仿函数:
1 仿函数比一般函数更灵巧,他可以拥有状态。
2 每个仿函数可以拥有其型别。可以将仿函数的型别当做template参数进行传递,从而指定某种行为模式。如此一来,容器的型别也会因仿函数的不同而不同。
3 在执行速度上,仿函数通常比函数指针更快。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
一 仿函数做排序准则
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<set>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person();
~Person();
public:
string firstname()const;
string lastname()const;
};
class PersonSortCriterion
{
public:
bool operator ()(const Person&p1,const Person&p2)const
{
return p1.firstname<p2.firstname ||
(!(p2.lastname<p1.lastname) &&
p1.firstname<p2.firstname);
}
};
int main()
{
//declare set type with special sorting criterion
typedef set<Person,PersonSortCriterion> PersonSet;
PersonSet coll;
//do something with the elements
PersonSet::iterator pos;
for (pos=coll.begin();pos!=coll.end();++pos)
{
...
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
一 拥有内部状态
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>using namespace std;
//template<class Iter,class Operation>
//Operation for_each(Iter act,Iter end,Operation op)
//{
// while(act != end)
// {
// op(*act);
// ++act;
// }
// return op;
//}class MeanValue
{
private:
long num;//number of elements
long sum;//sum of all element values
public:
MeanValue():num(0),sum(0){}
void operator()(int elem)
{
num++;
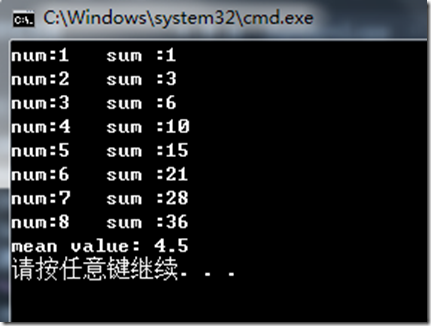
sum+=elem;cout<<"num:"<<num<<" "<<"sum :"<<sum<<endl;
}
double value()
{
return static_cast<double>(sum)/static_cast<double>(num);
}
};int main()
{
vector<int> coll;//insert element from 1 to 8
for(int i=1;i<=8;i++)
{
coll.push_back(i);
}
//process and print mean value
MeanValue mv = for_each<vector<int>::iterator,MeanValue> (coll.begin(),coll.end(),
MeanValue());
cout<<"mean value: "<<mv.value()<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出: