一、实验
实验要求:
- 完成一个简单的时间片轮转多道程序内核代码,代码见视频中或从mykernel找。
- 详细分析该精简内核的源代码并给出实验截图
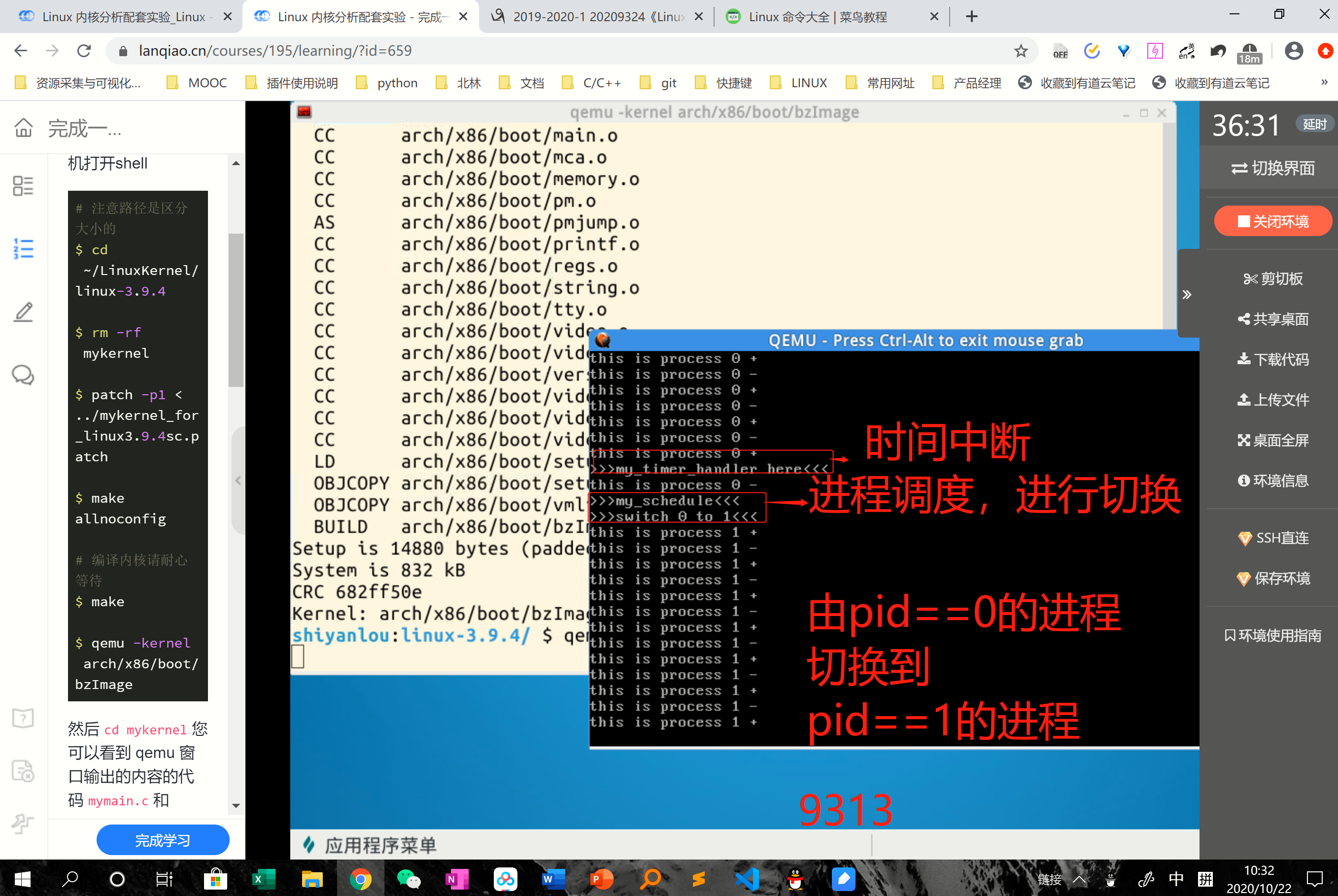
二、仔细分析进程的启动和进程的切换机制
- mymain.c
*
* linux/mykernel/mymain.c
*
* Kernel internal my_start_kernel
*
* Copyright (C) 2013 Mengning
*
*/
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include "mypcb.h"
tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
tPCB * my_current_task = NULL;
volatile int my_need_sched = 0;
void my_process(void);
void __init my_start_kernel(void)
{
int pid = 0;
int i;
/* Initialize process 0*/
task[pid].pid = pid;
task[pid].state = 0;/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
task[pid].next = &task[pid];
/*fork more process */
for(i=1;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++)
{
memcpy(&task[i],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB));
task[i].pid = i;
task[i].state = -1;
task[i].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[i].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
task[i].next = task[i-1].next;
task[i-1].next = &task[i];
}
/* start process 0 by task[0] */
pid = 0;
my_current_task = &task[pid];
asm volatile(
"movl %1,%%esp
" /* set task[pid].thread.sp to esp */
"pushl %1
" /* push ebp */
"pushl %0
" /* push task[pid].thread.ip */
"ret
" /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to eip */
"popl %%ebp
"
:
: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp) /* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/
);
}
void my_process(void)
{
int i = 0;
while(1)
{
i++;
if(i%10000000 == 0)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d -
",my_current_task->pid);
if(my_need_sched == 1)
{
my_need_sched = 0;
my_schedule();
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d +
",my_current_task->pid);
}
}
}
- mypcb.h
主要存放了头文件、PCB的定义和结构
/*
* linux/mykernel/mypcb.h
*
* Kernel internal PCB types
*
* Copyright (C) 2013 Mengning
*
*/
#define MAX_TASK_NUM 4
#define KERNEL_STACK_SIZE 1024*8
/* CPU-specific state of this task */
struct Thread {
unsigned long ip;
unsigned long sp;
};
typedef struct PCB{
int pid;
volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
char stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE];
/* CPU-specific state of this task */
struct Thread thread;
unsigned long task_entry;
struct PCB *next;
}tPCB;
void my_schedule(void);
- myinterrupt.c
主要实现中断信号的发出
/*
* linux/mykernel/myinterrupt.c
*
* Kernel internal my_timer_handler
*
* Copyright (C) 2013 Mengning
*
*/
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include "mypcb.h"
extern tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
extern tPCB * my_current_task;
extern volatile int my_need_sched;
volatile int time_count = 0;
/*
* Called by timer interrupt.
* it runs in the name of current running process,
* so it use kernel stack of current running process
*/
void my_timer_handler(void) //time_count调整时间片大小
{
#if 1
if(time_count%10 == 0 && my_need_sched != 1)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_timer_handler here<<<
");
my_need_sched = 1;
}
time_count ++ ;
#endif
return;
}
void my_schedule(void) //进程调度程序
{
tPCB * next;
tPCB * prev;
if(my_current_task == NULL
|| my_current_task->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_schedule<<<
");
/* schedule */
next = my_current_task->next;
prev = my_current_task;
if(next->state == 0)/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
{
my_current_task = next;
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>switch %d to %d<<<
",prev->pid,next->pid);
/* switch to next process * //进程切换
asm volatile(
"pushl %%ebp
" /* save ebp */
"movl %%esp,%0
" /* save esp */
"movl %2,%%esp
" /* restore esp */
"movl $1f,%1
" /* save eip */
"pushl %3
"
"ret
" /* restore eip */
"1: " /* next process start here */
"popl %%ebp
"
: "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip)
: "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip)
);
}
else
{
next->state = 0;
my_current_task = next;
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>switch %d to %d<<<
",prev->pid,next->pid);
/* switch to new process */
asm volatile(
"pushl %%ebp
" /* save ebp */
"movl %%esp,%0
" /* save esp */
"movl %2,%%esp
" /* restore esp */
"movl %2,%%ebp
" /* restore ebp */
"movl $1f,%1
" /* save eip */
"pushl %3
"
"ret
" /* restore eip */
: "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip)
: "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip)
);
}
return;
}
三、总结
阐明自己对“操作系统是如何工作的”理解。
操作系统通过三大法宝:中断、堆栈、冯.诺依曼结构,以及硬件实现各大作业的有序进行,通过进程调度实现资源的共享、调度,实现多进程高效编程。
通过建立堆栈,压入参数、EIP、被调用函数,实现顺序执行指令,实现了函数调用。