一直很好奇这些Java中注解是怎么实现的,所以就去了解了一番,做此记录。

1.元注解(meta-annotations),可以理解为为其他注解做注解。
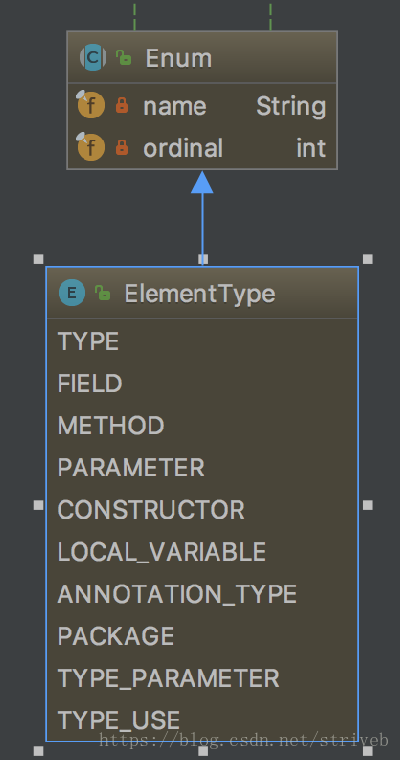
- @Target:描述注解的使用范围,主要返回了枚举类ElementType的值,其中ElementType的值主要有(最后两个为Java8新增的):
-
TYPE:说明该注解只能被声明在一个类上。
-
FIELD:说明该注解只能被声明在一个类的字段上。
-
METHOD:说明该注解只能被声明在一个类的方法上。
-
PARAMETER:说明该注解只能被声明在一个方法参数上。
-
CONSTRUCTOR:说明该注解只能声明在一个类的构造方法上。
-
LOCAL_VARIABLE:说明该注解只能声明在一个局部变量上。
-
ANNOTATION_TYPE:说明该注解只能声明在一个注解类型上。
-
PACKAGE:说明该注解只能声明在一个包名上。
-
TYPE_PARAMETER:说明该注解只能申明在一个参数类型上。
-
TYPE_USE:类型的作用。
-
@Target()可以存放数组默认值为任何元素。如下图所示,
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Target {
/**
* Returns an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type
* can be applied to.
* @return an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type
* can be applied to
*/
ElementType[] value();
}2.@Retention:定义注解的有效时间,会返回一个RetentionPolicy的值,主要有三个值,
作用:表示需要在什么级别保存该注释信息,用于描述注解的生命周期(即:被描述的注解在什么范围内有效)
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Retention {
/**
* Returns the retention policy.
* @return the retention policy
*/
RetentionPolicy value();
}public enum RetentionPolicy {
/**
* Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler.
*/
SOURCE,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler
* but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default
* behavior.
*/
CLASS,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and
* retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively.
*
* @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement
*/
RUNTIME
}- SOURCE:在源文件中有效(即源文件保留)
- CLASS:在class文件中有效(即class保留)
- RUNTIME:在运行时有效(即运行时保留)
3.@Documented:只是起一个标记的作用,可以被javadoc归档,只是一个标记注解,没有成员。
4.@Inherited:一个标记注解,@Inherited阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。如果一个使用了@Inherited修饰的annotation类型被用于一个class,则这个annotation将被用于该class的子类。
5.@AliasFor:作为互为别名使用,有时候两个属性起同样的作用,为了防止冲突,就需要用到这个注解。如下是远吗,可以看到方法名和属性名是倒过来的。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
public @interface AliasFor {
@AliasFor("attribute")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String attribute() default "";
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
}自定义注解
使用@interface自定义注解时,自动继承了java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口,由编译程序自动完成其他细节。在定义注解时,不能继承其他的注解或接口。@interface用来声明一个注解,其中的每一个方法实际上是声明了一个配置参数。方法的名称就是参数的名称,返回值类型就是参数的类型(返回值类型只能是基本类型、Class、String、enum)。可以通过default来声明参数的默认值。
格式:public @interface 注解名 {定义体}
可支持数据类型:
1.所有基本数据类型(int,float,boolean,byte,double,char,long,short)
2.String类型
3.Class类型
4.enum类型
5.Annotation类型
6.以上所有类型的数组
Annotation类型里面的参数该怎么设定:
第一,只能用public或默认(default)这两个访问权修饰.例如,String value();这里把方法设为defaul默认类型;
第二,参数成员只能用基本类型byte,short,char,int,long,float,double,boolean八种基本数据类型和 String,Enum,Class,annotations等数据类型,以及这一些类型的数组.例如,String value();这里的参数成员就为String;
第三,如果只有一个参数成员,最好把参数名称设为"value",后加小括号.例:下面的例子FruitName注解就只有一个参数成员。
链接:
annotation(@Retention@Target)详解:https://www.cnblogs.com/gmq-sh/p/4798194.html
Spring中的@AliasFor标签:https://blog.csdn.net/wolfcode_cn/article/details/80654730