i; Complex(T _r,T _i):r(_r),i(_i){} double getModulus() { return sqrt(r*r+i*i); } };
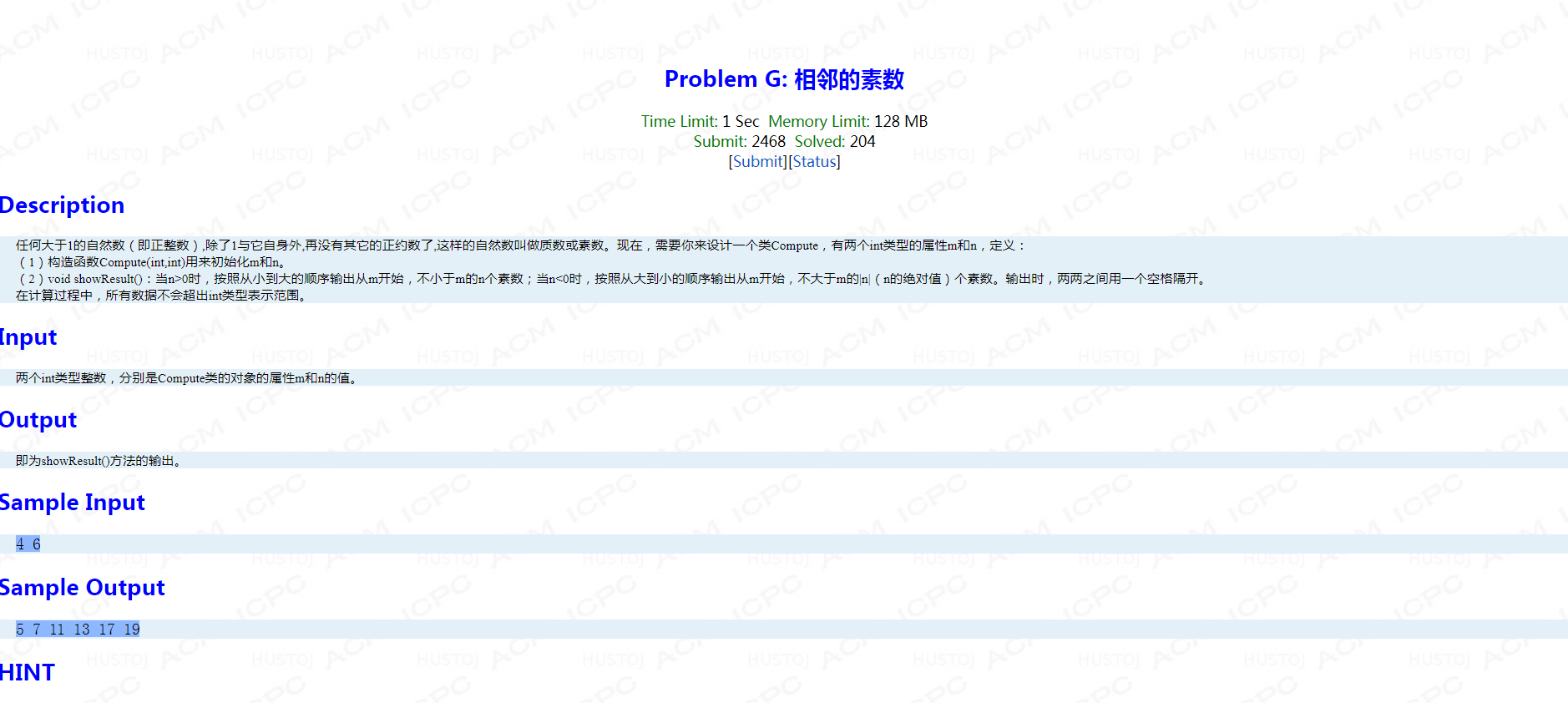
Problem G: 相邻的素数
题面:
main函数:
int main() { int a, b; cin>>a>>b; Compute compute(a, b); compute.showResult(); return 0; }
考点:毒瘤题,注意判断一下当要求输出数目大于满足条件素数的数目时,输出应该停止。
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; bool isPrime(LL x) { if(x<=1) return false; if(x==2) return true; for(LL i= 2; i*i<=x; i++) { if(x%i==0) return false; } return true; } class Compute { public: int m,n; Compute(int _m,int _n):m(_m),n(_n) {}; void showResult() { if(n>0) { LL num = m; int k = 0; while(k<n) { if(isPrime(num)) { if(k==0) cout << num ; else cout << " " << num; k++; } num++; } } else if(n<0) { n = abs(n); LL num = m; int k = 0; while(k<n&&num>1) { if(isPrime(num)) { if(k==0) cout << num ; else cout << " " << num; k++; } num--; } } cout << endl; } };
Problem H: 数组的平滑
题面: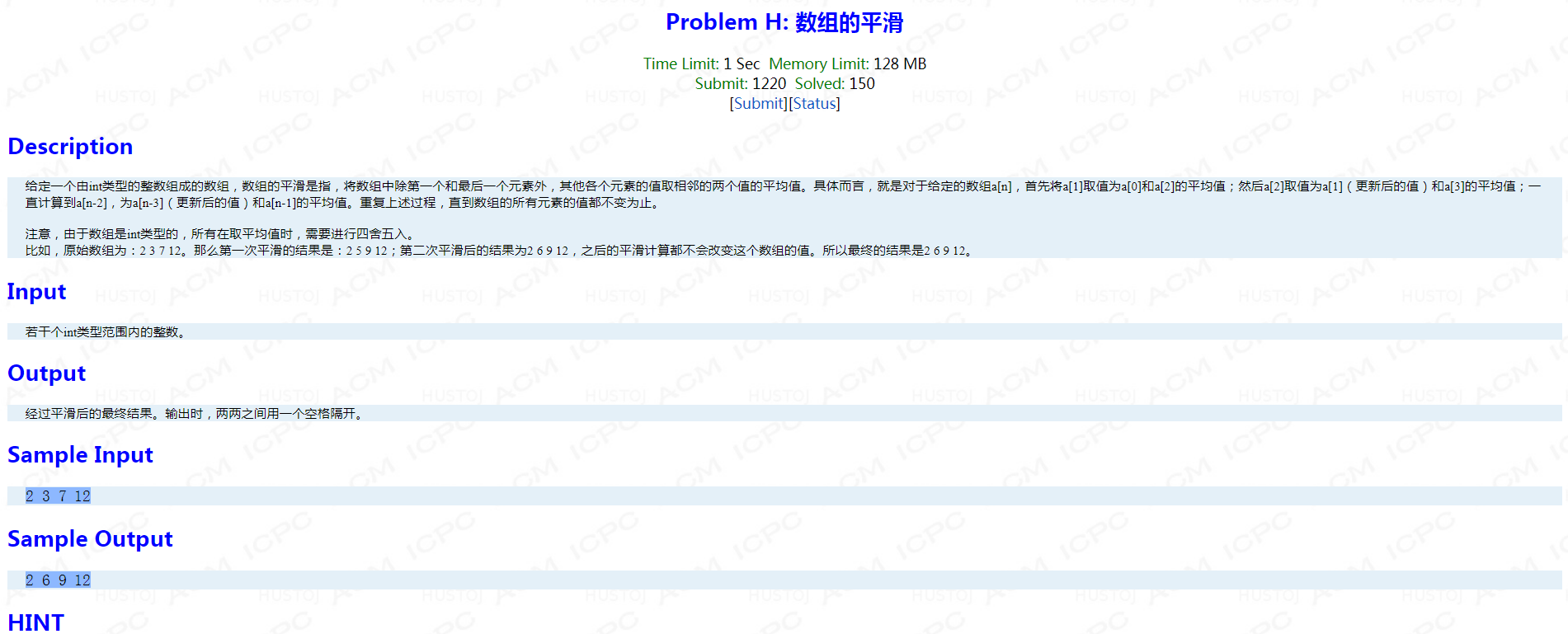
考点:vector的使用,以及负数的四舍五入等于其绝对值四舍五入结果取负。
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; vector<LL> vec,vec1; LL check = 0; void op() { for(int i = 1;i<vec.size()-1;i++) { LL num = vec[i-1]+vec[i+1]; LL n = abs(num); if(num<0) vec[i] = -(n+1)/2; else vec[i] = (n+1)/2; } while(vec1!=vec) { vec1 = vec; for(int i = 1;i<vec.size()-1;i++) { LL num = vec[i-1]+vec[i+1]; LL n = abs(num); if(num<0) vec[i] = -(n+1)/2; else vec[i] = (n+1)/2; } } return ; } int main() { LL num; while(cin >> num) { vec.push_back(num); vec1.push_back(num); } if(vec.size()<=2&&vec.size()>0) { cout << vec[0] ; for(int i = 1;i<vec.size();i++) cout << " " << vec[i]; cout << endl; } else if(vec.size()==0) return 0; else { check = vec[1]; op(); cout << vec[0]; for(int i = 1;i<vec.size();i++) cout << " " << vec[i]; cout << endl; } return 0; }
Problem I: 需要重载吗?
题面:
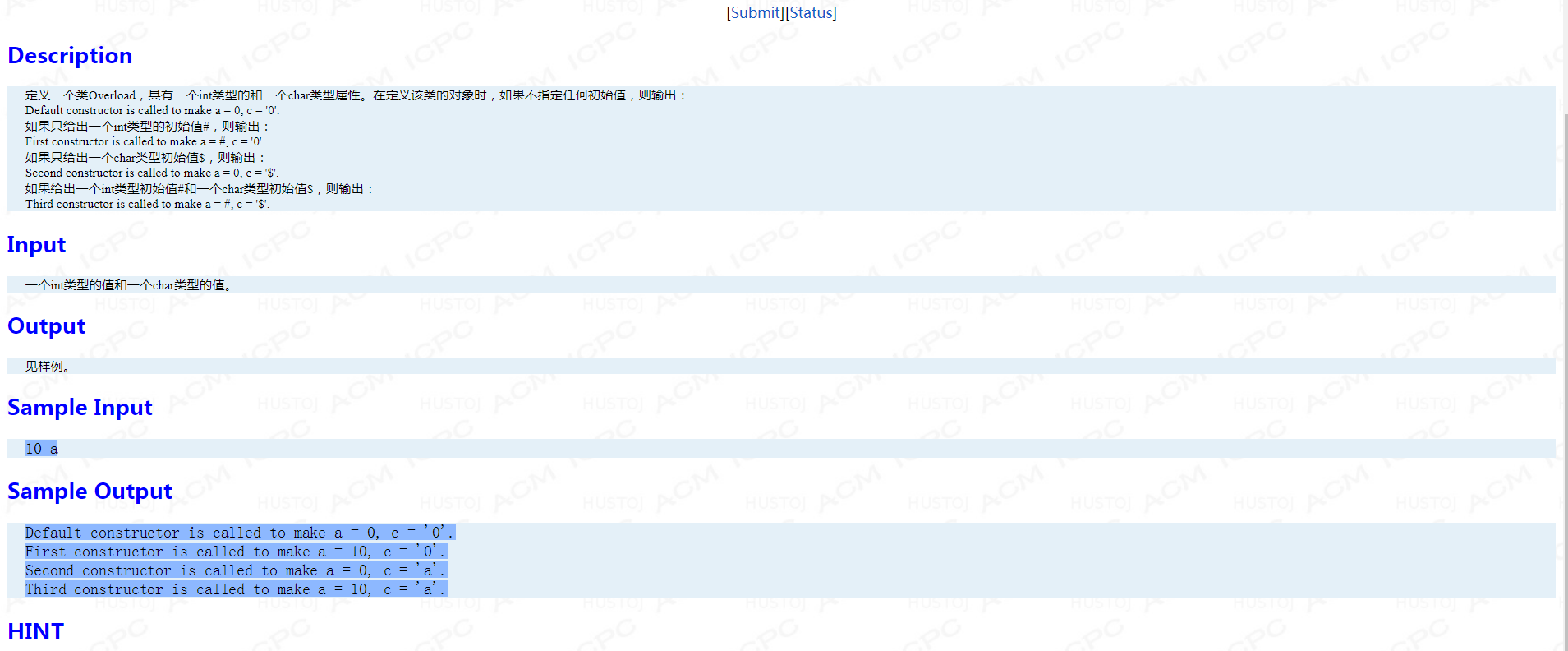
main函数:
int main() { int i; char ch; cin>>i>>ch; Overload t1, t2(i), t3(ch), t4(i, ch); return 0; }
考点:类的重载。
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Overload { public: int a; char c; Overload(){printf("Default constructor is called to make a = 0, c = '0'. "); } Overload(int i):a(i){printf("First constructor is called to make a = %d, c = '0'. ",i); } Overload(char _c):c(_c){printf("Second constructor is called to make a = 0, c = '%c'. ",c); } Overload(int i,char _c):a(i),c(_c){printf("Third constructor is called to make a = %d, c = '%c'. ",a,c); } };
Problem J: 很难的题
题面:
main函数:
int main() { int a; cin>>a; Difficult difficult(a); difficult.show(); return 0; }
考点:类的使用
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Difficult { public: int num; Difficult(int _n):num(_n){}; void show(){printf("%d ",abs(num)); } };
Problem K: 数组的归一化
题面:
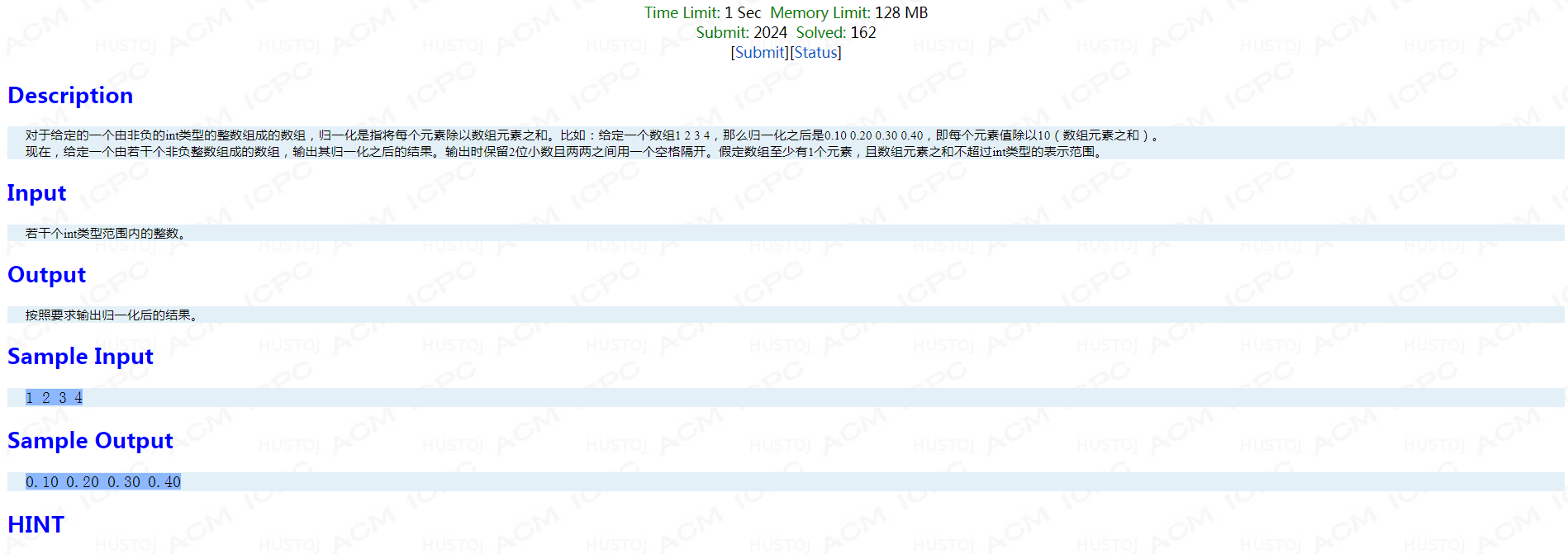
考点:毒瘤题,全为0时应该全输出1。
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; vector<int> vec; int main() { int num = 0; double sum = 0; while(cin >>num) { sum+=num; vec.push_back(num); } if(sum==0) { printf("%.2f",1.00); for(int i = 1;i<vec.size();i++) printf(" %.2f",1.00); printf(" "); } else { printf("%.2f",vec[0]/sum); for(int i = 1;i<vec.size();i++) printf(" %.2f",vec[i]/sum); printf(" "); } return 0; }