1、实现的功能:
根据test.xlsx中输入的的信息如下图1,首先先生成图2中test.v的代码,然后正则匹配test.v中的代码,并将其例化后写入到top.v中如图3。

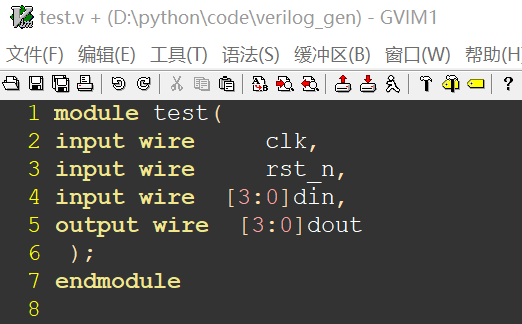

图1 test.xlsx 图2 test.v 图3 top.v
2、工程链接代码:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/aslmer/verilog_gen.rar
import os import re import openpyxl excel_name= "test.xlsx" input_file= os.getcwd()+"\"+excel_name #1、打开excel的工作表 wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(input_file) #2、获取工作表的名字test,返回的是一个list module_name= wb.sheetnames #3、list转为str top_name=''.join(module_name) #生成一个test.v,其中写入的是将test.xlsx中的信息转化为verilog的代码框架 gen_file= os.getcwd()+"\"+top_name+'.v' #每次运行的时候检测test.v是否存在,如果存在则删除 if os.path.exists(gen_file): os.remove(gen_file) print(''.join(module_name))#list ---> str #打开excel名字为test的工作表 table= wb[top_name] #open sheet by name #统计表格中的行数和列数 row_num = table.max_row col_num = table.max_column ##定义列表变量 ##端口名字 clk rst_n din dout port_name=[] ##位宽 1 1 4 3 port_width=[]## ## 端口方向 input output inout port_type=[] for i in range(row_num): port_name.append(table.cell(row=i+1, column=1).value)##excel中的第一列 port_type.append(table.cell(row=i+1,column=2).value)##excel中的第二列 port_width.append(table.cell(row=i+1,column=3).value)##excel中的第三列 print(port_name) print(port_type) print(port_width) ##打开test.v并写入从excel信息对应的verilog代码 with open(gen_file,'a') as file_obj: file_obj.write('module '+top_name+'( ') for i in range(row_num-1): if(port_type[i+1] == "I"): port_str="input" elif(port_type[i+1] == "O"): port_str='output' if(port_width[i+1]== 1): width_str=" " else: width_str=" ["+str(port_width[i+1]-1)+':0]' if(i<row_num-2): file_obj.write(port_str+" wire "+width_str +port_name[i+1]+', ') else: file_obj.write(port_str +" wire " + ' [' + str(port_width[i + 1] - 1) + ':0]' + port_name[i + 1] + ' ); endmodule') ##正则匹配re,获取需要的信息 s代表空格、制表符、换行符 + 前面的字符一个或一个以上 w代表数字、字母、下划线 # *代表重复次数为0~无限多次 |或 +:至少1个~更多个 ?代表前面的字符可以是0个或者最多1个 #对于标点符号比如 减号- 方括号[] 冒号:均需要用反斜杠进行转义 acquire_module=re.compile('(module)(s+)(w+)') acquire_ports =re.compile(".*(input|output|inout)(s+)(wire|reg)?(s+)([w+:0])?(w+)") with open(gen_file,'r') as file_obj: content = file_obj.read()#d读取test.v文件中的所有内容 print(content) module_obj = acquire_module.search(content)#从test.v中匹配到需要的字符串,search只返回一个匹配的结果 port_obj =acquire_ports.findall(content) #findall返回所有的匹配结果,返回一个list类型 print( module_obj.group(3))#group用()进行分组,group(0)或者group()代表所有组的集合,group(1)代表第一组(),依次递增 print(port_obj,type(port_obj)) ##1、打开一个文件top.v,将产生的test.v文件进行例化 inst_file=os.getcwd()+"\top.v" if os.path.exists(inst_file): os.remove(inst_file) print(inst_file) with open(inst_file,'a')as fp: fp.write(module_obj.group(3)+" u_"+module_obj.group(3)+' ( ') for i in range(len(port_obj)): if(i<len(port_obj)-1): fp.write(' .'+port_obj[i][5]+' ('+port_obj[i][5]+'), ') else: fp.write(' .' + port_obj[i][5] + ' (' + port_obj[i][5] + ') ); ')
一直断断续续,重蹈覆辙的说要学python,学习又放弃,这也许是第一个坚持写出来的自己想要的小工具,虽然可能方法很笨拙,也算是迈出了第一步。