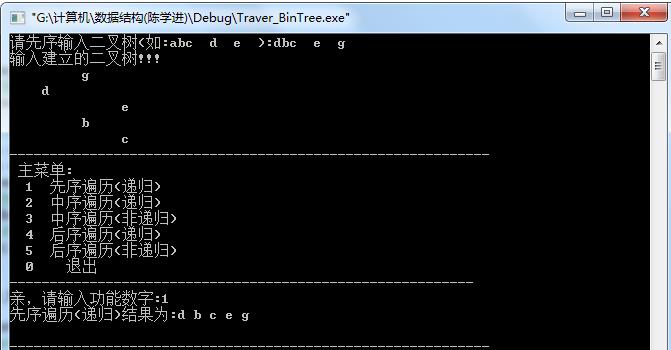
#include<stdlib.h> #include<stdio.h> #define MAX 50 #define MAS 20 #define CHAR 1 typedef char elem; //定义二叉树的数据结构 typedef struct node{ elem data;//二叉树的值 struct node *lchild; //左孩子 struct node *rchild;//右孩子 struct node *parent;//父节点 }BinTNode,*BinTree; //定义二叉树的初始化函数 BinTNode *Init_BinTree(BinTNode *tree){ tree=NULL; //将NULL赋值给tree return tree; //返回tree } //创建二叉树 BinTNode *Create_BinTree(BinTNode *tree){ elem ch; scanf("%c",&ch); //将键入值赋给二叉树的节点 if(ch==' ') // 以空格作为空左孩子和空右孩子的表示 tree=NULL; else{ //申请空间,以及通过对左右孩子的递归完成二叉树的创建 tree=(BinTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BinTNode)); if(!tree) exit(0); tree->data=ch; tree->parent=NULL; tree->lchild=Create_BinTree(tree->lchild); if(tree->lchild) tree->lchild->parent=tree; tree->rchild=Create_BinTree(tree->rchild); if(tree->rchild) tree->rchild->parent=tree; } return tree;//返回tree } //在屏幕上输出创建的二叉树,采用递归算法 void PrintTree(BinTNode *tree,int i){ if(tree!=NULL){ //采用条件编译对CHAR事先进行编译 PrintTree(tree->rchild,i+5); #if CHAR if(tree->data!=' ') printf("%*c ",i,tree->data); #else if(tree->data!=' ') printf("%*d ",i,tree->data); #endif PrintTree(tree->lchild,i+5); i=i-5; } } /*先序遍历(递归)*/ void Pre_Order(BinTNode *tree){ if(tree!=NULL){ printf("%c"" ",tree->data); Pre_Order(tree->lchild); Pre_Order(tree->rchild); } } /*中序遍历(递归)*/ void In_Order(BinTNode *tree){ if(tree!=NULL){ In_Order(tree->lchild); printf("%c"" ",tree->data); In_Order(tree->rchild); } } //中序遍历(非递归),利用栈结构存储数据 void In_OrderX(BinTNode *tree,void(*visit)(elem)){ BinTNode *p,*stack[MAS]; int top; top=0; p=tree; while(top!=0||p!=NULL){ while(p!=NULL){ stack[top]=p; top++; p=p->lchild; } if(top!=0){ p=stack[top-1]; top--; visit(p->data); p=p->rchild; } } } /*后序遍历(递归)*/ void Bac_Order(BinTNode *tree){ if(tree!=NULL){ Bac_Order(tree->lchild); Bac_Order(tree->rchild); printf("%c"" ",tree->data); } } /*后序遍历(非递归),利用栈结构存储数据 */ void Bac_OrderX(BinTNode *tree,void(*visit)(elem)){ BinTNode *p,*stack[MAS]; int top; top=0; stack[top]=tree; top++; while(top>0){ p=stack[top-1]; top--; while(p!=NULL){ visit(p->data); stack[top]=p->rchild; top++; p=p->lchild; } } } void visit(elem e){ printf("%c"" ",e); } int main() { int i; BinTree tree; tree=Init_BinTree(tree); #if CHAR printf("请先序输入二叉树(如:abc d e ):"); #else printf("请先序输入二叉树(如:a b 表示a为根结点,b为左子树的二叉树) "); #endif tree=Create_BinTree(tree); printf("输入建立的二叉树!!! "); PrintTree(tree,5); do{ printf("------------------------------------------------------------"); printf(" 主菜单:"); printf(" 1 先序遍历(递归)"); printf(" 2 中序遍历(递归)"); printf(" 3 中序遍历(非递归)"); printf(" 4 后序遍历(递归)"); printf(" 5 后序遍历(非递归)"); // printf(" 6 "); printf(" 0 退出"); printf(" ----------------------------------------------------------"); printf(" "); printf("亲,请输入功能数字:"); scanf("%d",&i); switch(i){ case 1: printf("先序遍历(递归)结果为:"); Pre_Order(tree); break; case 2: printf("中序遍历(递归)结果为:"); In_Order(tree); break; case 3: printf("中序遍历(非递归)结果为:"); In_OrderX(tree,visit) ; break; case 4: printf("后序遍历(递归)结果为:"); Bac_Order(tree); break; case 5: printf("后序遍历(非递归)结果为:"); Bac_Order(tree,visit); break; case 0: exit(0); default :printf("亲,请输入--菜单--中的功能数字!"); } printf(" "); } while(i>0||i<8); return 0; }
课题二
一、 目的
二叉树的遍历算法实现
二、 实习环境
个人计算机,Windows操作系统,Visual C++6.0编译开发环境
三、 实习内容、步骤与要求
遍历是对树的一种最基本的运算,所谓遍历二叉树,就是按一定的规则和顺序走遍二叉树的所有结点,使每一个结点都被访问一次,而且只被访问一次。由于二叉树是非线性结构,因此,树的遍历实质上是将二叉树的各个结点转换成为一个线性序列来表示。
递归算法的算法实现:
先序遍历:
若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
(1) 访问根结点;(2) 遍历左子树;(3) 遍历右子树。
中序遍历:
若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
(1)遍历左子树; (2)访问根结点;(3)遍历右子树。
后序遍历:
若二叉树非空,则依次执行如下操作:
(1)遍历左子树;(2)遍历右子树;(3)访问根结点。
非递归算法的实现:
中序遍历:
对于任一结点P,
1)若其左孩子不为空,则将P入栈并将P的左孩子置为当前的P,然后对当前结点P再进行相同的处理;
2)若其左孩子为空,则取栈顶元素并进行出栈操作,访问该栈顶结点,然后将当前的P置为栈顶结点的右孩子;
3)直到P为NULL并且栈为空则遍历结束
后序遍历:
要保证根结点在左孩子和右孩子访问之后才能访问,因此对于任一结点P,先将其入栈。
1) 如果P不存在左孩子和右孩子,则可以直接访问它;或者P存在左孩子或者右孩子,但是其左孩子和右孩子都已被访问过了,则同样可以直接访问该结点。
2) 若非上述两种情况,则将P的右孩子和左孩子依次入栈,这样就保证了每次取栈顶元素的时候,左孩子在右孩子前面被访问,左孩子和右孩子都在根结点前面被访问。
四:源程序:
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAX 50
#define MAS 20
#define CHAR 1
typedef char elem;
//定义二叉树的数据结构
typedef struct node{
elem data;//二叉树的值
struct node *lchild; //左孩子
struct node *rchild;//右孩子
struct node *parent;//父节点
}BinTNode,*BinTree;
//定义二叉树的初始化函数
BinTNode *Init_BinTree(BinTNode *tree){
tree=NULL; //将NULL赋值给tree
return tree; //返回tree
}
//创建二叉树
BinTNode *Create_BinTree(BinTNode *tree){
elem ch;
scanf("%c",&ch); //将键入值赋给二叉树的节点
if(ch==' ') // 以空格作为空左孩子和空右孩子的表示
tree=NULL;
else{ //申请空间,以及通过对左右孩子的递归完成二叉树的创建
tree=(BinTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BinTNode));
if(!tree)
exit(0);
tree->data=ch;
tree->parent=NULL;
tree->lchild=Create_BinTree(tree->lchild);
if(tree->lchild)
tree->lchild->parent=tree;
tree->rchild=Create_BinTree(tree->rchild);
if(tree->rchild)
tree->rchild->parent=tree;
}
return tree;//返回tree
}
//在屏幕上输出创建的二叉树,采用递归算法
void PrintTree(BinTNode *tree,int i){
if(tree!=NULL){ //采用条件编译对CHAR事先进行编译
PrintTree(tree->rchild,i+5);
#if CHAR
if(tree->data!=' ')
printf("%*c ",i,tree->data);
#else
if(tree->data!=' ')
printf("%*d ",i,tree->data);
#endif
PrintTree(tree->lchild,i+5);
i=i-5;
}
}
/*先序遍历(递归)*/
void Pre_Order(BinTNode *tree){
if(tree!=NULL){
printf("%c"" ",tree->data);
Pre_Order(tree->lchild);
Pre_Order(tree->rchild);
}
}
/*中序遍历(递归)*/
void In_Order(BinTNode *tree){
if(tree!=NULL){
In_Order(tree->lchild);
printf("%c"" ",tree->data);
In_Order(tree->rchild);
}
}
//中序遍历(非递归),利用栈结构存储数据
void In_OrderX(BinTNode *tree,void(*visit)(elem)){
BinTNode *p,*stack[MAS];
int top;
top=0; p=tree;
while(top!=0||p!=NULL){
while(p!=NULL){
stack[top]=p; top++;
p=p->lchild;
}
if(top!=0){
p=stack[top-1];
top--;
visit(p->data);
p=p->rchild;
}
}
}
/*后序遍历(递归)*/
void Bac_Order(BinTNode *tree){
if(tree!=NULL){
Bac_Order(tree->lchild);
Bac_Order(tree->rchild);
printf("%c"" ",tree->data);
}
}
/*后序遍历(非递归),利用栈结构存储数据 */
void Bac_OrderX(BinTNode *tree,void(*visit)(elem)){
BinTNode *p,*stack[MAS];
int top;
top=0;
stack[top]=tree; top++;
while(top>0){
p=stack[top-1];
top--;
while(p!=NULL){
visit(p->data);
stack[top]=p->rchild;
top++;
p=p->lchild;
}
}
}
void visit(elem e){
printf("%c"" ",e);
}
int main()
{
int i;
BinTree tree;
tree=Init_BinTree(tree);
#if CHAR
printf("请先序输入二叉树(如:abc d e ):");
#else
printf("请先序输入二叉树(如:a b 表示a为根结点,b为左子树的二叉树) ");
#endif
tree=Create_BinTree(tree);
printf("输入建立的二叉树!!! ");
PrintTree(tree,5);
do{
printf("------------------------------------------------------------");
printf(" 主菜单:");
printf(" 1 先序遍历(递归)");
printf(" 2 中序遍历(递归)");
printf(" 3 中序遍历(非递归)");
printf(" 4 后序遍历(递归)");
printf(" 5 后序遍历(非递归)");
// printf(" 6 ");
printf(" 0 退出");
printf(" ----------------------------------------------------------");
printf(" ");
printf("亲,请输入功能数字:");
scanf("%d",&i);
switch(i){
case 1: printf("先序遍历(递归)结果为:");
Pre_Order(tree); break;
case 2: printf("中序遍历(递归)结果为:");
In_Order(tree); break;
case 3: printf("中序遍历(非递归)结果为:");
In_OrderX(tree,visit) ; break;
case 4: printf("后序遍历(递归)结果为:");
Bac_Order(tree); break;
case 5: printf("后序遍历(非递归)结果为:");
Bac_Order(tree,visit); break;
case 0: exit(0);
default :printf("亲,请输入--菜单--中的功能数字!");
}
printf(" ");
}
while(i>0||i<8);
return 0;
}