实验目的
1、了解Linux操作系统中的设备驱动程序的组成
2、编写简单的字符设备驱动程序并进行测试
3、理解Linux操作系统的设备管理管理机制
4、实验内容:
编写Makefile文件,使之具备如下功能:
- 输入make,将自动编译scull.c和scull_test.c两个文件,并生成scull.o和scull_test文件
- 输入make clean-all,将清除生成的所有文件
- 输入make driver和make clean-driver,则分别实现生成和删除scull.o文件
- 输入make test和make clean-test,则分别实现生成和删除scull_test文件
编写一个简单的字符设备驱动程序,要求实现如下5个基本操作:
- scull_open()
- scull_write()
- scull_read()
- scull_ioctl()
- scull_release()
编写一个测试程序用来测试用户所编写的字符设备驱动程序
实验记录
我的虚拟机版本Ubuntu 20.04.1 x64,内核版本5.4.0-42-generic。
切换到root权限,随后编写scull.h、scull.c、scull_test.c和Makefile
scull.h
点击查看详细内容
#ifndef _SCULL_H
#define _SCULL_H
struct scull_dev {
void *data;
int quantum; // the current quantum size
int qset; // the current array size
unsigned long size;
unsigned int access_key; // used by sculluid and scullpriv
unsigned int usage; // lock the device while using it
unsigned int new_msg;
struct scull_dev *next;
};
struct scull_dev scull;
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#define SCULL_MAJOR 111
#define SCULL_NAME "scull"
#define DEVICE_FILE "/dev/scull"
#define SCULL_MAGIC SCULL_MAJOR
#define SCULL_RESET _IO(SCULL_MAGIC,0) // reset the data
#define SCULL_QUERY_NEW_MSG _IO(SCULL_MAGIC,1) // check for new message
#define SCULL_QUERY_MSG_LENGTH _IO(SCULL_MAGIC,2) // get message length
#define IOC_NEW_MSG 1
#endif
scull.c
点击查看详细内容
#ifndef __KERNEL__
#define __KERNEL__
#endif
#ifndef MODULE
#define MODULE
#endif
#include <linux/version.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/ioport.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/segment.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include "scull.h"
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
int new_msg;
static int Device_Open = 0;
int scull_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp){
Device_Open++;
printk("Char device %s is in open
", SCULL_NAME);
try_module_get(THIS_MODULE);
return 0;
}
ssize_t scull_write(struct file *filp, const char *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *off){
int cfu;
if(count < 0)
return -EINVAL;
if(scull.usage || scull.new_msg)
return -EBUSY;
scull.usage = 1;
kfree(scull.data);
scull.data = kmalloc(sizeof(char) * (count + 1), GFP_KERNEL);
if(!scull.data){
return -ENOMEM;
}
cfu = copy_from_user(scull.data, buffer, count+1);
scull.usage=0;
scull.new_msg=1;
return count;
}
ssize_t scull_read(struct file *filp, char *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *off){
int length, ctu;
if(count < 0)
return -EINVAL;
if(scull.usage)
return -EBUSY;
scull.usage=1;
if(count == 0)
return 0;
length = strlen(scull.data);
if(length < count)
count = length;
ctu = copy_to_user(buffer, scull.data, count+1);
scull.new_msg = 0;
scull.usage = 0;
return count;
}
int scull_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp){
Device_Open--;
printk("Char device %s is in release
", SCULL_NAME);
module_put(THIS_MODULE);
return 0;
}
long int unlocked_ioctl(struct file *filp,unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg){
switch(cmd){
case SCULL_RESET:
kfree(scull.data);
scull.data = NULL;
scull.usage = 0;
scull.new_msg = 0;
break;
case SCULL_QUERY_NEW_MSG:
if(scull.new_msg)
return IOC_NEW_MSG;
break;
case SCULL_QUERY_MSG_LENGTH:
if(scull.data == NULL) {
return 0;
} else {
return strlen(scull.data);
}
break;
default:
return -ENOTTY;
}
return 0;
}
struct file_operations scull_chops={
read: scull_read,
write: scull_write,
unlocked_ioctl: unlocked_ioctl,
open: scull_open,
release: scull_release
};
int init_scull(void){
int result;
printk("Initializing char device %s.
", SCULL_NAME);
result=register_chrdev(SCULL_MAJOR, SCULL_NAME, &scull_chops);
if(result < 0){
printk("Scull: Can't get major number!
");
return result;
}
return 0;
}
void cleanup_scull(void){
unregister_chrdev(SCULL_MAJOR, SCULL_NAME);
printk("Cleanup char device %s.
", SCULL_NAME);
}
module_init(init_scull);
module_exit(cleanup_scull);
scull_test.c
点击查看详细内容
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include "scull.h"
void write_proc(void);
void read_proc(void);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if(argc == 1) {
puts("Usage: scull_test [write|read]");
exit(0);
}
if(!strcmp(argv[1], "write")) {
write_proc();
}
else if(!strcmp(argv[1], "read")) {
read_proc();
}
else {
puts("scull_test: invalid command!");
}
return 0;
}
void write_proc() {
int fd, len, quit = 0;
char buf[100];
fd = open(DEVICE_FILE, O_WRONLY);
if(fd <= 0) {
printf("Error opening device file %s for writing!
", DEVICE_FILE);
exit(1);
}
printf("input 'exit' to exit!");
while(!quit) {
printf("
write>> ");
fgets(buf, 100, stdin);
if(!strcmp(buf, "exit
"))
quit = 1;
while(ioctl(fd, SCULL_QUERY_NEW_MSG))
usleep(1000);
len=write(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
if(len < 0) {
printf("Error writing to device %s!
", SCULL_NAME);
close(fd);
exit(1);
}
printf("%d bytes written to device %s!
", len - 1, SCULL_NAME);
}
//free(buf);
close(fd);
}
void read_proc() {
int fd, len, quit = 0;
char *buf = NULL;
fd = open(DEVICE_FILE, O_RDONLY);
if(fd<0) {
printf("Error opening device file %s for reading!
", DEVICE_FILE);
exit(1);
}
while(!quit) {
printf("
read<< ");
while(!ioctl(fd, SCULL_QUERY_NEW_MSG))
usleep(1000);
// get the msg length
len=ioctl(fd, SCULL_QUERY_MSG_LENGTH, NULL);
if(len) {
if(buf!=NULL)
free(buf);
buf = malloc(sizeof(char) * (len+1));
len = read(fd, buf, len);
if(len < 0) {
printf("Error reading from device %s!", SCULL_NAME);
}
else {
if(!strcmp(buf, "exit
")) {
ioctl(fd, SCULL_RESET); // reset
quit = 1;
printf("%s
",buf);
}
else
printf("%s
",buf);
}
}
}
free(buf);
close(fd);
}
Makefile
点击查看详细内容
obj-m+=scull.o
KDIR=/lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD:=$(shell pwd)
scull.o: scull.c
make -C $(KDIR) M=${PWD} modules # 在内核源码环境下编译scull.c
gcc -o scull_test.o scull_test.c # 编译scull_test.c
insmod scull.ko # 加载scull这个字符驱动设备
mknod /dev/scull c 111 0 # 创建一个设备文件
clean-all:
rm -rf *.ko *.mod.c *.o modules.* Module.symvers /dev/scull
driver:
make -C $(KDIR) M=${PWD} modules # 在内核源码环境下编译scull.c
clean-driver:
rm -f scull.o
test:
gcc -o scull_test.o scull_test.c # 编译scull_test.c
clean-test:
rm -f scull_test.o
.PHONY: clean clean-all driver clean-driver
实验过程
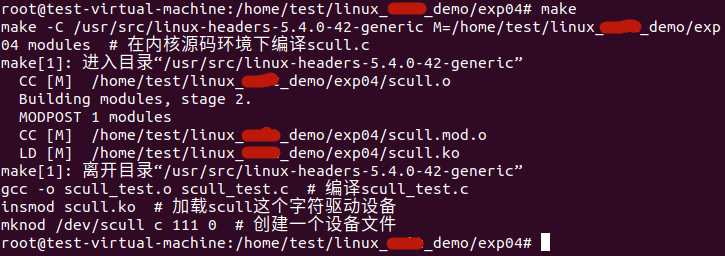
执行make命令
使用make test,生成可执行文件scull_test.o,然后输入./scull_test.o write和./scull_test.o read运行它,输入exit退出程序

输入rmmod scull卸载模块,并确认正在运行的模块中没有scull

最后使用dmesg | grep scull,查看日志内容
