部分引用自:http://blog.csdn.net/v5zsq/article/details/77255048

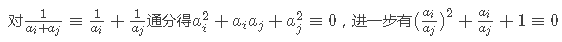
所以假设方程 x^2+x+1=0 在模p意义下的解为d,则答案就是满足(ai/aj) mod p = d的数对(i,j)的数量(i<j)。
现在把问题转化为解这个模意义下的二次方程。
x^2+x+1=0
配方:x^2+x+1/4+3/4=0
(x+1/2)^2+3/4=0
同乘4:(2x+1)^2+3=0
即(2x+1)^2=-3 (mod p)
换句话说,我们必须保证-3+p是p的一个二次剩余。
倘若-3+p不是p的一个二次剩余的话,无解。
如果是的话,我们就可以通过Cipolla算法得到2x+1的两个可能值,也就把二次同余方程变成了两个线性同余方程。
然后在一般情况下可以通过扩展欧几里得算法求得这两个个线性同余方程的最小非负整数解,也就得到了这个二次同余方程的两个解。
不过这题的情况有点特别,形式非常简单,根据大神的总结,在我们得到2x+1的两个值d1、d2之后,可以这样得到x1、x2。
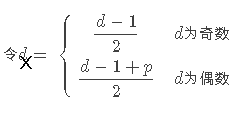
于是我们可以通过枚举+map来得到点对的个数。
注意特殊情况:①倘若x1或者x2为零的话,意味着(ai/aj)mod p=0,这是不可能的,注意不要统计这种。
②p为2时无解。
③p为3时有解,但是由于p-3等于零,所以不能直接用上面的方法。不过经过简单的推导,我们发现唯一合法的情况是ai=aj,且ai、aj均不为零,直接特判掉。
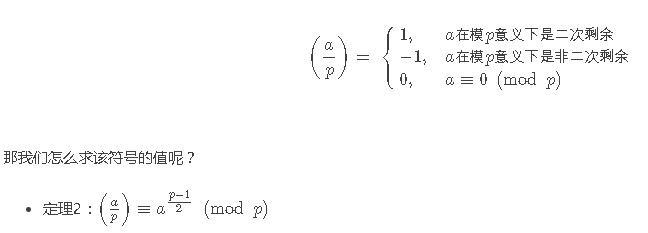
求解二次剩余的Cipolla算法:
http://blog.csdn.net/a_crazy_czy/article/details/51959546
http://blog.csdn.net/philipsweng/article/details/50000903
一句话:通过勒让德符号来判断n是不是模p的二次剩余,然后random一个a,使得(a^2-n)不是二次剩余,然后通过复数快速幂来求二次剩余的值。

#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll p,a[200005];
struct Complex{
ll a,b;
Complex(const ll &a,const ll &b){
this->a=a;
this->b=b;
}
Complex(){}
};
map<ll,int>ma;
int T,n;
ll Quick_Mul(ll x,ll p,ll mod){
if(!p){
return 0ll;
}
ll res=Quick_Mul(x,p>>1,mod);
res=(res+res)%mod;
if((p&1ll)==1ll){
res=(x%mod+res)%mod;
}
return res;
}
ll Quick_Pow(ll x,ll p,ll mod){
if(!p){
return 1ll;
}
ll res=Quick_Pow(x,p>>1,mod);
res=Quick_Mul(res,res,mod);
if((p&1ll)==1ll){
res=Quick_Mul(x%mod,res,mod);
}
return res;
}
ll aa,nn;
Complex Complex_Mul(const Complex &A,const Complex &B,const ll &p){
return Complex((Quick_Mul(A.a,B.a,p)+Quick_Mul(Quick_Mul(A.b,B.b,p),(Quick_Mul(aa,aa,p)-nn+p)%p,p))%p,
(Quick_Mul(A.a,B.b,p)+Quick_Mul(A.b,B.a,p))%p);
}
Complex Complex_Quick_Pow(Complex x,ll p,ll mod){
if(!p){
return Complex(1ll,0ll);
}
Complex res=Complex_Quick_Pow(x,p>>1,mod);
res=Complex_Mul(res,res,mod);
if((p&1ll)==1ll){
res=Complex_Mul(x,res,mod);
}
return res;
}
ll ran1(){
return ((rand()<<16)|rand());
}
ll ran(){
return ((ran1()<<16)|ran1());
}
pair<ll,ll> work(ll n,ll p){
aa=ran()%p;
nn=n;
while(Quick_Pow((Quick_Mul(aa,aa,p)-n+p)%p,(p-1ll)/2ll,p)!=p-1ll){
aa=ran()%p;
}
ll res=Complex_Quick_Pow(Complex(aa,1ll),(p+1ll)/2ll,p).a;
return make_pair(res,p-res);
}
ll ans;
ll f(ll x,ll p){
return (x&1ll)==1ll ? (x-1ll)/2ll : (x-1ll+p)/2ll;
}
int main(){
// freopen("1009.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("hdu6128.out","w",stdout);
srand(233);
scanf("%d",&T);
for(;T;--T){
ans=0;
ma.clear();
scanf("%d%lld",&n,&p);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
}
if(p==2ll || Quick_Pow(p-3ll,(p-1ll)/2ll,p)==p-1ll){
puts("0");
continue;
}
if(p==3ll){
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
if(a[i]){
ans+=ma[a[i]];
}
++ma[a[i]];
}
printf("%lld
",ans);
continue;
}
pair<ll,ll> d=work(p-3ll,p);
d.first=f(d.first,p);
d.second=f(d.second,p);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){
if(d.first){
ans+=ma[Quick_Mul(a[i],d.first%p,p)];
}
if(d.second){
ans+=ma[Quick_Mul(a[i],d.second%p,p)];
}
if(a[i]){
++ma[a[i]];
}
}
printf("%lld
",ans);
}
return 0;
}