原文转自:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7976145
暑假听了computer vision的一个Summer School,里面Jason J. Corso讲了他们运用Low-Mid-High层次结构进行Video Understanding 和 Activity Recognition的方法,受益颇深,在这里把他的方法总结一下:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. 层次结构表示:
- 底层part 重用
- 每个object都是一个由有向和无向边连接起来的混合图
- 底层通过非线性学习让原子节点形成时空线、平面和区域
人的活动呢,就是这些object在中层和高层连接的混合图
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2. Motion Perception——STS
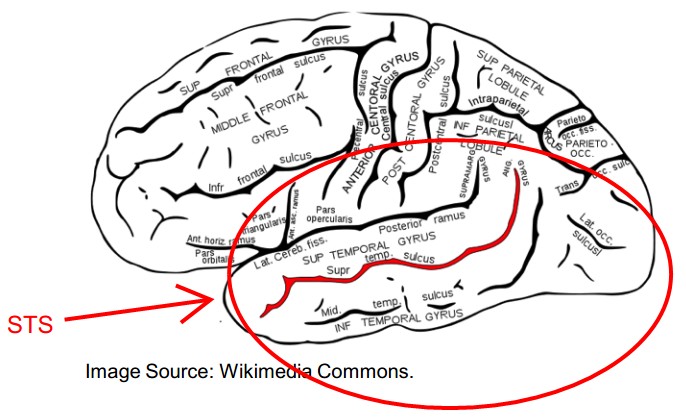
Different action stimulate different subpopulation of cells.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
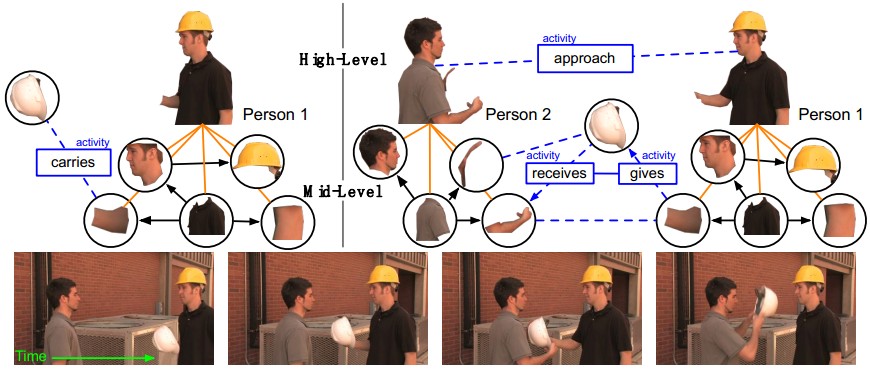
3. Activity Recognition
Corso的方法:
- Low-Level:底层最effective的做法是Bag of Features,特征为bottom-up / low level的时空特征,随着时间和层次不断update。通过模版进行底层object检测;
- Mid-Level:中间层从images中检测、跟踪2D骨架pose,并通过背景内容分析动态pose;
- High-Level:高层活动组合方法为,将不同时间点的feature组成时间-概率模型。时间上进行feature的时空跟踪,概率上根据组成语法进行概率模型的组合。
- Recognition的另一种表示方法:Segmentation
思想:建立Space-Time Patch Descriptors,组成visual Words直方图,建立多通道分类器。
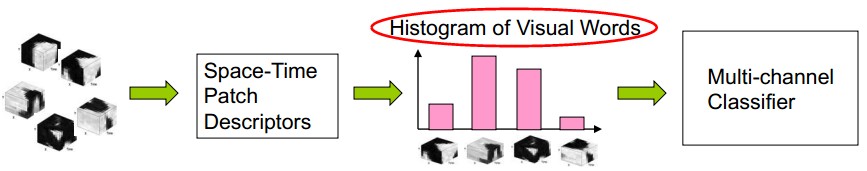
找出shikongHarris角点:
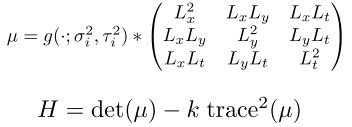
要求在feature上进行Densely Sample而非Sparse Sample。
提取Action Feature:f,用HOG/HOF描述
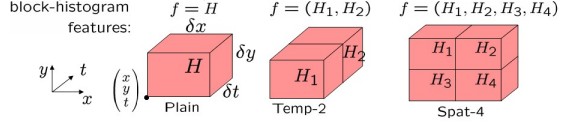
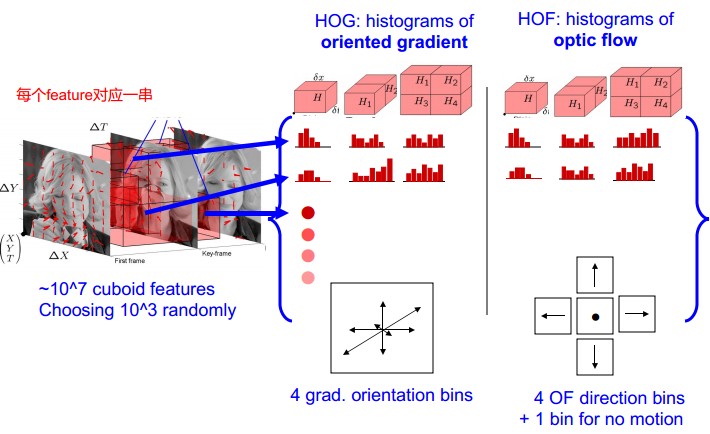
Space-Time Patch描述子形成histogram。每个histogram,是特征点在x,y,t三个分量上的直方图。
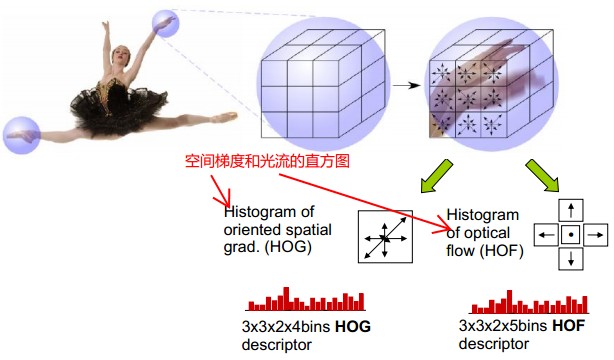
但是采用HOG、HOF存在问题,就是只能从前后帧去看,而不能考虑整个球的特征变化。出于这一想法,提出了HOG3D, 该特征在BMVC08中有文章进行具体描述,此处不予赘述,大家有兴趣去看文章吧。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4. 行为轨迹
采用 KLT: Kanade-Lucas-Tomasi Feature Tracker 进行特征点的跟踪,可作为局部特征检测的辅助手段。
- Trajectories by Local Keypoint Tracking
- Use Dense Trajectory(Dense sampling can improve object recognition and action recognition)
- CVPR 2011 Wang et al. “Action Recognition by Dense Trajectories.”中提出了一种方法,用一个单密度光流场跟踪轨迹
- 用HOG/HOF/MBH进行轨迹点描述

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5. Action Bank
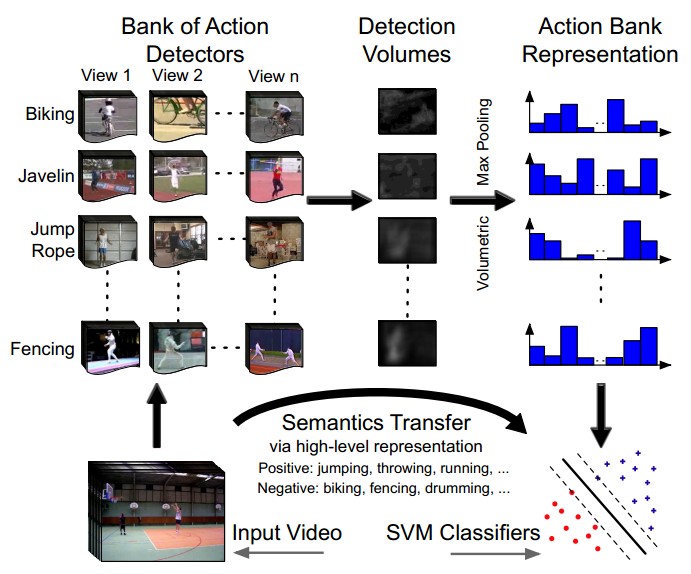
图中所示为Action bank的基本思想<CVPR 2012: Action Bank: A High-Level Representation of Activity in Video>
Action bank :
- 记录在不同scale和viewpoints的一个大action detector集合
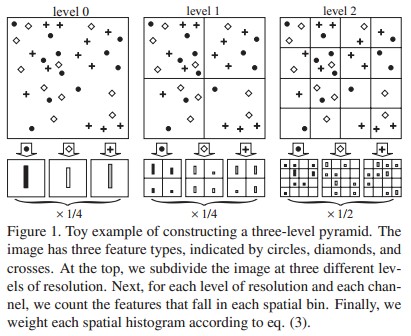
- 在Ns个scales上进行检测,action bank上有Na个detector,每组action-scale上有1^3+2^3+4^3=73维向量。所以action bank特征向量共有Na*Ns*73维(关于73怎么来的可以详细参考《Beyond Bags of Features: Spatial Pyramid Matching for Recognizing Natural Scene Categories》)
- 实际做的时候采用1-2个scale上的detector
- classifier 使用SVM分类器:
- 实现Action Bank的建立:
1. 选取UCF上的50个action,KTH上6个action和visint.org上的digging action,组成205 templates totally
2. 每个action选择3-6个不同视角、style或运动节奏的examples
3. 平均分辨率:50×120pixel;40-50frames/example
简单的说呢,就是根据不同视角、style和运动节奏来描述一个templates,由此组成了205个模版,描述57个action。
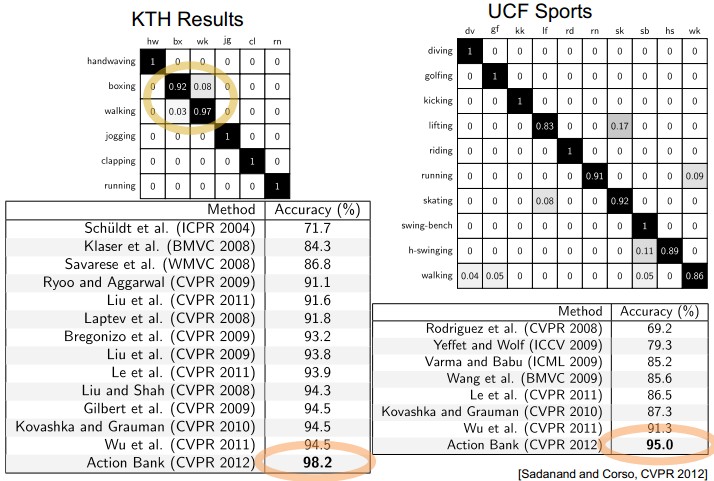
- 关于模版
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
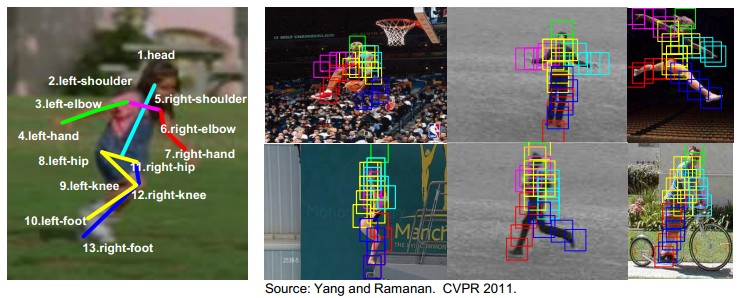
6. 基于Human Pose方法的Activity 识别
- 将人分为不同part,进行各部分的姿势估计可以清晰的进行model描述。
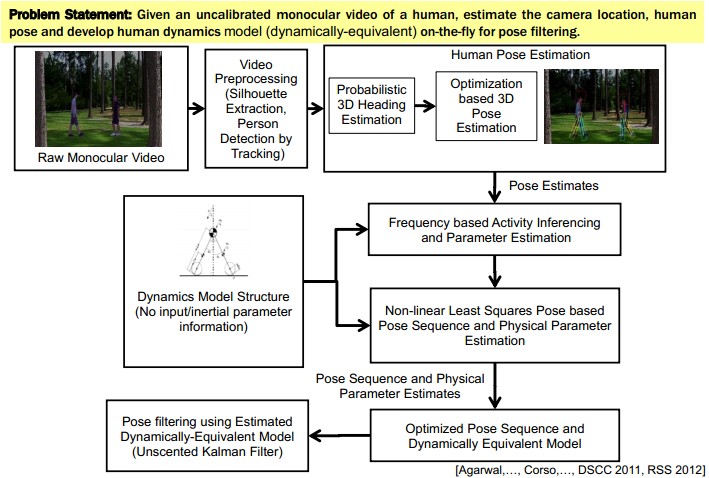
- 3D Human Pose Estimation:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
7. 基于Parts的Human Pose Estimation
模型结合了局部appearance和对称结构,有多篇文章涉及模型估计:
Pictorial Structures (Fischler & Elschlager 73, Felzenswalb and Huttenlocher 00)
Cardboard People (Yu et al 96)
Body Plans (Forsyth & Fleck 97)
Active Appearance Models (Cootes & Taylor 98)
Constellation Models (Burl et all 98, Fergus et al 03)
采用deformable part model
Slide credit: D. Ramanan. Method is from Yang and Ramanan, CVPR 2011.

Result:

- Dynamic Pose based Activity Recognition
2. For classification we use many one-versus-one histogram intersection kernel SVMs.
3. 处理dynamic pose和全局context都在动的情况,用 HoG3D and Dense Trajectory可得better效果。
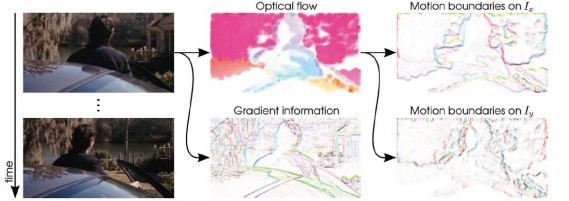
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
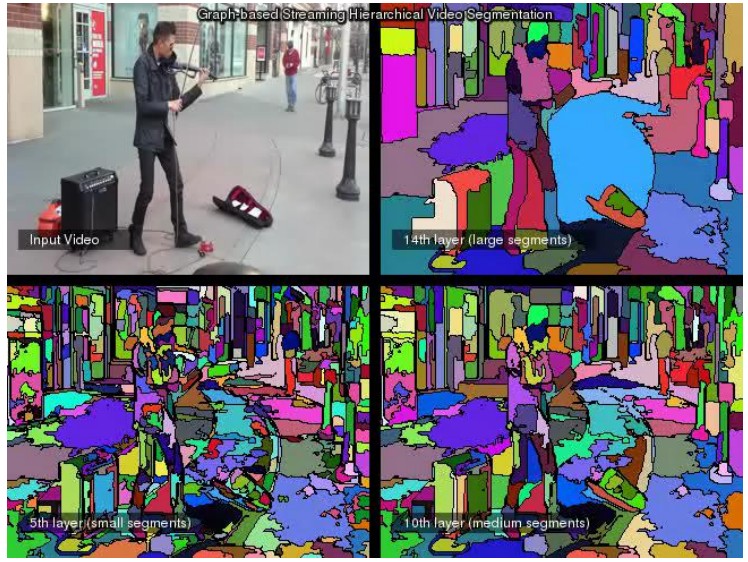
9.视频分割:Beyond Points for Video Understanding
标准方法:
- meanshift
- Graph-Based
- Hierarchical graph-based
- Nystrom normalized cuts
- Segmentation by weighted aggregation
ECCV 2012 Xu, Xiong and Corso的方法:将视频看做一个流,根据流向和时间上的马尔科夫假设建立一个估计构架,进行video分割。
Segmentation: S = {S1, S2, ... , Sm}
Input Video: V = {V1, V2, ... , Vm}(时间序列上的输入流)
取S*=arg min E(S|V)
在一个layer的分割中采取:

在整个hierarchy中采取同样假设:
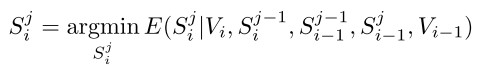


<ECCV 2012 Xu, Xiong and Corso>