1. 依赖包安装
pom.xml 加入:
- <!-- redis cache related.....start -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
- <version>1.6.0.RELEASE</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
- <artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
- <version>2.7.3</version>
- </dependency>
- <!-- redis cache related.....end -->
2. Spring 项目集成进缓存支持
要启用缓存支持,我们需要创建一个新的 CacheManager bean。CacheManager 接口有很多实现,本文演示的是和 Redis 的集成,自然就是用 RedisCacheManager 了。Redis 不是应用的共享内存,它只是一个内存服务器,就像 MySql 似的,我们需要将应用连接到它并使用某种“语言”进行交互,因此我们还需要一个连接工厂以及一个 Spring 和 Redis 对话要用的 RedisTemplate,这些都是 Redis 缓存所必需的配置,把它们都放在自定义的 CachingConfigurerSupport 中:
- /**
- * File Name:RedisCacheConfig.java
- *
- * Copyright Defonds Corporation 2015
- * All Rights Reserved
- *
- */
- package com.defonds.bdp.cache.redis;
- import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
- import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;
- import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
- /**
- *
- * Project Name:bdp
- * Type Name:RedisCacheConfig
- * Type Description:
- * Author:Defonds
- * Create Date:2015-09-21
- *
- * @version
- *
- */
- @Configuration
- @EnableCaching
- public class RedisCacheConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
- @Bean
- public JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
- JedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory();
- // Defaults
- redisConnectionFactory.setHostName("192.168.1.166");
- redisConnectionFactory.setPort(6379);
- return redisConnectionFactory;
- }
- @Bean
- public RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory cf) {
- RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<String, String>();
- redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(cf);
- return redisTemplate;
- }
- @Bean
- public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
- RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate);
- // Number of seconds before expiration. Defaults to unlimited (0)
- cacheManager.setDefaultExpiration(3000); // Sets the default expire time (in seconds)
- return cacheManager;
- }
- }
当然也别忘了把这些 bean 注入 Spring,不然配置无效。在 applicationContext.xml 中加入以下:
- <context:component-scan base-package="com.defonds.bdp.cache.redis" />
3. 缓存某些方法的执行结果
设置好缓存配置之后我们就可以使用 @Cacheable 注解来缓存方法执行的结果了,比如根据省份名检索城市的 provinceCities 方法和根据 city_code 检索城市的 searchCity 方法:
- // R
- @Cacheable("provinceCities")
- public List<City> provinceCities(String province) {
- logger.debug("province=" + province);
- return this.cityMapper.provinceCities(province);
- }
- // R
- @Cacheable("searchCity")
- public City searchCity(String city_code){
- logger.debug("city_code=" + city_code);
- return this.cityMapper.searchCity(city_code);
- }
4. 缓存数据一致性保证
CRUD (Create 创建,Retrieve 读取,Update 更新,Delete 删除) 操作中,除了 R 具备幂等性,其他三个发生的时候都可能会造成缓存结果和数据库不一致。为了保证缓存数据的一致性,在进行 CUD 操作的时候我们需要对可能影响到的缓存进行更新或者清除。
- // C
- @CacheEvict(value = { "provinceCities"}, allEntries = true)
- public void insertCity(String city_code, String city_jb,
- String province_code, String city_name,
- String city, String province) {
- City cityBean = new City();
- cityBean.setCityCode(city_code);
- cityBean.setCityJb(city_jb);
- cityBean.setProvinceCode(province_code);
- cityBean.setCityName(city_name);
- cityBean.setCity(city);
- cityBean.setProvince(province);
- this.cityMapper.insertCity(cityBean);
- }
- // U
- @CacheEvict(value = { "provinceCities", "searchCity" }, allEntries = true)
- public int renameCity(String city_code, String city_name) {
- City city = new City();
- city.setCityCode(city_code);
- city.setCityName(city_name);
- this.cityMapper.renameCity(city);
- return 1;
- }
- // D
- @CacheEvict(value = { "provinceCities", "searchCity" }, allEntries = true)
- public int deleteCity(String city_code) {
- this.cityMapper.deleteCity(city_code);
- return 1;
- }
业务考虑,本示例用的都是
@CacheEvict 清除缓存。如果你的 CUD 能够返回 City 实例,也可以使用 @CachePut 更新缓存策略。笔者推荐能用
@CachePut 的地方就不要用
@CacheEvict,因为后者将所有相关方法的缓存都清理掉,比如上面三个方法中的任意一个被调用了的话,provinceCities
方法的所有缓存将被清除。
5. 自定义缓存数据 key 生成策略
对于使用 @Cacheable 注解的方法,每个缓存的 key 生成策略默认使用的是参数名+参数值,比如以下方法:
- @Cacheable("users")
- public User findByUsername(String username)
这个方法的缓存将保存于 key 为 users~keys 的缓存下,对于 username 取值为 "赵德芳" 的缓存,key 为 "username-赵德芳"。一般情况下没啥问题,二般情况如方法 key 取值相等然后参数名也一样的时候就出问题了,如:
- @Cacheable("users")
- public Integer getLoginCountByUsername(String username)
这个方法的缓存也将保存于 key 为 users~keys 的缓存下。对于 username 取值为 "赵德芳" 的缓存,key 也为 "username-赵德芳",将另外一个方法的缓存覆盖掉。
解决办法是使用自定义缓存策略,对于同一业务(同一业务逻辑处理的方法,哪怕是集群/分布式系统),生成的 key 始终一致,对于不同业务则不一致:
- @Bean
- public KeyGenerator customKeyGenerator() {
- return new KeyGenerator() {
- @Override
- public Object generate(Object o, Method method, Object... objects) {
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- sb.append(o.getClass().getName());
- sb.append(method.getName());
- for (Object obj : objects) {
- sb.append(obj.toString());
- }
- return sb.toString();
- }
- };
- }
于是上述两个方法,对于
username 取值为 "赵德芳" 的缓存,虽然都还是存放在 key 为 users~keys 的缓存下,但由于 key 分别为
"类名-findByUsername-username-赵德芳" 和
"类名-getLoginCountByUsername-username-赵德芳",所以也不会有问题。
这对于集群系统、分布式系统之间共享缓存很重要,真正实现了分布式缓存。
笔者建议:缓存方法的 @Cacheable 最好使用方法名,避免不同的方法的 @Cacheable 值一致,然后再配以以上缓存策略。
6. 缓存的验证
6.1 缓存的验证
为了确定每个缓存方法到底有没有走缓存,我们打开了 MyBatis 的 SQL 日志输出,并且为了演示清楚,我们还清空了测试用 Redis 数据库。
先来验证 provinceCities 方法缓存,Eclipse 启动 tomcat 加载项目完毕,使用 JMeter 调用 /bdp/city/province/cities.json 接口: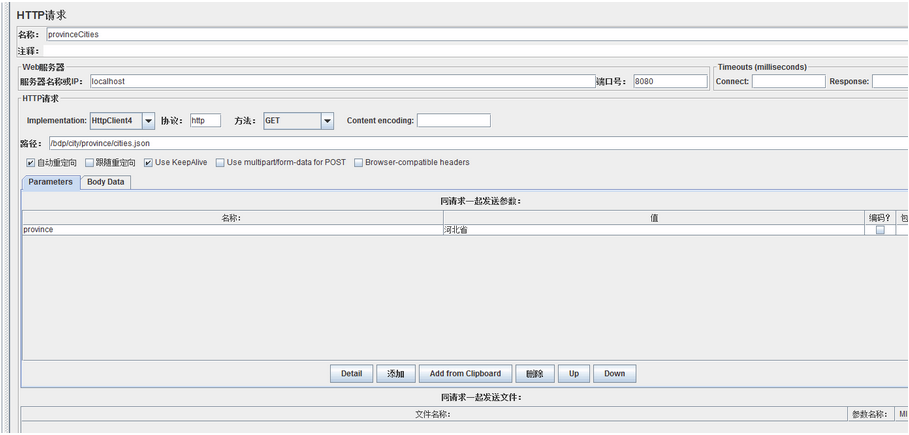
Eclipse 控制台输出如下: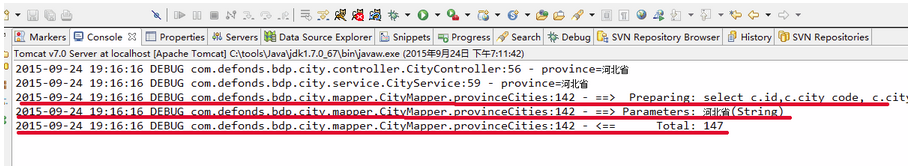
说明这一次请求没有命中缓存,走的是 db 查询。JMeter 再次请求,Eclipse 控制台输出: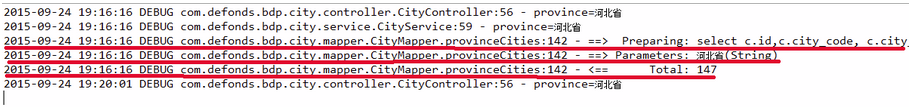
标红部分以下是这一次请求的 log,没有访问 db 的 log,缓存命中。查看本次请求的 Redis 存储情况: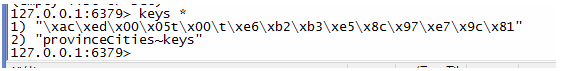
同样可以验证 city_code 为 1492 的 searchCity 方法的缓存是否有效: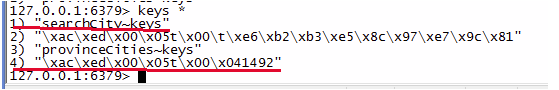
图中标红部分是 searchCity 的缓存存储情况。
6.2 缓存一致性的验证
先来验证 insertCity 方法的缓存配置,JMeter 调用 /bdp/city/create.json 接口: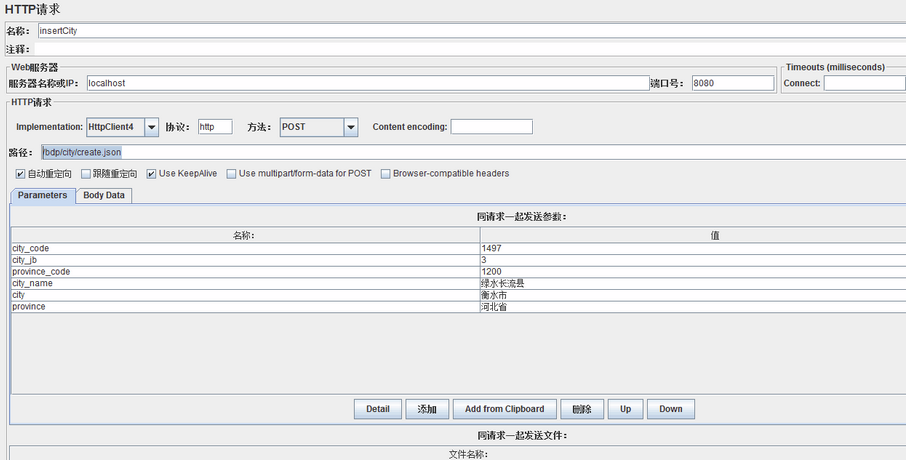
之后看 Redis 存储: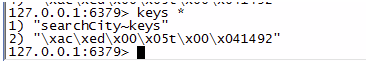
可以看出 provinceCities 方法的缓存已被清理掉,insertCity 方法的缓存奏效。
然后验证 renameCity 方法的缓存配置,JMeter 调用 /bdp/city/rename.json 接口: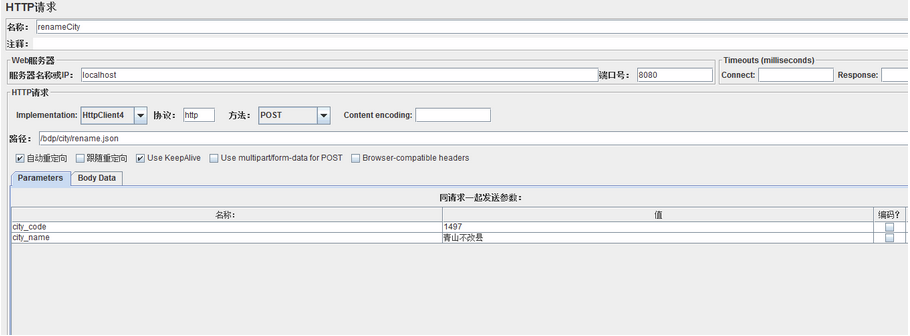
之后再看 Redis 存储: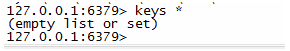
searchCity 方法的缓存也已被清理,renameCity 方法的缓存也奏效。
7. 注意事项
- 要缓存的 Java 对象必须实现 Serializable 接口,因为 Spring 会将对象先序列化再存入 Redis,比如本文中的 com.defonds.bdp.city.bean.City 类,如果不实现 Serializable 的话将会遇到类似这种错误:nested exception is java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: DefaultSerializer requires a Serializable payload but received an object of type [com.defonds.bdp.city.bean.City]]。
- 缓存的生命周期我们可以配置,然后托管 Spring CacheManager,不要试图通过 redis-cli 命令行去管理缓存。比如 provinceCities 方法的缓存,某个省份的查询结果会被以 key-value 的形式存放在 Redis,key 就是我们刚才自定义生成的 key,value 是序列化后的对象,这个 key 会被放在 key 名为 provinceCities~keys key-value 存储中,参考下图"provinceCities 方法在 Redis 中的缓存情况"。可以通过 redis-cli 使用 del 命令将 provinceCities~keys 删除,但每个省份的缓存却不会被清除。
- CacheManager 必须设置缓存过期时间,否则缓存对象将永不过期,这样做的原因如上,避免一些野数据“永久保存”。此外,设置缓存过期时间也有助于资源利用最大化,因为缓存里保留的永远是热点数据。
- 缓存适用于读多写少的场合,查询时缓存命中率很低、写操作很频繁等场景不适宜用缓存。
