http://ace.delos.com/usacoprob2?a=GOVL6gcgbQL&S=packrec
嗯,一道无比恶心的题。。。。
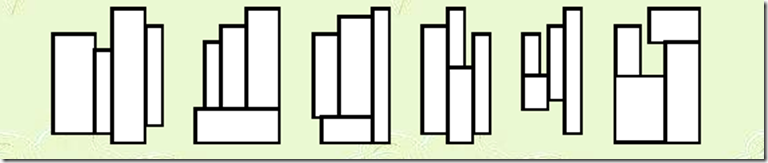
观察好这几个图形,基本上就要靠这几个图形做题了。这题恶心的地方除了这几个图形,还有就是暴搜的方法,要全排列生成4个矩形的排列,然后才能按照上面几个图形来划分cases。注意了,第四个和第五个图形是一样的,只不过把中间的一列和左边的一列交换了位置。还有一个恶心的地方就是最后一个图形了,这里是这道题无比恶心的源泉啊(+﹏+)~狂晕。。。。
至于第六个图形,主要是讨论下面两个矩阵对整个大矩阵的宽的影响。
具体的用笔画一下吧,不再累赘了。。。。
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; struct node{ int w,h; friend bool operator < (node a,node b) { return a.w<b.w; } }r[5]; int per[5]={0,1,2,3,4}; int sum=0,square=99999999; node f[1000]; void swap(node &a) { int x; x=a.w; a.w=a.h; a.h=x; } int max2(int xx,int yy) { return (xx>yy)?xx:yy; } int max3(int xx,int yy,int zz) { return (max2(max2(xx,yy),zz)); } int max4(int xx,int yy,int zz,int aa) { return (max2(max2(xx,yy),max2(zz,aa))); } void check(int ww,int hh) { if (ww*hh<square) { square=ww*hh; sum=0; f[++sum].w=min(ww,hh); f[sum].h=max(ww,hh); } else if (ww*hh==square) { f[++sum].w=min(ww,hh); f[sum].h=max(ww,hh); } } void case1(node a,node b,node c,node d) //图形1 { int ww=a.w+b.w+c.w+d.w; int hh=max4(a.h,b.h,c.h,d.h); check(ww,hh); } void case2(node a,node b,node c,node d) //图形2 { int ww=max2(a.w+b.w+c.w,d.w); int hh=max3(a.h,b.h,c.h)+d.h; check(ww,hh); } void case3(node a,node b,node c,node d) //图形3 { int ww=max2(a.w+b.w,c.w)+d.w; int hh=max2(max2(a.h,b.h)+c.h,d.h); check(ww,hh); } void case4(node a,node b,node c,node d) //图形4和图形5 { int ww=a.w+max2(b.w,c.w)+d.w; int hh=max3(a.h,b.h+c.h,d.h); check(ww,hh); } void case5(node a,node b,node c,node d) //无比恶心的图形6,注意好大于小于等于,注意.w和.h了。。。 { int ww=0; if (c.h>=b.h+d.h) ww=max3(a.w,b.w+c.w,c.w+d.w); else if (c.h>d.h && c.h<b.h+d.h) ww=max3(a.w+b.w,c.w+b.w,c.w+d.w); else if (c.h<d.h && a.h+c.h>d.h) ww=max3(a.w+b.w,a.w+d.w,c.w+d.w); else if (d.h>=a.h+c.h) ww=max3(b.w,a.w+d.w,c.w+d.w); else if (c.h==d.h) ww=max2(a.w+b.w,c.w+d.w); int hh=max2(a.h+c.h,b.h+d.h); check(ww,hh); } void work(node a,node b,node c,node d) { case1(a,b,c,d); case2(a,b,c,d); case3(a,b,c,d); case4(a,b,c,d); case5(a,b,c,d); } int main() { freopen("packrec.in","r",stdin); freopen("packrec.out","w",stdout); for (int i=1;i<=4;i++) cin>>r[i].w>>r[i].h; //这里要用do..while,用while的话,第一种原始排列就没有了 do //每一个swap都是矩阵的旋转 { for (int i=1;i<=2;i++) { swap(r[1]); for (int j=1;j<=2;j++) { swap(r[2]); for (int k=1;k<=2;k++) { swap(r[3]); for (int l=1;l<=2;l++) { swap(r[4]); work(r[per[1]],r[per[2]],r[per[3]],r[per[4]]); } } } } }while (next_permutation(per+1,per+5)); //全排列生成法,要感谢STL了 cout<<square<<endl; sort(f+1,f+sum+1); for (int i=1;i<=sum;i++) { if (f[i].w==f[i-1].w && f[i].h==f[i-1].h) continue; cout<<f[i].w<<" "<<f[i].h<<endl; } return 0; }
借用了zephyrQ的思想:
http://www.cnblogs.com/kissfinger/archive/2011/03/08/1977720.html