css解释
<div style="color: red"> ares </div>
显示效果如下:

<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!--在头部指定好CSS样式然后,在标签里使用class="样式名应用"--> <style> .re{ color: green; } #name{ background-color: red; } /*所有span标签都会引用*/ span{ font-size: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div style="color: red"> ares </div> <span class="re"> <!--这里应用指定好的CSS样式名即可--> ares ares </span> <div style="color: red" id="name"> aresaresares </div> </body>
显示效果如下:

CSS的外部引用
写一个独立的文件存储css样式代码如下:

html代码如下:
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>ares</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="common.css"> <!--这里通过link导入样式,有点类似与python导入模块中的import *--> </head> <body> <!--这里直接应用指定好的CSS样式名即可--> <div class="re"> ares </div> </body>
显示效果如下:

CSS样式应用中通过class应用CSS样式即可,还有两种方式代码如下:
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>ares</title> <!--在头部指定好CSS样式然后,在标签里使用class="样式名应用"--> <style> #name{ background-color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <!--这里不需要指定,只要id=name的就会自动应用头部指定的CSS样式--> <div style="color: red" id="name"> aresaresares </div> </body>
显示效果如下:

标签应用,为指定标签统一设置格式:在头部<style>p{....}</style> 这里的p是标签的名称,也可以是div这样就会给所有的div设置格式,与name类似
CSS常用属性
background 【背景】
background-color 背景颜色 代码如下:
<div style="background-color: aqua;font-size: 50px"> ares </div>
显示效果如下:

background-image 背景图片 代码如下:
<div style="background-image: url(favicon.ico);height: 80px;" >
</div>
显示效果如下:

首先确认,div是块级别的标签,我们的图片仅仅是一个小的图片,但是现在是平铺,所以看下面的代码:
<div style="background-image: url(favicon.ico);height: 80px;background-repeat: no-repeat" >
</div>
显示效果如下图:

border 【边框】
设置边框,效果图如下图:

代码如下:
<!--border:有3个参数:线的粗细、线的样式(实线、点、虚线等)、线的颜色--> <!--第一种:线的粗细为1像素,实线、红色--> <div style="border:1px solid red;height:50px" ></div> <!--第二种:线的粗细为1像素,点、蓝色--> <div style="border:1px dotted blue;height:50px" ></div> <!--第三种:线的粗细为1像素、虚线、紫色--> <div style="border:1px dashed purple;height:50px" ></div>
边框可以单独的设置一边的边框、上、下、左、右
代码如下:
<!--边框--> <div style="border-left: 30px green solid;">aresssss</div> <div style="border-right: 30px green solid;">aresssss</div>
显示效果如下:

cursor 鼠标停放所显示的效果
代码如下(鼠标停放在字体位置会变成相应形状):
<div style="cursor:pointer">停放在这里显示小手(pointer)</div>
<div style="cursor:help">停放在这里显示问号(help)</div>
<div style="cursor:wait">停放在这里显示问号(wait)</div>
<div style="cursor:move">停放在这里显示移动(move)</div>
<div style="cursor:crosshair">停放在这里显示定位(crosshair)</div>
浮动 float (用的非常多,用来布局使用)
效果图如下:

代码如下:
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>ares</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="common.css"> <style> .w-left{ width: 30%; background-color: blue; height: 100px; float: left; } .w-right{ width: 70%; background-color: green; height: 100px; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="re"> ares </div> <div> <div class="w-left"></div> <div class="w-right"></div> </div>
注:有一种情况,如果不给父div设置高度,并且设置了float之后,子的float可能会覆盖父div的颜色,解决办法是在父的div内加一条:
<div style="clear:both;"></div>
CSS选择器
标签选择器
为类型标签设置样式例如:<div>、<a>、等标签设置一个样式,代码如下:
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>ares</title> <style> /*标签选择器*/ div{ font-size: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div>ares</div> </body>
显示效果如下:

ID选择器
为指定的ID设置样式,代码如下(id选择器中ID不可以重复):
<style>
/*ID选择器*/
#i1{
background-color:red;
}
</style>
<body>
/*为所有id为i1的ID应用样式,注意咱们是为了测试,在实际的生产中ID不能相同*/
<a id="i1"> id 选择器 </a> <a id="i1"> id 选择器 </a> <a id="i2"> 如果ID不同,那么将不会应用样式 </a> </body>
效果图如下:

类选择器
class选择器,id是可以相同的,代码如下:
<style>
/*类选择器标签*/
.cls{
background-color:blue;
font-size: 15px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--任何类型的标签都可以调用类选择器-->
<div class="cls">
class test div
</div>
<a class="cls">
class test a
</a>
<span class="cls">
class test span
</span>
</body>
注:上面的3个选择器一般不要用标签&id选择器
关联选择器
<body> <style> .container li{ /*为一个标签应用了,类选择器,下的li标签设置样式*/ background-color: red; } </style> <!--下面的div应用了container类选择器,那么他下面的所有的li标签将应用上面设置的样式--> <div class="container"> <ul> <li>ares</li> <li>ares</li> <li>ares</li> </ul> </div> </body>
显示效果如下:

关联选择器:应用场景为某标签下面的标签设置指定的样式:当然可以再在每个li标签内定义class
问:如果在上面的代码基础上为li标签下的a标签设置样式怎么办呢?在li后面再加个a即可!
<style> .container li{ /*为一个标签应用了,类选择器,下的li标签设置样式*/ background-color: red; } .container li a{ background-color: green; } </style> <!--下面的div应用了container类选择器,那么他下面的所有的li标签将应用上面设置的样式--> <div class="container"> <ul> <li>ares</li> <li>ares</li> <li>ares</li> <li> <a>ares</a> </li> </ul> </div>
显示效果如下:

组合选择器
有这么一个场景,看下面的关联组合器,cc1和cc2都要使用相同的样式怎么办?重写一遍?
.container .a .cc1 {
background-color: pink;
}
.container .a .cc2 {
background-color: pink;
}
解决方法代码如下:组合选择器1
.container .a .cc1,.container .a .cc2 {
background-color: pink;
}
上面cc1后面的“逗号”就是或的关系,如果路径都是相同的话可以进行改良代码如下:
.container .a .cc1,.cc2 {
background-color: pink;
}
这里组合的时候他是按照第一个出现的逗号来进行处理的,看下面的代码:
/*组合选择器*/
.container b ,.a .cc1,.cc2 {
background-color: pink;
}
/*组合选择器分解,上面的分解完成之后谁来应用:background-color: pink;这个样式呢?*/
.container b
.container b .a .cc1
.container b .cc2
......这里需要注意,“逗号”是或的关系,一般这个不常用,常用的是上面的方法
属性选择器
写表单验证的时候最常用,举个例子来说看下面的代码:
我要在这么input下找到type为text的标签并且给他设置样式,在上面咱们知道了组合标签,但是组合选择器最小单元是标签,他不能定位到type属性
<div>
<input type="text" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="checkbox"/>
<input type="button"/>
<input type="reset"/>
</div>
怎么做呢?在组合选择器后面加个[type=“text”]即可
<style>
/*input和[之间不能有空格]*/
.con input[type="text"] {
border:3px solid red;
}
</style>
效果如下:

需求又来了,我想找到input标签为type为text并且name为“ares”的那个input标签
<div class="con">
<input type="text" />
<input type="text" name="ares"/>
<input type="password" />
<input type="file" />
<input type="checkbox"/>
<input type="button"/>
<input type="reset"/>
</div>
解决方法:在增加一个属性就行了(注意中括号之间没有空格不会报错但是没有效果),代码如下:
<style> /*input和[之间不能有空格]*/ .con input[type="text"][name="ares"] { border:3px solid red; } </style>
效果图如下:

属性标签经常用,要记住
也可以使用自定义属性来定义,并且所有的标签都可以使用自定义属性:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>shuaige</title> <style> /*input和[之间不能有空格]*/ .con input[type="text"][ares="cainiao"] { border:3px solid red; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="con"> <input type="text" /> <input type="text" ares="cainiao" /> <input type="password" /> <input type="file" /> <input type="checkbox"/> <input type="button"/> <input type="reset"/> </div> </body> </html>
background-position 图片位移
应用场景,在实际的生产环境中咱们在网页上看到的小图片不是一个一个的零散的小图片的,咱们只是看到了大图片的一部分。比如一个大图片,我只让他显示一部分并不全部显示怎么做?
可以这么想:
有一个窗口,你在窗口的一边,只能通过窗口来看外面,你不能动,我们可以通过移动这个窗口来让你看到不同的场景,当然你看到的大小和窗口的大小有关!
代码如下:
<style> .chuangkou{ /*定义一个图片*/ background-image: url('content_images.jpg'); /*定义一个窗口,指定长和宽*/ height: 30px; width:30px; /*设置图片不重复*/ background-repeat:no-repeat; background-position: 3px 10px ; } </style> <body> <div class="chuangkou"> </div> </body>
显示效果如下:

内、外边距
内边距,代码如下:
<div style="background-color: green;height: 200px;"> <div style="margin-left: auto; margin-right:auto; background-color: blue; height: 20px; 20px; "> </div> </div>
效果图如下:

要达到让蓝色在中间的效果怎么办呢?在绿色的基础上在进行填充,代码如下:
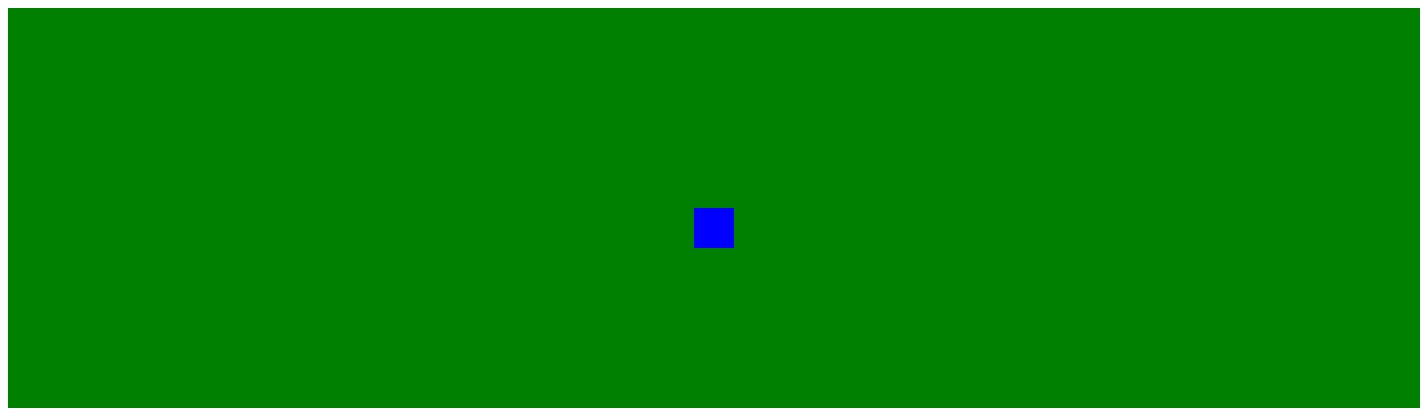 我在原有的绿色的div标签内部的顶端又填充了100px这样看起来的效果就变成蓝色的在中间了
我在原有的绿色的div标签内部的顶端又填充了100px这样看起来的效果就变成蓝色的在中间了
外边框
同样的图下面,我在蓝色的方框外面的顶部增加30px效果就向往下移动了30px
<div style="background-color: green;height: 100px;padding-top: 100px;"> <div style="margin-left: auto; margin-right:auto; background-color: blue; height: 20px; 20px; margin-top: 30px; "> </div> </div>
效果图如下:
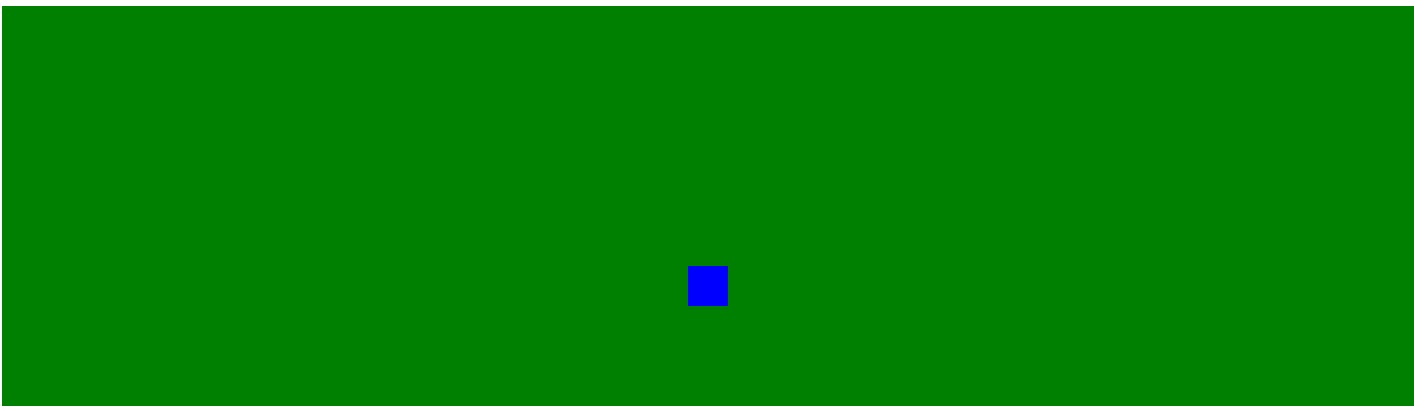
这里需要注意:使用padding会继承原有的颜色在内部填充,使用margin在外面扩张并且没有颜色
如果padding&margin不指定在上、下、左、右增加边框的话默认上下左右都添加边框!
定位position
position的四个属性值:
- static
- fixed
- relative
- absolute
1、position的默认值,一般不设置position属性时,会按照正常的文档流进行排列。
2、fixed是特殊的absolute,即fixed总是以body为定位对象的,按照浏览器的窗口进行定位。
举例,代码如下:
<body> <div style="height:2000px;background-color: blueviolet;"> <!--这里设置position:fixed 并且靠右边和底部各30px--> <a style="position: fixed;right: 30px;bottom: 30px;"> 跳转到顶部 </a> </div> </body>
3、relative
代码如下:
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>shuaige</title> <style> #sub1 { position: relative; padding: 5px; top: 5px; left: 5px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="parent"> <div style="background-color:blueviolet;" id="sub1">sub1</div> <div style="background-color:blue;" id="sub2">sub2</div> </div> </body>
显示效果如下:

注:
sub1这个div如果没有设置:position: relative会按照正常的文档位置进行定位,如果设置了,并给他设置了边距那么,他会根据他本身进行偏移,并且他的偏移不影响sub2。
4、absolute
absolute这个属性总是有人给出误导。说当position属性设为absolute后,总是按照浏览器窗口来进行定位的,这其实是错误的。实际上,这是fixed属性的特点。
当sub1的position设置为absolute后,其到底以谁为对象进行偏移呢?这里分为两种情况:
- 当sub1的父对象(或曾祖父,只要是父级对象)parent也设置了position属性,且position的属性值为absolute或者relative时,也就是说,不是默认值的情况,此时sub1按照这个parent(在父对象内)来进行定位。
- 如果sub1不存在一个有着position属性的父对象,那么那就会以body为定位对象,按照浏览器的窗口进行定位,这个比较容易理解
代码如下:
<div style="position:relative;background-color: blue;height:100px;"> <!--当sub1的父对象(或曾祖父,只要是父级对象)parent也设置了position属性--> <div style="position:absolute;right: 0px;bottom:0px;background-color: blueviolet">su1</div> </div> <div style="background-color: blueviolet;height: 2000px;"> <!--如果父对象内没有,positionabsolute或者relative时,那么会按照你打开网页时的位置进行固定,然后滑动浏览器的时候也随之变化--> <div style="position:absolute;right: 30px;bottom: 30px;"> su1 </div> </div>
样式:overflow
应用场景,有这么一种情况,在一个div内有很多的的内容,如果div的框体不是很大超出去了怎么办?详细情况如下图,代码
代码如下:
<body> <div style="height:100px;background-color:green;"> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> ares<br> </div> </body>
显示效果如下:

解决方法:增加overflow样式,代码如下:

可以看到自动加上了滚动条
还有一个样式:hidden超出div区域的将会自动隐藏
<div style="overflow:hidden;height:100px;">
透明度
透明度,用的比较多,需要注意,简单代码例子如下:
<div style="background-color:blue;height:100px;padding-top:30px"> <!--这里设置内部的div的透明度--> <div style="opacity: 0.5;background-color:pink;height:30px;margin-left: 30px;margin-right:30px;"> </div> </div>
效果图如下:

z-index
用来设置展示在浏览器中的页面的层级
CSS布局页面实例

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>shuaige</title> <style> .pg-hander { height:48px; background-color: cornflowerblue; } .pg-body .pg-left { /*往左飘*/ position:absolute; top: 50px; left: 0px; bottom: 0px; width:200px; overflow: auto; background-color: #dddddd; } .pg-body .pg-right { position: absolute; top:50px; bottom:0px; /*这里离左边是200像素,因为上面设置的宽为200px*/ left:200px; right:0px; overflow: auto; background-color: lightblue; } </style> </head> <body style="margin:0 auto"> <!--定义把整个窗体分为2大部分上,下 <!--上部分--> <div class="pg-hander"> </div> <!--下部分--> <div class="pg-body"> <!--左部分--> <div class="pg-left"> <a>menu list for Mr.心弦</a> </div> <!--右部分--> <div class="pg-right"> <div style="height:1000px"> 帅哥 </div> </div> </div> </body> </html> css布局页面实例

