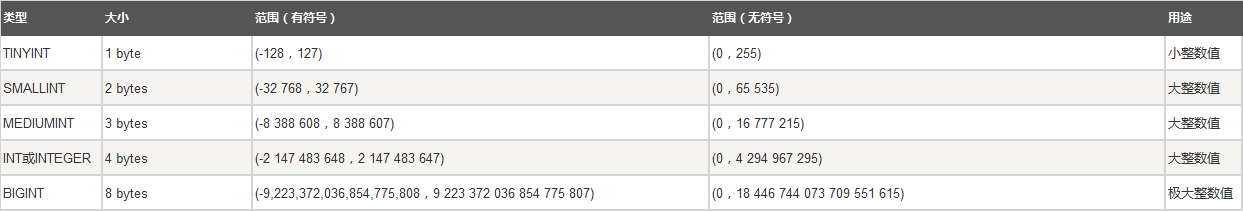
一、整数类型
1.1、tinyint [(M)][unsigned][zerofill]
1.2、smallint [(M)][unsigned][zerofill]
1.3、mediumint [(M)][unsigned][zerofill]
1.4、int [(M)][unsigned][zerofill]
1.5、bigint [(M)][unsigned][zerofill]
参数说明:
M:取值范围。
unsigned:无符号,控制是否有正负数。
zerofill:用来进行前导零填充,如tinyint的值为1,而其最长取值位数是3位,则填充后的结果会变成001。类型后面写了zerofill,默认就是unsigned无符号。
示例1:无参数控制
create table study01 (id01 tinyint,id02 int); desc study01; insert into study01 (id01,id02) values (100,101); insert into study01 (id01,id02) values (-1,-2); select * from study01;
示例2:有参数控制1
create table study02 (id01 tinyint(3) unsigned zerofill,id02 int(3) unsigned zerofill); desc study02; insert into study02 (id01,id02) values (1,1); insert into study02 (id01,id02) values (12,1234); select * from study02;
示例3:有参数控制2
create table study03 (id01 tinyint(3) unsigned,id02 int(3) unsigned); desc study03; insert into study03 (id01,id02) values (1,1); insert into study03 (id01,id02) values (12,1234); select * from study03;
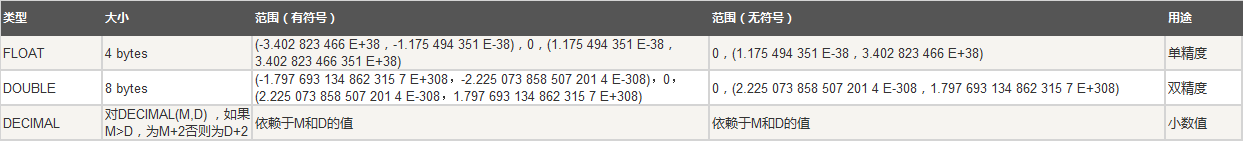
二、小数类型
2.1、decimal (M,D)
2.2、float (M,D)
2.3、double (M,D)
参数说明:
zerofill
unsigned
示例1:无参数控制
create table studyf1 (f1 float,f2 double); desc studyf1; insert into studyf1 (f1,f2) values (-12.123,-1234.5678); select * from studyf1;
示例2:有参数控制1
create table studyf2 (f1 float(5,2),f2 double(6,3) zerofill); desc studyf2; insert into studyf2 (f1,f2) values (12.34,12.34); insert into studyf2 (f1,f2) values (1.1,1.2); insert into studyf2 (f1,f2) values (123.45,123.456); /*科学计数法(E),小数点移动几位。*/ insert into studyf2 (f1,f2) values (0.1234E2,0.123456E3); /*插入多了,就会四舍五入。*/ insert into studyf2 (f1,f2) values (12.126,12.34); select * from studyf2;
示例3:有参数控制2
create table studyf3 (f1 float(10,4) unsigned zerofill); desc studyf3; insert into studyf3 (f1) values (12.345); insert into studyf3 (f1) values (12.3456); insert into studyf3 (f1) values (12.34567); select * from studyf3;
三、日期类型
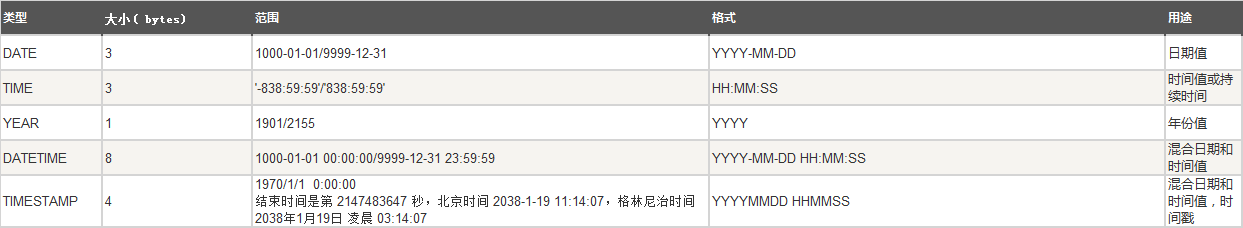
3.1、datetime(年月日时分秒)
create table studyd1 (mydate datetime); insert into studyd1 (mydate) values ('20200902230130'); insert into studyd1 (mydate) values (20200902230130); insert into studyd1 (mydate) values ('2020-09-02 23:01:30'); insert into studyd1 (mydate) values (null); select * from studyd1;
3.2、timestamp(年月日时分秒/整数)
create table studyd2 (mytime timestamp); insert into studyd2 (mytime) values ('20200902230130'); insert into studyd2 (mytime) values ('2020-09-02 23:01:30'); select * from studyd2; /*+0 查看时间戳,显示整数。*/ select mytime+0 from studyd2;
3.3、date(年月日)
create table studyd3 (mydate date); insert into studyd3 (mydate) values ('20200902'); insert into studyd3 (mydate) values ('2020-09-02'); select * from studyd3;
3.4、time(时分秒)
create table studyd4 (mytime time); insert into studyd4 (mytime) values ('10:10:10'); /*D HH:MM:SS,D代表天,最大可以是34天,代表过去多少时间。*/ insert into studyd4 (mytime) values ('5 10:10:10'); select * from studyd4;
3.5、year
create table studyd5 (myyear year); insert into studyd5 (myyear) values ('2020'); insert into studyd5 (myyear) values ('2021'); select * from studyd5;
四、字符类型
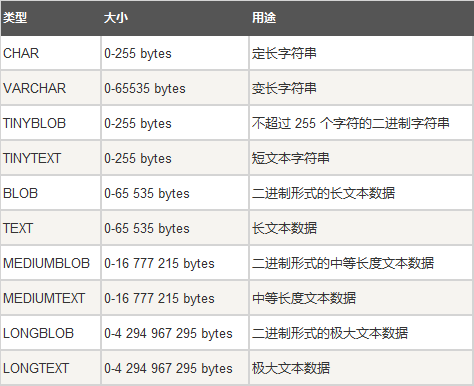
4.1、char(M),M表示字符固定长度,最大为255字节。
create table studyz1 (mychar char(255)); insert into studyz1 (mychar) values ('YES'); insert into studyz1 (mychar) values ('NO'); insert into studyz1 (mychar) values ('Y '); insert into studyz1 (mychar) values (' N'); select * from studyz1; select mychar,length(mychar) `length` from studyz1;
4.2、varchar(M),M表示字符可变长度,最大65535字节,需要1-2字节来保存信息,超过255的长度就用2个字节来保存。
utf8:一个字符占用3个字节 65535/3=21845 -1 -2=21844/21843
gbk:一个字符占用2个字节 65535/2=32767 -1 -2=32766/32765
最大长度是受最大65535字节和所使用的字符集有关。
create table studyz2 (myvarchar varchar(21844)); insert into studyz2 (myvarchar) values ('YES'); insert into studyz2 (myvarchar) values ('NO'); insert into studyz2 (myvarchar) values ('Y '); insert into studyz2 (myvarchar) values (' N'); select * from studyz2; select myvarchar,length(myvarchar) `length` from studyz2;
4.3、text
text和blob区别:blob用来保存二进制数据,text保存字符数据。
text和char/varchar区别:text不需要指定长度。
存储长度:1字节-4GB
/*tinytext:最大256 bytes,1字节开销,少于255个字符的,就比较好,比如:文章摘要。*/ create table text1 (id int,name tinytext); /*text:最大64k,相当于65535个字符,2字节开销,比如:文章正文。*/ create table text2 (id int,name text); /*mediumtext:最大16MB,相当于16777215个字符,3字节开销,存储相对大的文本数据,比如书籍文本,白皮书。*/ create table text3 (id int,name mediumtext); /*longtext:最大4GB,4字节开销。*/ create table text4 (id int,name longtext);
4.4、blob
/*tinyblob:最大256 bytes*/ create table blob1 (id int,name tinyblob); /*blob:最大64k*/ create table blob2 (id int,name blob); /*mediumblob:最大16MB*/ create table blob3 (id int,name mediumblob); /*longblob:最大4GB*/ create table blob4 (id int,name longblob);
4.5、enum:最多65535个枚举项,2字节开销,相于单项选择题。
create table studye1 (myenum enum('Y','N')); insert into studye1 (myenum) values ('Y'); insert into studye1 (myenum) values ('N'); insert into studye1 (myenum) values ('1'); insert into studye1 (myenum) values ('2'); select * from studye1; select myenum+0 from studye1;
4.6、set:集合,相当于多项选择题。
create table studys1 (myset set('A','B','C','D')); insert into studys1 values ('A'); insert into studys1 values ('A,B'); insert into studys1 values ('C'); insert into studys1 values ('C,D'); select * from studys1;