Farm Irrigation |
| Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) |
| Total Submission(s): 79 Accepted Submission(s): 46 |
|
Problem Description
Benny has a spacious farm land to irrigate. The farm land is a rectangle, and is divided into a lot of samll squares. Water pipes are placed in these squares. Different square has a different type of pipe. There are 11 types of pipes, which is marked from A to K, as Figure 1 shows.
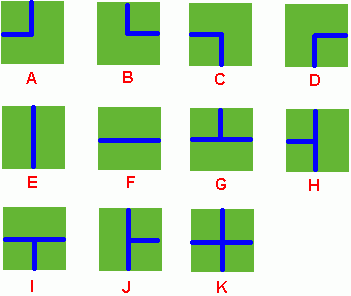 ADC FJK IHE then the water pipes are distributed like 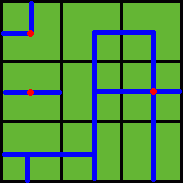 Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him? Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show. |
|
Input
There are several test cases! In each test case, the first line contains 2 integers M and N, then M lines follow. In each of these lines, there are N characters, in the range of 'A' to 'K', denoting the type of water pipe over the corresponding square. A negative M or N denotes the end of input, else you can assume 1 <= M, N <= 50.
|
|
Output
For each test case, output in one line the least number of wellsprings needed.
|
|
Sample Input
2 2 DK HF 3 3 ADC FJK IHE -1 -1 |
|
Sample Output
2 3 |
|
Author
ZHENG, Lu
|
|
Source
Zhejiang University Local Contest 2005
|
|
Recommend
Ignatius.L
|
分析:运用并查集后,统计有多少个根即需要多少个水源。
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> int door[2510][4]; int fa[2510]; int root[2510]; char s[55][55]; int find(int x) { if (x != fa[x]) fa[x] = find(fa[x]); return fa[x]; } void merge(int x, int y) { int fx, fy; fx = find(x); fy = find(y); if (fx != fy) fa[fx] = fy; } int main() { int m, n, i, j, a, b, cnt, t; while (scanf("%d%d", &m, &n) != EOF && m >= 0) { cnt = 0; memset(door, 0, sizeof (door)); memset(root, 0, sizeof (root)); for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) scanf("%s", s[i]); t = 0; for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) { for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) { switch (s[i][j]) { case 'A':door[t][0] = door[t][1] = 1; break; case 'B':door[t][1] = door[t][2] = 1; break; case 'C':door[t][0] = door[t][3] = 1; break; case 'D':door[t][2] = door[t][3] = 1; break; case 'E':door[t][1] = door[t][3] = 1; break; case 'F':door[t][0] = door[t][2] = 1; break; case 'G':door[t][0] = door[t][1] = door[t][2] = 1; break; case 'H':door[t][0] = door[t][1] = door[t][3] = 1; break; case 'I':door[t][0] = door[t][3] = door[t][2] = 1; break; case 'J':door[t][3] = door[t][1] = door[t][2] = 1; break; case 'K':door[t][0] = door[t][1] = door[t][2] = door[t][3] = 1; break; } fa[t] = t; ++t; } } for (i = 0; i < m - 1; ++i) { for (j = 0; j < n - 1; ++j) { // printf("i=%d j=%d ",i,j); a = i * n + j; b = a + 1; if (door[a][2] && door[b][0]) { merge(a, b); // printf("ok1 \n"); } b = a + n; if (door[a][3] && door[b][1]) { merge(a, b); // printf("ok2\n"); } } a = i * n + j; b = a + n; if (door[a][3] && door[b][1]) { merge(a, b); // printf("i=%d j=%d ok3\n",i,j); } } for (j = 0; j < n - 1; ++j) { a = i * n + j; b = a + 1; if (door[a][2] && door[b][0]) { merge(a, b); } } for (i = 0; i < t; ++i) { root[find(i)] = 1; // printf("i=%d find(i)=%d\n",i,find(i)); } for (i = 0; i < t; ++i) { if (root[i]) { // printf("r==1 %d\n",i); ++cnt; } } printf("%d\n", cnt); } return 0; }