一切的执行从MapperProxy开始,MapperProxy是MapperProxyFactory使用SqlSession创建出来的。所以MapperProxy中包含SqlSession。
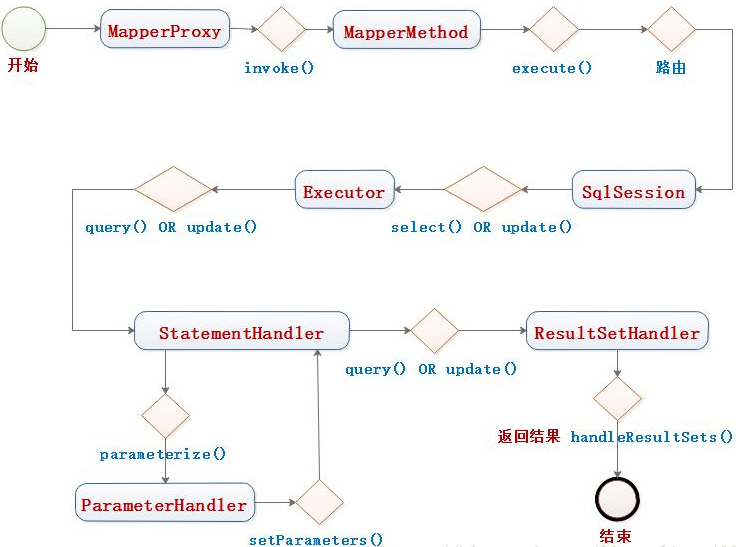
可以看到MapperProxy调用invoke方法,进而调用MapperMethod的execute(),这些MapperMethod就是和你要执行的命令相关,比如执行select语句,则会通过SqlSession的select()方法,最终调用到Executor的query方法。Executor会再协调另外三个核心组件。
- MapperProxyFactory用来创建MapperProxy,这个factory其实主要就是完成了InvokeHandler的bindTarget的功能。而MapperProxy只需要完成invoke方法的功能。
- MapperProxy包含SqlSession
- SqlSesion包含四大组件Executor,StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,ResultHandler。还包含Configuration
- Configuration可以创建四大组件,同时Configuration还包含InterceptorChain,通过调用interceptorChain的pluginAll()方法,完成针对四大组件的插件的动态代理链的创建。
MapperProxy:
- 因为Mapper接口不能直接被实例化,Mybatis利用JDK动态代理,创建MapperProxy间接实例化Mapper对象。
- MapperProxy还可以缓存MapperMethod对象
MapperMethod:
- 负责解析Mapper接口的方法,并封装成MapperMethod对象
- 将Sql命令的执行路由到恰当的SqlSesison方法上
1 public class MapperMethod { 2 3 // 保存了Sql命令的类型和键id 4 private final SqlCommand command; 5 // 保存了Mapper接口方法的解析信息 6 private final MethodSignature method; 7 8 public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) { 9 this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method); 10 this.method = new MethodSignature(config, method); 11 } 12 13 // 根据解析结果,路由到恰当的SqlSession方法上 14 public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { 15 Object result; 16 if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) { 17 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); 18 result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)); 19 } else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) { 20 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); 21 result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)); 22 } else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) { 23 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); 24 result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param)); 25 } else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) { 26 if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { 27 executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); 28 result = null; 29 } else if (method.returnsMany()) { 30 result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args); 31 } else if (method.returnsMap()) { 32 result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args); 33 } else { 34 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); 35 result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param); 36 } 37 } else if (SqlCommandType.FLUSH == command.getType()) { 38 result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); 39 } else { 40 throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName()); 41 } 42 if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) { 43 throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() 44 + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ")."); 45 } 46 return result; 47 } 48 // ...
插件的构建:
谈原理首先要知道StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,Result Handler都是代理,他们是Configuration创建,在创建过程中会调用interceptorChain.pluginAll()方法,为四大组件组装插件(再底层是通过Plugin.wrap(target,XX, new Plugin( interceptor))来来创建的)。
插件链是何时构建的:
在执行SqlSession的query或者update方法时,SqlSession会通过Configuration创建Executor代理,在创建过程中就调用interceptor的pluginAll方法组装插件。然后executor在调用doQuery()方法的时候,也会调用Configuration的newStatementHandler方法创建StatemenHandler(和上面描述的一样,这个handler就是个代理,也是通过interceptorChain的pluginAll方法构建插件)
插件如何执行:
以statementhandler的prepare方法的插件为例,正如前面所说,statementhandler是一个proxy,执行他的prepare方法,将调用invokeHandler的invoke方法,而invokeHandler就是Plugin.wrap(target, xxx, new Plugin(interceptor))中的第三个参数,所以很自然invokeHanlder的invoke的方法最终就会调用interceptor对象的intercept方法。