变化多端的列表
概述:集合大家都不陌生,但是实际应用确实有时候让人无从下手。其比数组最大的好处就是针对多变的动态的元素降服之功能!妙哉,笔者通过《C#高级编程》集合章节发现集合也会“博大精深,变化多端”的。但是有不同于书本,那么大一本厚书,让人敬而远之,特别一些些一套套理论的东西更是头大。笔者准备从集合的列表,队列,栈,链表,有序表,字典,等分系列发布。尽可呢避免大篇理论(核心的还是要强调的)。然后笔者自己做一些小实例,通过自己总结描述设计思想,结合代码实现,加以重点强调语句。最后配上运行结果!尽可能达到初学者有所悟吧。
C#系列文章导航
- C#实现队列读写操作(一)
- 变化多端的列表(二)
- VS自动内存管理(垃圾回收集)(三)
- C#忽略基础知识点梳理(四)
- 什么是框架的接口(五)
- 程序集的加载与反射(六)
- CLR寄宿和应用程序域(七)
- 异常(八)
【列表】:针对列表适合于动态创建元素。下面结合多变的创建方法,多种方法添加元素,插入元素,访问元素的几种方式,删除搜索和排序。来一一揭示列表的妙处和用途!
实例描述:创建student.cs类(继承IComparable<student>, IFormattable),包含姓名,性别,年龄属性。带参数的构造函数,重载ToString(实现根据条件查询),以及自定义ToString,排序方法,IFormattable的使用
主程序:实现多方法添加,插入,删除,查询等
[1],创建列表,添加数据的三种形式:
方式一:对象添加法,逐一创建对象,然后在泛型列表中添加对象。
student stu1 = new student("小华", "男", 21);
student stu2 = new student("小明", "男", 22);
student stu3 = new student("小丽", "女", 19);
List<student> students = new List<student>() { stu1, stu2, stu3 };
方式二:对象添加法,逐一创建对象,然后在泛型列表中添加对象。
students.Add(new student("小花", "女", 23));
方式三:批量添加
students.AddRange(new student[]{
new student("小王", "女", 19),
new student("小白", "女", 19)
});
运行结果:
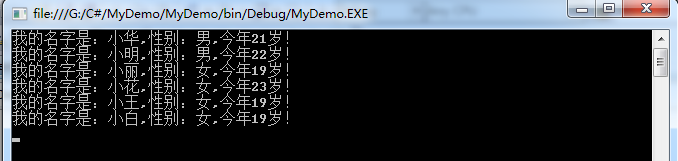
[2]泛型空间大小根据容量自动增加。即:初始为n,第一次自增2n,第二次自增4n。诸如此类,每次容量是上次2倍大小。
students.Capacity = 100;//手动设置泛型空间大小
[3]插入元素
students.Insert(2, new student("新人小王", "女", 22));
运行结果: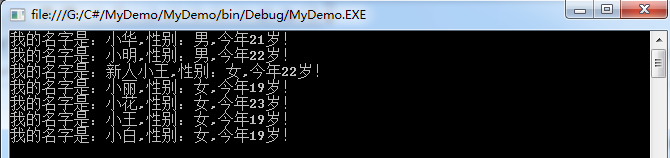
[4]读取数据的几种方法
1,object类的四个基本方法之一就是ToString,它是个虚方法,可以重载,设置自己想要的效果
//重载ToString()方法
public override string ToString()
{
return String.Format("我的名字是:{0},性别:{1},今年{2}岁!", name, sex, age);
}
2,自定义ToString(T)方法,format是T的参数
//自定义
public string ToString(string format)
{
return ToString(format, null);//如果找到该实例则根据format查找相应结果,反之为null
}
3,根据条件通过ToString(T)筛选数据
public string ToString(string format, IFormatProvider formatProvider)
{
switch (format.ToUpper())
{
case null:
case "N":
return name;
case "S":
return sex;
case "A":
return String.Format("{0},{1}年龄:{2}", name, sex, age);
default:
return String.Format("你输入的{0}不合法!",format);
//throw new FormatException(String.Format(formatProvider, "Format{0}is not supported", format));
}
}
方法一:for循环student所有对象原则查询
1:根据名字(N)查询
for (int i = 0; i < students.Count; i++)
{
//1,根据自定义ToString访问
//方法1:根据条件N查询name
Console.WriteLine(students[i].ToString("N"));
}
运行结果:
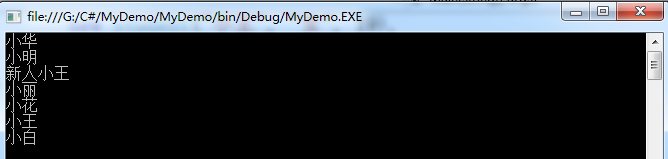
2:根据条件A查询全部信息
for (int i = 0; i < students.Count; i++)
{
//方法2:根据条件A查询全部信息
Console.WriteLine(students[i].ToString("A"));
}
运行结果:
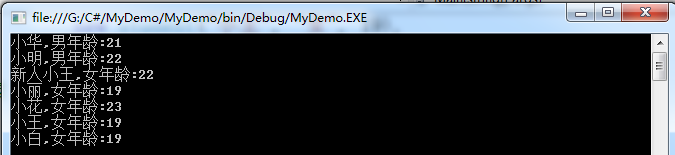
3:利用重载ToString()查询
for (int i = 0; i < students.Count; i++)
{
//方法3:利用重载ToString()查询
Console.WriteLine(students[i].ToString());
}
运行结果:
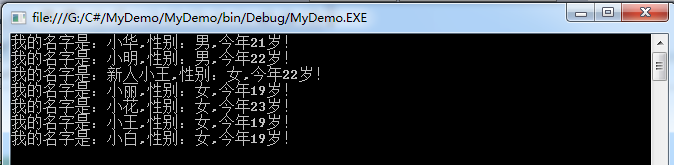
4利用非法条件查询
for (int i = 0; i < students.Count; i++)
{
//方法4:利用非法条件查询
Console.WriteLine(students[i].ToString("T"));
}
运行结果:
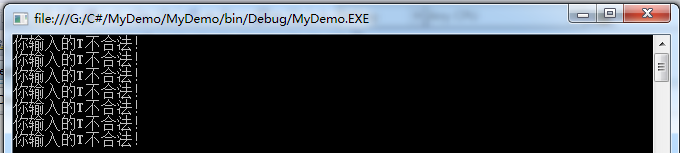
方法二:根据索引
student s1 = students[3];
Console.WriteLine(s1);
方法三:List<T>执行接口IEnumerable,foreach迭代法
foreach (student stu in students)
{
Console.WriteLine(stu);
}
方法四:ForEach查询:以下两句效果一样,第一句拉姆达查询
students.ForEach(r => Console.WriteLine("{0:A}", r));
students.ForEach(delegate(student r) { Console.WriteLine("{0:A}", r); });
方法三/四结果:
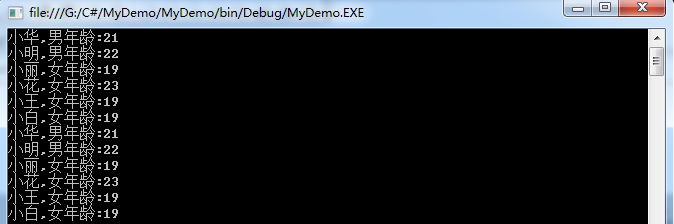
[5]删除元素
students.RemoveAt(2);
运行结果:(同上图相比较)
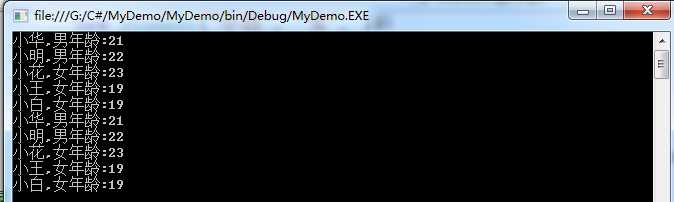
[6]搜索的几种方法
根据名字搜索类,以下创建查找方法,便于下文使用。
public class FindName
{
public string name;
public FindName(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public bool FindNamePredicate(student stu)
{
if (stu == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("stu");
//Console.WriteLine("您查询的对象不存在!");
}
else
{
return stu.name == name;
}
}
}
三种搜索方式
//1 查询对象索引
int index1 = students.IndexOf(stu2);
Console.WriteLine(index1);
//2 根据名字查询
int index2 = students.FindIndex(new FindName("小白").FindNamePredicate);
Console.WriteLine(index2);
//3 拉姆达查询
int index3 = students.FindIndex(r => r.name == "小白");
Console.WriteLine(index3);
结果:
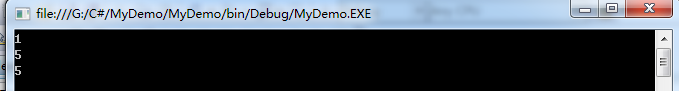
[7]在student类中排序方法如下:
//排序
public int CompareTo(student other)
{
int compare = this.age.CompareTo(other.age);
if (compare == 0)
{
return this.name.CompareTo(other.name);
}
return compare;
}
以下四种排序方法:
//1 拉姆达方法
int s = stu2.CompareTo(stu1);
students.Sort((r1, r2) => r1.age.CompareTo(r2.age));
//升序
students.Sort();
//降序
students.Reverse();
//ForEach指定
students.ForEach(r => Console.WriteLine("{0:A}", r));
Console.WriteLine(s);
[8]本demo完整代码:
1,两个类的设计如下:student和FindName
 View Code
View Code
public class student :IComparable<student>, IFormattable
{
//设置属性:姓名,性别,年龄
public string name { get; set; }
public string sex { get; set; }
public int age { get; set; }
//构造自定义方法
public student(string name, string sex, int age)
{
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
//重载ToString()方法
public override string ToString()
{
return String.Format("我的名字是:{0},性别:{1},今年{2}岁!", name, sex, age);
}
//自定义
public string ToString(string format)
{
return ToString(format, null);//如果找到该实例则根据format查找相应结果,反之为null
}
public string ToString(string format, IFormatProvider formatProvider)
{
switch (format.ToUpper())
{
case null:
case "N":
return name;
case "S":
return sex;
case "A":
return String.Format("{0},{1}年龄:{2}", name, sex, age);
default:
return String.Format("你输入的{0}不合法!",format);
//throw new FormatException(String.Format(formatProvider, "Format{0}is not supported", format));
}
}
//排序
public int CompareTo(student other)
{
int compare = this.age.CompareTo(other.age);
if (compare == 0)
{
return this.name.CompareTo(other.name);
}
return compare;
}
}
public class FindName
{
public string name;
public FindName(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public bool FindNamePredicate(student stu)
{
if (stu == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("stu");
//Console.WriteLine("您查询的对象不存在!");
}
else
{
return stu.name == name;
}
}
}
2客户端效果:
 View Code
View Code
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
//添加数据的三种形式
//方式一
student stu1 = new student("小华", "男", 21);
student stu2 = new student("小明", "男", 22);
student stu3 = new student("小丽", "女", 19);
List<student> students = new List<student>() { stu1, stu2, stu3 };
//泛型空间大小根据容量自动增加。即:初始为n,第一次自增2n,第二次自增4n。诸如此类,每次容量是上次2倍大小。
students.Capacity = 100;//手动设置泛型空间大小
//方式二
students.Add(new student("小花", "女", 23));
//方式三
students.AddRange(new student[]{
new student("小王", "女", 19),
new student("小白", "女", 19)
});
//插入元素
students.Insert(2, new student("新人小王", "女", 22));
#region for
//读取数据的几种方法
//for (int i = 0; i < students.Count; i++)
//{
// //1,根据自定义ToString访问
// //方法1:根据条件N查询name
// Console.WriteLine(students[i].ToString("N"));
// //方法2:根据条件A查询全部信息
// Console.WriteLine(students[i].ToString("A"));
// //方法3:利用重载ToString()查询
// Console.WriteLine(students[i].ToString());
// //方法4:利用非法条件查询
// Console.WriteLine(students[i].ToString("T"));
// //2,根据索引
// //student s1 = student[3];
//}
#endregion
#region foreach
//3,List<T>执行接口IEnumerable,foreach迭代法
//foreach (student stu in students)
//{
// Console.WriteLine(stu);
//}
#endregion
#region ForEach
//students.ForEach(r => Console.WriteLine("{0:A}", r));
//students.ForEach(delegate(student r) { Console.WriteLine("{0:A}", r); });
#endregion
//删除元素
// students.RemoveAt(2);
//搜索的几种方法
//int index1 = students.IndexOf(stu2);//查询对象索引
////int index2 = students.FindIndex(new FindName("小白").FindNamePredicate);
//int index3 = students.FindIndex(r=>r.name=="小白");
//Console.WriteLine(index3);
//排序
//int s=stu2.CompareTo(stu1);
// students.Sort((r1, r2) => r1.age.CompareTo(r2.age));
//students.Sort();
students.Reverse();
students.ForEach(r => Console.WriteLine("{0:A}", r));
//Console.WriteLine(s);
}
catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
【结尾】:本文重点突出集合列表的用法,特别多种用法的掌握。比如一个添加数据,与其逐个对象的添加,不如分组效果好。还有查询时,for循环性能不高而且代码比较多。foreach就比较好理解啦,看起来也简便。最简便的当然拉姆达法则啦。诸如此类,可以总结很多东西。明白它的构造和使用方法。才能灵活运行!
