一.文件输入输出流
程序运行期间,大部分数据都是在内存中进行操作,当程序结束或关闭时,这些数据将消失。如果需要将数据永久保存,可使用文件输入输出流与指定的文件建立连接,将需要的数据永久保存到文件中。
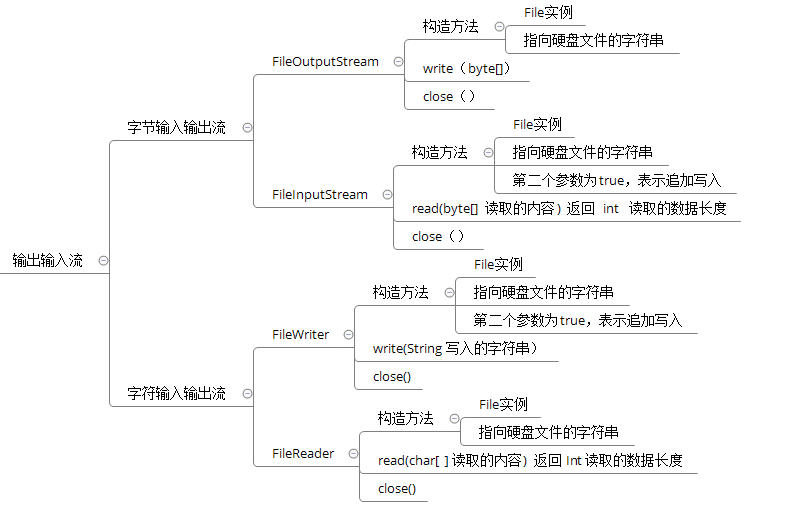
1.字节输入输出流
FileInputStream类与FileOutputStream类都是用来操作磁盘文件的。如果用户的文件读取需求比较简单,则可以使用FileInputStream类。该类继承自InputStream类。 FileInputStream类与FileOutputStream类对应,提供了基本的文件写入能力。FileOutputStream类是OutputStream类的子类。
FileInputStream类常用的构造方法如下:
FileInputStream(String name)
FileInputStream(File file)
第一个构造方法使用给定的文件名name创建—个FileInputStream对象,第二个构造方法使用File对象创建FileInputStream对象。第一个构造方法比较简单,但第二个构造方法允许在把文件连接输入流之前对文件作进一步分析。
FileInputStream类与FileOutputStream类相同参数的构造方法,创建一个FileOutputStream对象时,可以指定不存在的文件名,但此文件不能是—个已被其他程序打开的文件。
注意:虽然Java语言在程序结束时自动关闭所有打开的流,但是当使用完流后,显式地关闭任何打开的流仍是一个好习惯。一个被打开的流有可能会用尽系统资源,这取决于平台和实现。如果没有将打开的流关闭,当另一个程序试图打开另一个流时,这些资源可能会得不到。
FileInputStream类与FileOutputStream类方法代码:
(1)
 FileOutputStream与FileInputStream
FileOutputStream与FileInputStream
 覆盖与true 追加写入
覆盖与true 追加写入

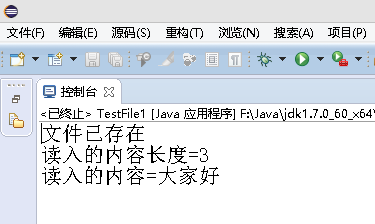
1 package org.hanqi.ex; 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 5 public class TestFile1 { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 10 File f1=new File("d:\test.txt"); 11 12 if(f1.exists()) 13 { 14 System.out.println("文件已存在"); 15 16 //输入输出 17 try 18 { 19 //从内存向硬盘上的文件输出文字 20 21 //构造方法 1.传入File的实例 2.传入文件名 22 FileOutputStream fo=new FileOutputStream(f1); 23 24 String str ="大家好"; 25 26 //以字节数组的形式写入 27 byte[] b=str.getBytes(); 28 29 fo.write(b);//导入 30 31 fo.close();//关闭输出流,释放文件 32 33 34 //从硬盘文件读入文字 35 36 37 //构造方法,指明从哪个文件读入 38 FileInputStream fi=new FileInputStream(f1); 39 40 41 //用来装载读入的数据,实现指定一个默认大小 42 byte[] c=new byte[1024]; 43 44 45 //返回值表示读入数据的长度 46 //传入引用类型 47 int i=fi.read(c); 48 49 //转换指定位数的字符串 50 String str1=new String(c,0,i); 51 52 System.out.println("读入的内容长度="+str1.length()); 53 54 System.out.println("读入的内容="+str1); 55 56 fi.close(); 57 58 } 59 catch (FileNotFoundException e) 60 { 61 System.out.println("要输出的文件不存在"); 62 63 e.printStackTrace(); 64 } catch (IOException e) { 65 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 66 e.printStackTrace(); 67 } 68 69 } 70 else 71 { 72 try 73 { 74 if(f1.createNewFile()) 75 { 76 System.err.println("文件创建成功"); 77 } 78 } 79 catch (IOException e) 80 { 81 e.printStackTrace(); 82 } 83 } 84 85 } 86 87 }
(2)

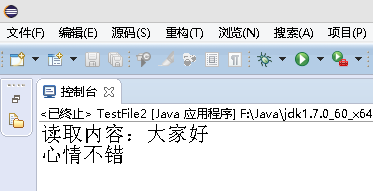
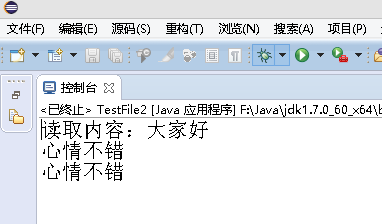
1 package org.hanqi.ex; 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 5 public class TestFile2 { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 10 try 11 { 12 //覆盖写入 13 //true 追加写入 14 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("d:\test.txt",true); 15 16 String str=" 心情不错"; 17 18 fos.write(str.getBytes());//覆盖写入 19 20 //追加写入 21 22 fos.close(); 23 24 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("d:\test.txt"); 25 26 byte[] b=new byte[200]; 27 28 int i=fis.read(b); 29 30 String str1=new String(b,0,i); 31 32 System.out.println("读取内容:"+str1); 33 34 35 } 36 catch (Exception e) 37 { 38 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 42 } 43 44 }
2.字符输入输出流
使用FileOutputStream类向文件中写入数据与使用FileInputStream类从文件中将内容读出来,存在一点不足,即这两个类都只提供了对字节或字节数组的读取方法。由于汉字在文件中占用两个字节,如果使用字节流,读取不好可能会出现乱码现象。此时采用字符流FileReader或FileWriter类即可避免这种现象。
FileReader、FileWriter字符流对应了FileInputStream、FileOutputStream。FileReader流顺序地读取文件,只要不关闭流。每次调用read()方法就顺序地读取源中其余的内容,直到源的末尾或流被关闭。
FileReader与FileWriter类代码:

1 package org.hanqi.ex; 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 5 public class TestFile3 { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 try 10 { 11 FileReader fr=new FileReader("d:\test.txt"); 12 13 char[] c=new char[200]; 14 15 int i=fr.read(c); 16 17 String str=new String(c,0,i); 18 19 System.out.println("读取:"+str); 20 21 fr.close(); 22 23 //写入 24 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("d:\test.txt",true); 25 26 fw.write(" 新追加的内容"); 27 28 fw.close(); 29 } 30 catch (Exception e) 31 { 32 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } 35 36 37 38 } 39 40 }

小结: