今天看到看到一篇MSDN文章《Parallelizing Operations With Dependencies》,作者是微软Parallel Computing Platform团队的一个开发经理。文中提供出一种用于并行执行一组具有依赖关系的操作的解决方案,这不由得想起我在一年之前写的一个具有相同的功能的组件。于是翻箱倒柜找了出来,进行了一些加工,与大家分享一下。
一、问题分析
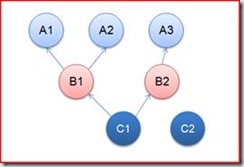
我们知道,较之串行化的操作,并行计算将多个任务同时执行,从而充分利用了资源,提高了应用的整体性能。对于多个互不相干的操作,我们可以直接按照异步的方式执行就可以。但是,我们遇到的很多情况下是,部分操作之间具有相互依赖的关系,一个操作需要在其他依赖的操作执行完成后方可执行。 以下图为例,每一个圆圈代表要执行的操作,操作之间的肩头代表它们之间的依赖关系。
我们需要一个组件,帮助我们完成这样的工作:将相应的操作和依赖关系直接添加到一个容器中,我们的组件能够自动分析操作之间的依赖关系,在执行的时候根据依赖编排执行顺序。
二、采用并行操作执行器
使用我所提供的这样一个并行操作执行器(ParallelExecutor),可以帮我们解决这个问题。首先对操作本身进行抽象,用以下三个属性来描述一个并行计算场景中的操作:
- Operation ID: 操作的唯一标识,字符类型
- Action:操作具体执行的功能,使用Action代理表示
- Depedencies:依赖操作列表
在使用ParallelExecutor对操作进行并行执行之前,我们需要通过ParallelExecutor的两个AddOperation方法添加需要执行的操作。AddOperation定义如下。其中dependencies代表以来操作ID数组,返回值为当前创建的操作ID。
1: public class ParallelExecutor
2: { 3: 4: public string AddOperation(string id, Action action)
5: {6: //省略实现
7: } 8: 9: public string AddOperation(string id, Action action, string[] dependencies)
10: {11: //省略实现
12: } 13: } 14: 对于上图中的操作的依赖结构,我们通过下面的代码将所有的操作添加到创建的ParallelExecutor之中并执行。在这里的具体实现的操作仅仅是打印出操作的ID,以便我们清楚地知道操作执行的先后顺序是否满足依赖关系:
1: static void Main(string[] args)
2: {3: Action<string> action = id=> {Console.WriteLine(id);};
4: 5: var executor = new ParallelExecutor();
6: var a1 = executor.AddOperation("A1", () => action("A1"));
7: var a2 = executor.AddOperation("A2", () => action("A2"));
8: var a3 = executor.AddOperation("A3", () => action("A3"));
9: 10: var b1 = executor.AddOperation("B1", () => action("B1"), new string[] { a1, a2 });
11: var b2 = executor.AddOperation("B2", () => action("B2"), new string[] { a3 });
12: 13: var c1 = executor.AddOperation("C1", () => action("C1"), new string[] { b1,b2 });
14: var c2 = executor.AddOperation("C2", () => action("C2"));
15: 16: executor.Execute(); 17: Console.Read(); 18: } 19: 由于是操作的并行执行,线程调度的不确定性使每次输出的结果各有不同。但是无论如何,需要满足上图中展现的依赖关系。下面是其中一种执行结果,可以看出这是合理的执行顺序。
1: A3 2: B2 3: A1 4: A2 5: C2 6: B1 7: C1三、操作是如何被执行的
实现这样的并行计算有很多种解决方案。不同的解决方案大都体现在对于单一的操作该如何执行上。在我们提供这个解决方案中,我按照这样的方案来执行任意一个操作:
直接执行无依赖的操作
如果需要执行的操作并不依赖于任何一个操作(比如C2),那么我们直接运行就好了,这没有什么好说的。
先执行依赖操作,通过注册事件的方式执行被依赖的操作
如果一个操作依赖于一组操作,在执行之前注册依赖操作的结束事件实现,被依赖操作的执行发生在某个一个依赖操作的Completed事件触发后。具体来讲,上图中C1具有两个以来操作B1和B2,在初始化时,C1上会有一个用于计算尚未执行的依赖操作的个数,并注册B1和B2得操作结束事件上面。当B1和B2执行结束后,会触发该事件。每次事件触发,C1上的计数器将会减1,如果计数器为0,则表明所有的依赖操作执行结束,则执行C1相应的操作。
四、具体实现
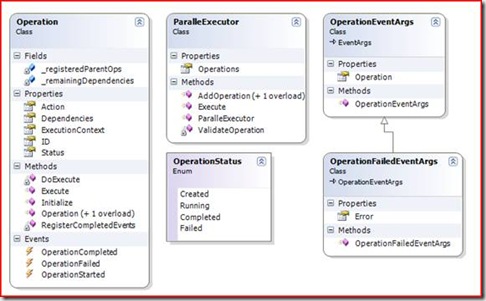
现在我们来看看详细设计和具体实现。首先通过下面的类图看看涉及到的所有类型。其中Operation类型是最为重要的一个类型,它代表一个具体的操作。
操作的属性
一个操作具有如下属性:
- ID:String类型,操作的唯一标识
- Action:Action类型,操作具体是实现的功能
- Dependencies:Operation数组,依赖的操作
- Status:Operation枚举,操作当前的状态
- ExecutionContext:ExecutionContext类型,用于传递线程执行的上下文
1: public class Operation
2: { 3: //其他成员
4: public string ID
5: { get; private set; }
6: 7: public Action Action
8: { get; private set; }
9: 10: public Operation[] Dependencies
11: { get; private set; }
12: 13: public OperationStatus Status
14: { get; private set; }
15: 16: public ExecutionContext ExecutionContext
17: { get; private set; }
18: 19: public Operation(string id, Action action)
20: {21: if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(id))
22: {23: throw new ArgumentNullException("id");
24: } 25: 26: if (null == action)
27: {28: throw new ArgumentNullException("action");
29: }30: this.Status = OperationStatus.Created;
31: this.ID = id;
32: this.Action = action;
33: this.Dependencies = new Operation[0];
34: } 35: 36: public Operation(string id, Action action, Operation[] dependencies)
37: : this(id, action)
38: {39: if (null == dependencies)
40: {41: throw new ArgumentNullException("dependencies");
42: } 43: 44: this.Dependencies = dependencies;
45: } 46: } 47: 操作事件
当前操作执行的状态通过OperationStatus表示,四个枚举值分别表示被创建、正在运行、运行结束和失败(抛出异常)。
1: public enum OperationStatus
2: { 3: Created, 4: Running, 5: Completed, 6: Failed 7: }操作还具有三个时间,分别在开始执行、结束执行和执行失败时触发。这三个事件名称分别为OperationStarted、OperationCompleted和OperationFailed。
1: public class Operation
2: {3: //其他成员
4: public event EventHandler<OperationEventArgs> OperationStarted;
5: public event EventHandler<OperationFailedEventArgs> OperationFailed;
6: public event EventHandler<OperationEventArgs> OperationCompleted;
7: } 8: OperationStarted和OperationCompleted事件对应的参数类型为OperationEventArgs。OperationEventArgs直接继承自EventArgs,并定义了一个Operation属性代表对应的Operation对象。
1: public class OperationEventArgs : EventArgs
2: {3: public OperationEventArgs(Operation operation)
4: {5: if (null == operation)
6: {7: throw new ArgumentNullException("operation");
8: } 9: 10: this.Operation = operation;
11: } 12: 13: public Operation Operation
14: { get; private set; }
15: } 16: OperationFailed的事件参数类型为OperationFailedEventArgs。继承自OperationEventArgs,在此基础上添加了一个Exception类型的Error属性,表示抛出的异常。
操作初始化和事件注册
在第三节中已经谈到过了,被依赖操作的执行通过的依赖操作执行完成后触发OperationCompleted事件的是实现。事件注册必须在ParallelExecutor执行之前完成,在这里我定义了一个Initialize方法,在里面完成事件注册工作:
1: public class Operation
2: {3: //其他成员
4: private int _remainingDependencies;
5: private List<Operation> _registeredParentOps = new List<Operation>();
6: 7: private static void RegisterCompletedEvents(Operation operation)
8: { 9: operation._remainingDependencies = operation.Dependencies.Length;10: foreach (var op in operation.Dependencies)
11: {12: if (op._registeredParentOps.Contains(operation))
13: {14: continue;
15: } 16: RegisterCompletedEvents(op); 17: op.OperationCompleted += (sender, args) => 18: { 19: operation._remainingDependencies--;20: if (operation._remainingDependencies <= 0)
21: { 22: operation.DoExecute(); 23: } 24: }; 25: op._registeredParentOps.Add(operation); 26: } 27: } 28: 29: public void Initialize()
30: {31: RegisterCompletedEvents(this);
32: } 33: }操作执行
ParallelExecutor通过调用Operation的Execute方法执行相应的操作。在Execute方法中,如果是独立的操作,则执行执行,否则异步执行依赖操作,这是一个递归的过程。操作的具体实现定义在DoExecute方法中。
1: public class Operation
2: { 3: //其他成员
4: private void DoExecute()
5: {6: if (this.Status != OperationStatus.Created)
7: {8: return;
9: } 10: 11: if (null != this.OperationStarted)
12: {13: this.OperationStarted(this, new OperationEventArgs(this));
14: } 15: 16: this.Status = OperationStatus.Running;
17: try
18: {19: if (null != this.ExecutionContext)
20: {21: ExecutionContext.Run(this.ExecutionContext.CreateCopy(), state => this.Action(), null);
22: }23: else
24: {25: this.Action();
26: } 27: 28: this.Status = OperationStatus.Completed;
29: if (null != this.OperationCompleted)
30: {31: this.OperationCompleted(this, new OperationEventArgs(this));
32: } 33: }34: catch (Exception ex)
35: {36: this.Status = OperationStatus.Failed;
37: if (null != this.OperationFailed)
38: {39: this.OperationFailed(this, new OperationFailedEventArgs(this, ex));
40: } 41: } 42: } 43: 44: [MethodImplAttribute(MethodImplOptions.Synchronized)]45: public void Execute()
46: {47: if (this.Dependencies.Length == 0)
48: {49: this.DoExecute();
50: } 51: 52: foreach (var operation in this.Dependencies)
53: { 54: var op = operation;55: ThreadPool.UnsafeQueueUserWorkItem(state => op.Execute(), null);
56: } 57: 58: } 59: } 60: ParallelExecutor
ParallelExecutor提供操作的添加和整体执行。添加操作实现在两个重载的AddOperation方法中,逻辑并不复杂。当执行Execute方法对所有的操作进行并行执行的时候,需要调用Initialize方法对每个操作进行初始化。然后异步调用每个操作的Execute方法即可。
1: public class ParallelExecutor
2: {3: public ParallelExecutor()
4: {5: this.Operations = new Dictionary<string, Operation>();
6: } 7: 8: public IDictionary<string, Operation> Operations
9: { get; private set; }
10: 11: public void Execute()
12: {13: foreach (var operation in this.Operations.Values)
14: { 15: operation.Initialize(); 16: } 17: 18: foreach (var operation in this.Operations.Values)
19: { 20: var op = operation;21: ThreadPool.UnsafeQueueUserWorkItem(state => op.Execute(), null);
22: } 23: } 24: 25: public string AddOperation(string id, Action action)
26: { 27: ValidateOperation(id, action);28: this.Operations.Add(id, new Operation(id, action));
29: return id;
30: } 31: 32: private void ValidateOperation(string id, Action action)
33: {34: if (null == action)
35: {36: throw new ArgumentNullException("action");
37: } 38: 39: if (this.Operations.ContainsKey(id))
40: {41: throw new ArgumentException(string.Format("There is an existing operation whose ID is \"{0}\"", id));
42: } 43: } 44: 45: public string AddOperation(string id, Action action, string[] dependencies)
46: { 47: ValidateOperation(id, action);48: if (null == dependencies)
49: {50: throw new ArgumentNullException("dependencies");
51: } 52: 53: foreach (var op in dependencies)
54: {55: if (!this.Operations.ContainsKey(op))
56: {57: throw new ArgumentException(string.Format("The operation whose ID is \"{0}\" does not exist!", op));
58: } 59: } 60: 61: var operation = new Operation(id, action,
62: this.Operations.Values.
63: Where(op => Array.Exists<string>(dependencies, opId => opId == op.ID)).ToArray<Operation>());
64: 65: this.Operations.Add(id, operation);
66: return id;
67: } 68: } 69: 出处:http://artech.cnblogs.com
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。