AbstractMap
HashMap继承制AbstractMap,很多通用的方法,比如size()、isEmpty(),都已经在这里实现了。来看一个比较简单的方法,get方法:
1 public V get(Object key) { 2 Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator(); 3 if (key==null) { 4 while (i.hasNext()) { 5 Entry<K,V> e = i.next(); 6 if (e.getKey()==null) 7 return e.getValue(); 8 } 9 } else { 10 while (i.hasNext()) { 11 Entry<K,V> e = i.next(); 12 if (key.equals(e.getKey())) 13 return e.getValue(); 14 } 15 } 16 return null; 17 }
单从这里看看不到Map的搜索策略,这里显示的仅仅就是遍历全部元素挨个测试是否匹配。
remove方法中先匹配到元素,然后利用迭代器Iterator的remove方法将元素从记录中删除。
1 public V remove(Object key) { 2 Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator(); 3 Entry<K,V> correctEntry = null; 4 if (key==null) { 5 while (correctEntry==null && i.hasNext()) { 6 Entry<K,V> e = i.next(); 7 if (e.getKey()==null) 8 correctEntry = e; 9 } 10 } else { 11 while (correctEntry==null && i.hasNext()) { 12 Entry<K,V> e = i.next(); 13 if (key.equals(e.getKey())) 14 correctEntry = e; 15 } 16 } 17 18 V oldValue = null; 19 if (correctEntry !=null) { 20 oldValue = correctEntry.getValue(); 21 i.remove(); 22 } 23 return oldValue; 24 }
transient和volatile
终于看到存储key和value的地方了,这里马上出现了两个Java关键字,transient和volatile:
transient volatile Set<K> keySet = null; transient volatile Collection<V> values = null;
transient关键字的意思是说改字段不会被持久化和反持久化,这个会在对象序列化到文件时用到。参考这里。
volatile就比较复杂一点儿了,一旦一个共享变量(类的成员变量、类的静态成员变量)被volatile修饰之后,那么就具备了两层语义:
1)保证了不同线程对这个变量进行操作时的可见性,即一个线程修改了某个变量的值,这新值对其他线程来说是立即可见的。
2)禁止进行指令重排序。
有点儿线程安全的意思,就是说一个变量被另外一个线程修改了,其他在使用这个变量的线程也会知道。
文章中所举例子:
1 //线程1 2 boolean stop = false; 3 while(!stop){ 4 doSomething(); 5 } 6 7 //线程2 8 stop = true
以上代码是有可能死循环的。
接下来初始化Entry时,如果用一个Map去初始化另外一个Map,那么这个Map的初始大小将为原先Map的2倍:
1 public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { 2 this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1, 3 DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); 4 inflateTable(threshold); 5 6 putAllForCreate(m); 7 } 8 9 private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) { 10 // assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative"; 11 return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY 12 ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY 13 : (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1; 14 } 15 16 /** 17 * Inflates the table. 18 */ 19 private void inflateTable(int toSize) { 20 // Find a power of 2 >= toSize 21 int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize); 22 23 threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); 24 table = new Entry[capacity]; 25 initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); 26 }
Integer.highestOneBit(num)
拿到原先Map的size之后初始化一个新的Entry数组,这个数组的的size增加到原先Map的2倍。方法Integer.highestOneBit(num)的作用是得到比num还大的但是是2的指数倍的数。这些数其实就是2,4,8,16,32,64,128,256,512
可以看出JDK源码中很多地方对于*2这种操作都不是直接乘以2,而是采用向左位移一位,比如:
1 (number - 1) << 1
HashMap数据结构
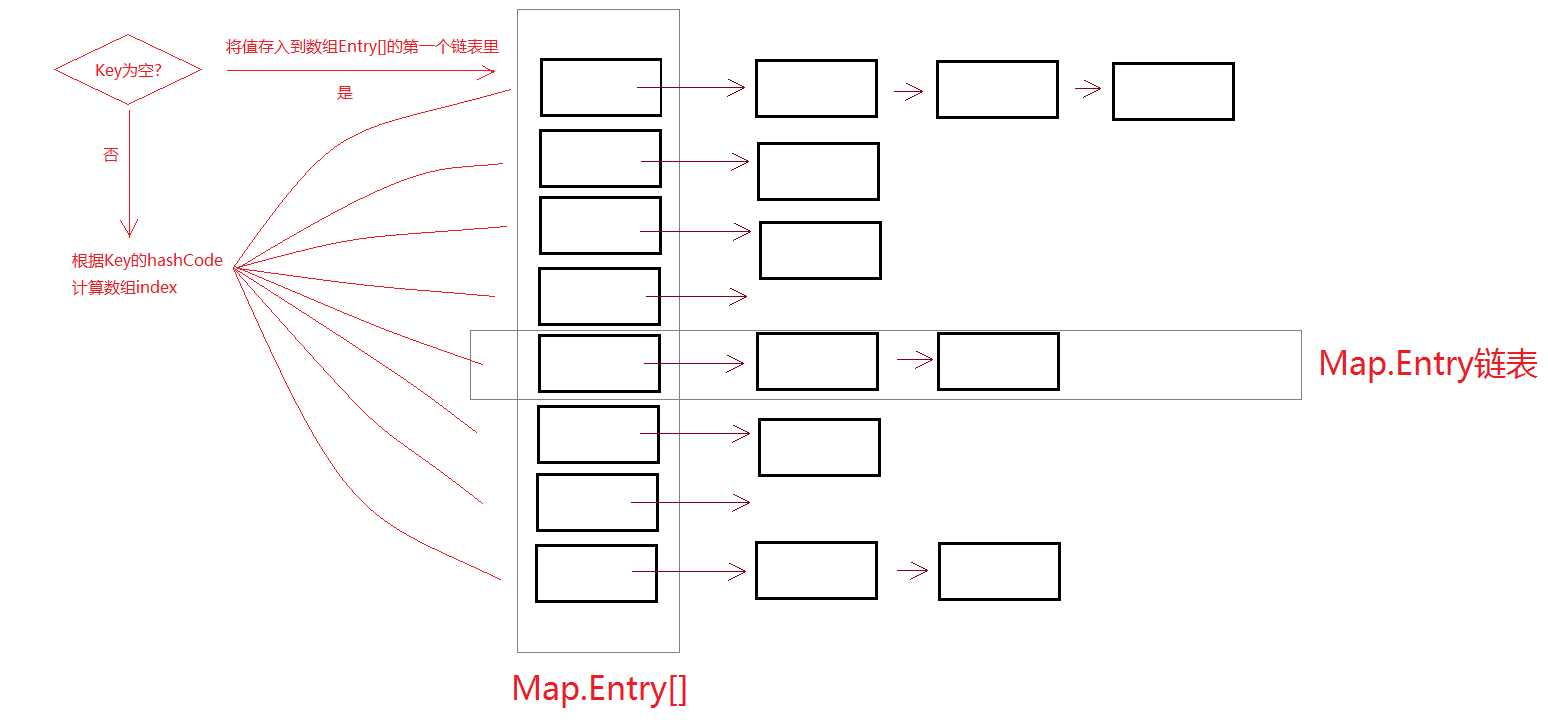
插入元素
1、key为null的Entry存放在数组Entry[]的第一位的Entry链表中,即Entry[0],仔细看看,Map.put()方法其实是有返回值的,这个返回值就是被替换掉的Value(如果存在的话)。
2、key不为空,通过Hash散列之后存入数组不同位置的链表中。散列中用到了按位与(&)运算:
1 /** 2 * Returns index for hash code h. 3 */ 4 static int indexFor(int h, int length) { 5 // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; 6 return h & (length-1); 7 }
如何进行Hash散列
按位与运算规则如下:
0 & 0 = 1
0 & 1 = 0
1 & 0 = 0
1 & 1 = 1
也就是只有同时两个都为1时才等于1。这里要求数组的长度必须是2指数倍是有原因的。比如length = 256(2的8次方),那么它换算成二进制就是1后面8个0:
100000000
256 - 1 换算成二进制刚好是7个1:
1111111
用这个数与任意的数N进行按位与运算的效果是:保留N的后7位:
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 & 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 ------------------------------- 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0
后面这7位就像亮着的几盏灯,亮几盏就能截取多少位。正是这样实现了数据的Hash散列。
从上面的代码可以看出,Hash散列时仅用到了了Object.hashCode()的后几位,如果n - 1 = 15即0x1111,那么发送Hash冲突的可能性会非常大,为了解决这个问题,可以理解为需要在原先的Object.hashClde()基础之上做一些混淆,即使整个原始HashCode都会影响最终的散列。
1 final int hash(Object k) { 2 int h = hashSeed; 3 if (0 != h && k instanceof String) { 4 return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); 5 } 6 7 h ^= k.hashCode(); 8 9 // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by 10 // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded 11 // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor). 12 h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); 13 return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); 14 }
这里通过高位与低位(向右位移的距离不一样)的异或运算进行“混淆”。
总结
HashMap的实现原理?
通过元素的哈希码来做映射,将数据散列到一个数组中,如果发生了哈希冲突则将冲突的元素形成一个链表进行存储。Java8中进行了优化,冲突的元素多到一定程度时,将改链表为红黑树,这样有效提高了高冲突时的性能;
HashMap需要注意些什么?
注意两个参数:
容量(Capacity):容器也可以叫做数组的初始大小,如果元素增加到一定程度(也就是负载因子),就会将容量翻倍。
负载因子(Load factor):默认负载因子是0.75,也就是当元素超过四分之三的时候会增加数组的大小。
需要注意的是,如果你想要HashMap遍历得更快,应该把容量设计得小点儿、负载因子设计大点儿,这样其实是让HashMap的数组存储地更密集些,能提高遍历速度。