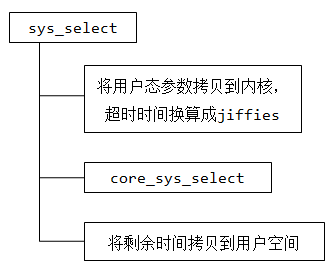
select源码结构图:

源码分析:
#undef __NFDBITS
#define __NFDBITS (8 * sizeof(unsigned long))
#undef __FD_SETSIZE
#define __FD_SETSIZE 1024
#undef __FDSET_LONGS
#define __FDSET_LONGS (__FD_SETSIZE/__NFDBITS)
typedef struct {
unsigned longfds_bits [__FDSET_LONGS]; //1024个bit。
} __kernel_fd_set;
//由上可以看到可以支持1024个描述符
//系统调用(内核态)
//参数为 maxfd, r_fds, w_fds, e_fds, timeout。
asmlinkage long sys_select(int n, fd_set __user *inp, fd_set __user *outp, fd_set __user *exp, struct timeval __user *tvp)
{
s64 timeout = -1;
struct timeval tv;
int ret;
//将超时时间换成jiffies
if (tvp) {
if (copy_from_user(&tv, tvp, sizeof(tv))) //将用户态参数拷贝到内核态
return -EFAULT;
if (tv.tv_sec < 0 || tv.tv_usec < 0)
return -EINVAL;
/* Cast to u64 to make GCC stop complaining */
if ((u64)tv.tv_sec >= (u64)MAX_INT64_SECONDS)
timeout = -1; /* infinite */
else {
timeout = ROUND_UP(tv.tv_usec, USEC_PER_SEC/HZ);
timeout += tv.tv_sec * HZ;
}
}
// (***) 调用 core_sys_select
ret = core_sys_select(n, inp, outp, exp, &timeout);
//将剩余时间拷贝回用户空间进程
if (tvp) {
struct timeval rtv;
if (current->personality & STICKY_TIMEOUTS) //判断当前环境是否支持修改超时时间(不确定)
goto sticky;
rtv.tv_usec = jiffies_to_usecs(do_div((*(u64*)&timeout), HZ));
rtv.tv_sec = timeout;
if (timeval_compare(&rtv, &tv) >= 0)
rtv = tv;
if (copy_to_user(tvp, &rtv, sizeof(rtv))) {
sticky:
/*
* 如果应用程序将timeval值放在只读存储中,
* 我们不希望在成功完成select后引发错误(修改timeval)
* 但是,因为没修改timeval,所以我们不能重启这个系统调用。
*/
if (ret == -ERESTARTNOHAND)
ret = -EINTR;
}
}
return ret;
}
//主要的工作在这个函数中完成
staticint core_sys_select(int n, fd_set __user *inp, fd_set __user *outp, fd_set __user *exp, s64 *timeout)
{
fd_set_bits fds;
/* fd_set_bits 结构如下:
typedef struct {
unsigned long *in, *out, *ex;
unsigned long *res_in, *res_out, *res_ex;
} fd_set_bits;
这个结构体中定义的全是指针,这些指针都是用来指向描述符集合的。
*/
void *bits;
int ret, max_fds;
unsigned int size;
struct fdtable *fdt;
/* Allocate small arguments on the stack to save memory and be faster 先尝试使用栈(因为栈省内存且快速)*/
long stack_fds[SELECT_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)]; // SELECT_STACK_ALLOC=256
ret = -EINVAL;
if (n < 0)
goto out_nofds;
/* max_fds can increase, so grab it once to avoid race */
rcu_read_lock(); //rcu锁
fdt = files_fdtable(current->files); //读取文件描述符表
/* struct fdtable 结构如下:
struct fdtable {
unsigned int max_fds;
struct file **fd;
...
};
*/
max_fds = fdt->max_fds; //从files结构中获取最大值(当前进程能够处理的最大文件数目)
rcu_read_unlock();
if (n > max_fds)// 如果传入的n大于当前进程最大的文件描述符,给予修正
n = max_fds;
/* 我们需要使用6倍于最大描述符的描述符个数,
* 分别是in/out/exception(参见fd_set_bits结构体),
* 并且每份有一个输入和一个输出(用于结果返回) */
size = FDS_BYTES(n);// 以一个文件描述符占一bit来计算,传递进来的这些fd_set需要用掉多少个字
bits = stack_fds;
if (size > sizeof(stack_fds) / 6) { // 除以6,因为每个文件描述符需要6个bitmaps上的位。
//栈不能满足,先前的尝试失败,只能使用kmalloc方式
/* Not enough space in on-stack array; must use kmalloc */
ret = -ENOMEM;
bits = kmalloc(6 * size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bits)
goto out_nofds;
}
//设置fds
fds.in = bits;
fds.out = bits + size;
fds.ex = bits + 2*size;
fds.res_in = bits + 3*size;
fds.res_out = bits + 4*size;
fds.res_ex = bits + 5*size;
// get_fd_set仅仅调用copy_from_user从用户空间拷贝了fd_set
if ((ret = get_fd_set(n, inp, fds.in)) ||
(ret = get_fd_set(n, outp, fds.out)) ||
(ret = get_fd_set(n, exp, fds.ex)))
goto out;
// 对这些存放返回状态的字段清0
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_in);
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_out);
zero_fd_set(n, fds.res_ex);
//执行do_select,完成监控功能
ret = do_select(n, &fds, timeout);
if (ret < 0) //有错误
goto out;
if (!ret) {// 超时返回,无设备就绪
ret = -ERESTARTNOHAND;
if (signal_pending(current))
goto out;
ret = 0;
}
if (set_fd_set(n, inp, fds.res_in) ||
set_fd_set(n, outp, fds.res_out) ||
set_fd_set(n, exp, fds.res_ex))
ret = -EFAULT;
out:
if (bits != stack_fds)
kfree(bits);
out_nofds:
return ret;
}
#define POLLIN_SET (POLLRDNORM | POLLRDBAND | POLLIN | POLLHUP | POLLERR)
#define POLLOUT_SET (POLLWRBAND | POLLWRNORM | POLLOUT | POLLERR)
#define POLLEX_SET (POLLPRI)
int do_select(int n, fd_set_bits *fds, s64 *timeout)
{
struct poll_wqueues table;
/*
struct poll_wqueues {
poll_table pt;
struct poll_table_page *table;
struct task_struct *polling_task; //保存当前调用select的用户进程struct task_struct结构体
int triggered; // 当前用户进程被唤醒后置成1,以免该进程接着进睡眠
int error; // 错误码
int inline_index; // 数组inline_entries的引用下标
struct poll_table_entry inline_entries[N_INLINE_POLL_ENTRIES];
};
*/
poll_table *wait;
int retval, i;
rcu_read_lock();
//根据已经设置好的fd位图检查用户打开的fd, 要求对应fd必须打开, 并且返回最大的fd。
retval = max_select_fd(n, fds);
rcu_read_unlock();
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
n = retval;
/* 一些重要的初始化:
poll_wqueues.poll_table.qproc函数指针初始化,
该函数是驱动程序中poll函数(fop->poll)实现中必须要调用的poll_wait()中使用的函数。 */
poll_initwait(&table);
wait = &table.pt;
if (!*timeout)
wait = NULL; // 用户设置了超时时间为0
retval = 0;
for (;;) {
unsigned long *rinp, *routp, *rexp, *inp, *outp, *exp;
long __timeout;
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
inp = fds->in; outp = fds->out; exp = fds->ex;
rinp = fds->res_in; routp = fds->res_out; rexp = fds->res_ex;
// 所有n个fd的循环
for (i = 0; i < n; ++rinp, ++routp, ++rexp) {
unsigned long in, out, ex, all_bits, bit = 1, mask, j;
unsigned long res_in = 0, res_out = 0, res_ex = 0;
const struct file_operations *f_op = NULL;
struct file *file = NULL;
// 先取出当前循环周期中的32(设long占32位)个文件描述符对应的bitmaps
in = *inp++; out = *outp++; ex = *exp++;
all_bits = in | out | ex;// 组合一下,有的fd可能只监测读,或者写,或者err,或者同时都监测
if (all_bits == 0) {
i += __NFDBITS; //如果这个字没有待查找的描述符, 跳过这个长字(32位,__NFDBITS=32),取下一个32个fd的循环中
continue;
}
// 本次32个fd的循环中有需要监测的状态存在
for (j = 0; j < __NFDBITS; ++j, ++i, bit <<= 1) {
int fput_needed;
if (i >= n)
break;
if (!(bit & all_bits)) // bit每次循环后左移一位的作用在这里,用来跳过没有状态监测的fd
continue;
file = fget_light(i, &fput_needed);//得到file结构指针,并增加引用计数字段f_count
if (file) {// 如果file存在(这个文件描述符对应的文件确实打开了)
f_op = file->f_op;
mask = DEFAULT_POLLMASK;
if (f_op && f_op->poll) //这个文件对应的驱动程序提供了poll函数(fop->poll)。
mask = (*f_op->poll)(file, retval ? NULL : wait);//调用驱动程序中的poll函数。
/* 调用驱动程序中的poll函数,以evdev驱动中的evdev_poll()为例
* 该函数会调用函数poll_wait(file, &evdev->wait, wait),
* 继续调用__pollwait()回调来分配一个poll_table_entry结构体,
* 该结构体有一个内嵌的等待队列项,
* 设置好wake时调用的回调函数后将其添加到驱动程序中的等待队列头中。 */
fput_light(file, fput_needed); // 释放file结构指针,实际就是减小他的一个引用计数字段f_count。
//记录结果。poll函数返回的mask是设备的状态掩码。
if ((mask & POLLIN_SET) && (in & bit)) {
res_in |= bit; //如果是这个描述符可读, 将这个位置位
retval++; //返回描述符个数加1
}
if ((mask & POLLOUT_SET) && (out & bit)) {
res_out |= bit;
retval++;
}
if ((mask & POLLEX_SET) && (ex & bit)) {
res_ex |= bit;
retval++;
}
}
/*
* cond_resched()将判断是否有进程需要抢占当前进程,
* 如果是将立即发生调度,这只是为了增加强占点。
* (给其他紧急进程一个机会去执行,增加了实时性)
* 在支持抢占式调度的内核中(定义了CONFIG_PREEMPT),
* cond_resched是空操作。
*/
cond_resched();
}
//返回结果
if (res_in)
*rinp = res_in;
if (res_out)
*routp = res_out;
if (res_ex)
*rexp = res_ex;
}
wait = NULL;
if (retval || !*timeout || signal_pending(current)) // signal_pending(current)检查当前进程是否有信号要处理
break;
if(table.error) {
retval = table.error;
break;
}
if (*timeout < 0) {
/* Wait indefinitely 无限期等待*/
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT;
} elseif (unlikely(*timeout >= (s64)MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1)) {
/* Wait for longer than MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT. Do it in a loop */
__timeout = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT - 1;
*timeout -= __timeout;
} else {
__timeout = *timeout;
*timeout = 0;
}
/* schedule_timeout 用来让出CPU;
* 在指定的时间用完以后或者其它事件到达并唤醒进程(比如接收了一个信号量)时,
* 该进程才可以继续运行 */
__timeout = schedule_timeout(__timeout);
if (*timeout >= 0)
*timeout += __timeout;
}
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
poll_freewait(&table);
return retval;
}
参考链接: http://blog.csdn.net/lizhiguo0532/article/details/6568964