研究对象:MOT中的数据关联算法,包括基于IOU的贪婪匹配、基于匈牙利和KM算法的线性偶图匹配、基于图论的离线数据关联。
1 Background
目前主流的MOT框架是DBT框架,这种框架的特点就是离不开数据关联算法,不论是对不同帧之间跟踪轨迹的关联还是跟踪轨迹和观测量的关联, 有数据关联才能更好的保证目标ID的连续性。
不得不说IOU Tracker和他的改进版V-IOU Tracker算是多目标跟踪算法中的一股清流,方法特别简单粗暴,对于检测质量很好的场景效果比较好。首先我们交代一下IOU的度量方式:

IOU Tracker的跟踪方式没有跟踪,只有数据关联,关联指标就是IOU,关联算法就是一种基于IOU的贪婪匹配算法:

这里留到下一节讲,作者会利用不同的贪婪方式进行IOU匹配。那么V-IOU的改进就是:由于IOU Tracker仅仅是对观测量进行了关联,当目标丢失或者检测不到的时候,便无法重建轨迹,因此V-IOU加入了KCF单目标跟踪器来弥补这一漏洞,也很粗暴。
2.2 IOU Matching基于贪婪算法的数据关联的核心思想就是,不考虑整体最优,只考虑个体最优。这里作者设计了两种贪婪方式,第一种Local IOU Matching,即依次为每条跟踪轨迹分配观测量,只要IOU满足条件即可,流程如下:

IOU Tracker就是采用的这种局部贪心方式,这种贪心策略的特点是每次为当前跟踪轨迹选择与之IOU最大的观测量。那么我们再提出一种全局的贪婪策略,即每次选择所有关联信息中IOU最大的匹配对,流程如下:

两种贪婪方式的代码如下:
def GreedyAssignment(cost, threshold = None, method = 'global'): """Using iou matching to make linear assignment Parameters ---------- cost : ndarray A NxM matrix for costs between each track_ids with dection_ids threshold: float if cost > threshold, then will not be considered method: str eg: global, local Returns ------- row_idx: List of matched tracks (<=N,) assigned tracklets' id col_idx: List of matched dets (<=M,) assigned dets' id unmatched_rows: List of unmatched tracks unassigned tracklets' id unmatched_cols: List of unmatched dets unassigned dets' id """ cost_c = np.atleast_2d(cost) sz = cost_c.shape if threshold is None: threshold = 1.0 row_idx = [] col_idx = [] if method == 'global': vector_in = list(range(sz[0])) vector_out = list(range(sz[1])) while min(len(vector_in), len(vector_out)) > 0: v = cost_c[np.ix_(vector_in, vector_out)] min_cost = np.min(v) if min_cost <= threshold: place = np.where(v == min_cost) row_idx.append(vector_in[place[0][0]]) col_idx.append(vector_out[place[1][0]]) del vector_in[place[0][0]] del vector_out[place[1][0]] else: break else: vector_in = [] vector_out = list(range(sz[1])) index = 0 while min(sz[0] - len(vector_in), len(vector_out)) > 0: if index >= sz[0]: break place = np.argmin(cost_c[np.ix_([index], vector_out)]) if cost_c[index, vector_out[place]] <= threshold: row_idx.append(index) col_idx.append(vector_out[place]) del vector_out[place] else: vector_in.append(index) index += 1 vector_in += list(range(index, sz[0])) return np.array(row_idx), np.array(col_idx), np.array(vector_in), np.array(vector_out)
可以看到跟踪效果并不是很差,那么我们观察二者定量的结果则为:
Local: MOTA=0.77, IDF1=0.83
Global: MOTA=0.79, IDF1=0.88
相比之下全局的贪心策略比局部的要好。
3 线性匹配
3.1 匈牙利算法和KM算法
线性分配问题也叫指派问题,通常的线性分配任务是给定N个workers和N个tasks,结合相应的N×N的代价矩阵,就能得到匹配组合。其模型如下:
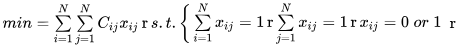
上述模型有个问题,即要求workers和tasks的数量对等,然而在MOT问题中待匹配的跟踪轨迹和检测数量大概率不相同,而且我们经常还会设定阈值来限制匹配。
匈牙利算法是专门用来求解指派问题的算法,并且通常用于求解二分图最大匹配的。也就是说我们需要先利用规则判断边是否连接,然后匹配,因此不会出现非边节点存在匹配,只有可能出现剩余未匹配:

匈牙利算法的问题在于一旦确定边之后就没有相对优劣了,所以我们这里介绍带权二分图匹配KM,顾名思义,就是求最小代价,只不过是不对等匹配:

这里我们可以看到有一个维度的和要求是1,原因就是必须要保证有一个维度满分配,不然就会直接不建立连接了。
3.2 实验对比
借用scipy工具箱实现:
inf_cost = 1e+5 def LinearAssignment(cost, threshold = None, method = 'KM'): """Using Hungarian or KM algorithm to make linear assignment Parameters ---------- cost : ndarray A NxM matrix for costs between each track_ids with dection_ids threshold: float if cost > threshold, then will not be considered method : str 'KM': weighted assignment 'Hungarian': 01 assignment Returns ------- row_idx: List of matched tracks (<=N,) assigned tracklets' id col_idx: List of matched dets (<=M,) assigned dets' id unmatched_rows: List of unmatched tracks unassigned tracklets' id unmatched_cols: List of unmatched dets unassigned dets' id min_cost: float cost of assignments """ cost_c = deepcopy(np.atleast_2d(cost)) sz = cost_c.shape if threshold is not None: cost_c = np.where(cost_c > threshold, inf_cost, cost_c) if method == 'Hungarian': t = threshold if threshold is not None else inf_cost cost_c = np.where(cost_c < t, 0, cost_c) # linear assignment row_ind, col_ind = linear_sum_assignment(cost_c) if threshold is not None: t = inf_cost - 1 if threshold == inf_cost else threshold mask = cost_c[row_ind, col_ind] <= t row_idx = row_ind[mask] col_idx = col_ind[mask] else: row_idx, col_idx = row_ind, col_ind unmatched_rows = np.array(list(set(range(sz[0])) - set(row_idx))) unmatched_cols = np.array(list(set(range(sz[1])) - set(col_idx))) min_cost = cost[row_idx, col_idx].sum() return row_idx, col_idx, np.sort(unmatched_rows), np.sort(unmatched_cols), min_cost
同样地,为了更好地对比,我们以IOU为代价指标,分别以匈牙利算法和KM算法为数据关联算法进行实验,有意思的是对于MOT-04-SDP视频而言,二者并没有太大区别,整体效果跟Global IOU Assignment一致。
完整代码参见:https://github.com/nightmaredimple/libmot作者:黄飘
链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/111114497
来源:知乎