一、隐式
implicit分类: (1)隐式参数 (2)隐式转换类型 (3)隐式类 特点:让代码变得更加灵活
(一)隐式参数
1、ImplicitTest
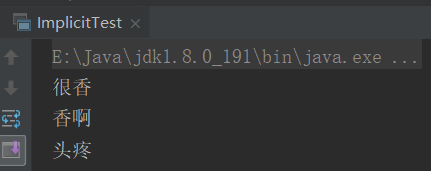
object ImplicitTest { //此参数 def sleep(how:String):Unit = {println(how)} //此参数如果被implicit修饰的话,调用可以不写参数 直接sleep2 def sleep2(implicit how:String = "香啊") = {println(how)} def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { sleep("很香") sleep2 implicit val how = "头疼" sleep2 } }
结果:
2、ImplicitTest1
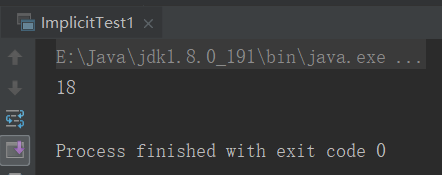
//隐式转换类型 object ImplicitTest1 { //类型转换 implicit def double2Int(d:Double) = {d.toInt} def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val a:Int = 18.8 println(a) } }
结果:
3、KelihuaImplicit
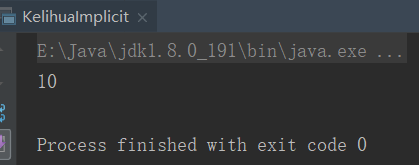
object KelihuaImplicit { //柯理化 def sum(a:Int)(implicit b:Int) = {a + b} def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //定义隐式值 implicit val b = 9 println(sum(1)) } }
结果:
(二)隐式转换类型
4、FileMain
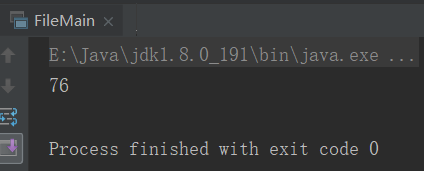
import java.io.File //扫描文件的数据条数 object FileMain { //定义隐式转换 implicit def file2RichFile(file:File) = new RichFile(file) def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //1.加载文件 val file = new File("e:/weblog.log") //2.打印条数 println(file.count()) } }
5、RichFile
import java.io.{BufferedReader, File, FileReader} class RichFile(file:File) { def count():Int = { //读取数据 val fileReader = new FileReader(file) val bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader) //计数器 var sum = 0 try { while (bufferedReader.readLine() != null){ sum += 1 } } catch { case _:Exception => sum } finally { bufferedReader.close() fileReader.close() } sum } }
结果:
(三)隐式类
6、ReadImplicit
import scala.io.Source object ReadImplicit { //定义隐式类 implicit class FileRead(file:File){ //读取文件 def read = Source.fromFile(file).mkString } def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val file = new File("e:/weblog.log") println(file.read) } }
结果:

二、泛型
type
如何定义scala中的泛型?
1、Anything
//加入泛型 T代表任意类型 abstract class Anything[T](m:T)
2、Intthing
class Intthing[Int](m:Int) extends Anything(m) { }
3、Stringthing
class Stringthing[String](m:String) extends Anything { }
4、Person
class Person[A,B,C](val age:A,val high:B,val face:C) { }
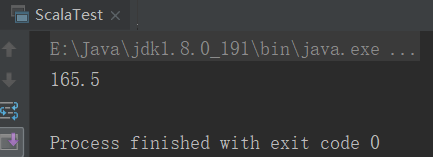
5、ScalaTest
object ScalaTest { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val p = new Person[Int,Double,Double](18,165.5,99) println(p.high) } }
结果:
三、类型约束
java中Comparable Scala中的比较的特质: Ordered 上界(upper Bounds) <T extends Person>表示T类型是Person的子类型 <? extends Person> [T <: Person]此时T是Person的子类,这种形式是上界 [_ <: Person] def pr(list:List[_<:Any]){ list.foreach(print) } 下界(lower Bounds) <T super Person> <? super Person> [T >: Person] [_ >: Person] 视图界定(View Bounds) <% 视图界定发生了隐式转换 上下文界定 comparator scala->ordering 上下文界定发生了隐式转换
(一)java中Comparable
1、Person1
public class Person1 implements Comparable<Person1>{ //定义属性 private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Person1(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public int compareTo(Person1 o) { //升序 return this.age - o.age; } }
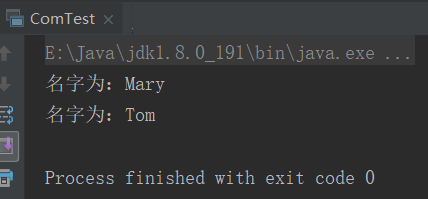
2、ComTest
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; public class ComTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { Person1 p1 = new Person1("Tom",18); Person1 p2 = new Person1("Mary",16); List<Person1> person = new ArrayList<Person1>(); person.add(p1); person.add(p2); Collections.sort(person); for (Person1 p : person) { System.out.println("名字为:" + p.getName()); } } }
结果:
(二)Scala中类型约束
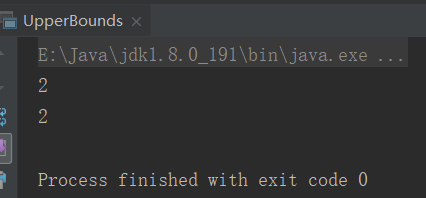
1、上届UpperBounds
//定义一个比较的方式 class CompareInt(a:Int,b:Int){ def compare = if(a > b) a else b } //定义比较类型 class CompareC[T <: Comparable[T]](o1:T,o2:T){ def compare = if(o1.compareTo(o2) > 0) o1 else o2 } object UpperBounds { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val big = new CompareInt(1,2) System.out.println(big.compare) val comc = new CompareC(Integer.valueOf(1),Integer.valueOf(2)) System.out.println(comc.compare) } }
结果:
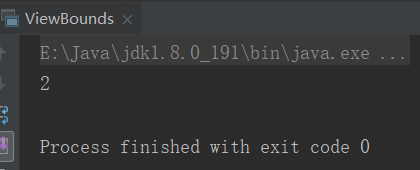
2、视图界定ViewsBounds
//视图界定 class CompareCC[T <% Comparable[T]](o1:T,o2:T){ def big = if(o1.compareTo(o2) > 0) o1 else o2 } object ViewBounds { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //视图界定发生了隐式转换 val comc = new CompareCC(1,2) println(comc.big) } }
结果:
3、上下文界定ContextBounds
class Compp[T:Ordering](o1:T,o2:T)(implicit comt:Ordering[T]){ def big = if(comt.compare(o1,o2) > 0) o1 else o2 } class Personss(val name:String,val age:Int){ override def toString: String = this.name + "," + this.age } //上下文界定 同样发生了隐式转换 object ContextBounds { //比较器定义 比较规则 implicit val comparatorPersonss = new Ordering[Personss]{ override def compare(x: Personss, y: Personss): Int = x.age - y.age } def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val p1 = new Personss("Tom",18) val p2 = new Personss("John",15) val comc = new Compp(p1, p2) println(comc.big) } }
结果:
