循环结构
什么是循环结构
循环结构就是重复执行某段代码块
为什么要用循环结构
人类某些时候需要重复做某件事情
所以程序中必须有相应的机制来控制计算机具备人的这种循环做事的能力
While循环(条件循环)
while循环:适用于循环次数未知的场景,要有退出条件
Python 编程中 while 语句用于循环执行程序,即在某条件下,循环执行某段程序,以处理需要重复处理的相同任务。其基本形式为:
while 判断条件: 执行语句……
执行语句可以是单个语句或语句块。判断条件可以是任何表达式,任何非零、或非空(null)的值均为true。
当判断条件假false时,循环结束。
执行流程图如下:
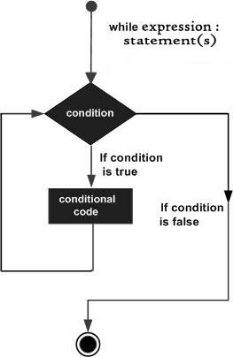
//实例
#实例1
#!/usr/bin/python count = 0 while (count < 9): print 'The count is:', count count = count + 1 print "Good bye!" 以上代码执行输出结果: The count is: 0 The count is: 1 The count is: 2 The count is: 3 The count is: 4 The count is: 5 The count is: 6 The count is: 7 The count is: 8 Good bye!
#实例2(验证登入,可以输错三次)
user_name="egon"
user_pwd="123"
count=0
while count<3:
name_inp=input("请输入账号:")
pwd_inp=input("请输入密码:")
if name_inp == user_name and pwd_inp == user_pwd:
print("登入成功")
while True:
cmd=input("请输入命令>:")
if cmd == "q":
break #当输入q退出,会直接退出程序,并不会执行最外层while链接的else,
else:
print("命令{}正在运行".format(cmd))
break #此break是在cmd输入q后执行,如果没有此break,当cmd输入为q且count<3,还是会执行外层循环
else:
print("账号或密码错误")
count+=1
else: #当count不小于3才执行
print("输错三次")
continue 和 break 用法
while 语句时还有另外两个重要的命令 continue,break 来跳过循环,continue 用于跳过该次循环,break 则是用于退出循环,此外"判断条件"还可以是个常值,表示循环必定成立,具体用法如下:
i = 1 while i < 10: i += 1 if i%2 > 0: # 非双数时跳过输出 continue print i # 输出双数2、4、6、8、10 i = 1 while 1: # 循环条件为1必定成立 print i # 输出1~10 i += 1 if i > 10: # 当i大于10时跳出循环 break
pass语句
pass语句什么也不做,一般作为占位符或者创建占位程序,pass语句不会执行任何操作,比如:
while False:
pass
pass语句在函数中的作用
当你在编写一个程序时,执行语句部分思路还没有完成,这时你可以用pass语句来占位,也可以当做是一个标记,是要过后来完成的代码。比如下面这样:
def iplaypython():
pass
定义一个函数iplaypython,但函数体部分暂时还没有完成,又不能空着不写内容,因此可以用pass来替代占个位置。
pass语句在循环中的作用
pass也常用于为复合语句编写一个空的主体,比如说你想一个while语句的无限循环,每次迭代时不需要任何操作,你可以这样写:
while True:
pass
以上只是举个例子,现实中最好不要写这样的代码,因为执行代码块为pass也就是空什么也不做,这时python会进入死循环。
//无限循环(死循环)
如果条件判断语句永远为 true,循环将会无限的执行下去,如下实例:
实例 #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- var = 1 while var == 1 : # 该条件永远为true,循环将无限执行下去 num = raw_input("Enter a number :") print "You entered: ", num print "Good bye!" 或者 var = 1 while True: # 该条件永远为true,循环将无限执行下去 num = raw_input("Enter a number :") print "You entered: ", num print "Good bye!" # 以上实例输出结果: Enter a number :20 You entered: 20 Enter a number :29 You entered: 29 Enter a number :3 You entered: 3 Enter a number between :Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 5, in <module> num = raw_input("Enter a number :") KeyboardInterrupt # 注意:以上的无限循环你可以使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环。
循环语句中else使用
在 python 中,while … else 在循环条件为 false 时执行 else 语句块:
#没有被break切断的情况下,则是循环正常结束才执行else,在while和for一样
# 实例 #!/usr/bin/python count = 0 while count < 5: print count, " is less than 5" count = count + 1 else: print count, " is not less than 5" 以上实例输出结果为: 0 is less than 5 1 is less than 5 2 is less than 5 3 is less than 5 4 is less than 5 5 is not less than 5
for循环(取值循环)
Python for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串。
语法:
for循环的语法格式如下:
for iterating_var in sequence: statements(s)
//流程图
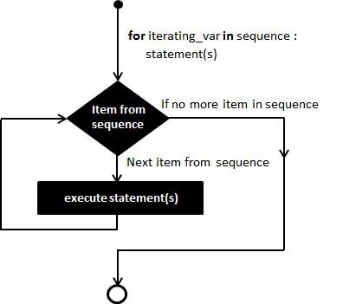
//实例
实例1 #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for letter in 'Python': # 第一个实例 print ('当前字母 :', letter) fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango'] for fruit in fruits: # 第二个实例 print ('当前水果 :', fruit) print ("Good bye!") 以上实例输出结果: 当前字母 : P 当前字母 : y 当前字母 : t 当前字母 : h 当前字母 : o 当前字母 : n 当前水果 : banana 当前水果 : apple 当前水果 : mango Good bye! 另外一种执行循环的遍历方式是通过索引,如下实例: 实例2 #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango'] for index in range(len(fruits)): print ('当前水果 :', fruits[index]) print ("Good bye!") 以上实例输出结果: 当前水果 : banana 当前水果 : apple 当前水果 : mango Good bye! 以上实例我们使用了内置函数 len() 和 range(),函数 len() 返回列表的长度,即元素的个数。 range返回一个序列的数。
循环嵌套
for循环嵌套
for iterating_var in sequence: for iterating_var in sequence: statements(s) statements(s)
while循环嵌套
while expression: while expression: statement(s) statement(s) 你可以在循环体内嵌入其他的循环体,如在while循环中可以嵌入for循环, 反之,你可以在for循环中嵌入while循环。
循环控制语句
循环控制语句可以更改语句执行的顺序。Python支持以下循环控制语句:
|
控制语句 |
描述 |
|
break语句 |
在语句块执行过程中终止循环,并且跳出整个循环 |
|
continue语句 |
在语句块执行过程中终止当前循环,跳出该次循环,执行下一次循环。 |
|
pass语句 |
pass是空语句,是为了保持程序结构的完整性。 |