前言
重学c#系列继续更新,简单看一下字典的源码。
看源码主要是解释一下江湖中的两个传言:
-
字典foreach 顺序是字典添加的顺序
-
字典删除元素后,字典顺序将会改变
正文
那么就从实例化开始看起,这里我们假定key 是string 情况下开始看。
一般我们之间实例化:
Dictionary<string, string> keys = new Dictionary<string, string>();
那么看下内部的实例化是怎么样的。
public Dictionary() : this(0, null) { }
看下这个this 是什么:
public Dictionary(int capacity, IEqualityComparer<TKey>? comparer)
{
if (capacity < 0)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.capacity);
}
if (capacity > 0)
{
Initialize(capacity);
}
if (comparer != null && comparer != EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default) // first check for null to avoid forcing default comparer instantiation unnecessarily
{
_comparer = comparer;
}
// Special-case EqualityComparer<string>.Default, StringComparer.Ordinal, and StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase.
// We use a non-randomized comparer for improved perf, falling back to a randomized comparer if the
// hash buckets become unbalanced.
if (typeof(TKey) == typeof(string))
{
if (_comparer is null)
{
_comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>)NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.WrappedAroundDefaultComparer;
}
else if (ReferenceEquals(_comparer, StringComparer.Ordinal))
{
_comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>)NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.WrappedAroundStringComparerOrdinal;
}
else if (ReferenceEquals(_comparer, StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
_comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>)NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.WrappedAroundStringComparerOrdinalIgnoreCase;
}
}
}
首先有个参数,capacity 这个表示容量,然后有另外一个参数comparer,从名字上看来是用来比较排序的。
那么这时候可以大胆猜测一下字典的遍历循环是否和比较器(comparer)有关呢?不过这里默认是空的,暂时就不关心了。
继续往下看:
if (typeof(TKey) == typeof(string))
{
if (_comparer is null)
{
_comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>)NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.WrappedAroundDefaultComparer;
}
else if (ReferenceEquals(_comparer, StringComparer.Ordinal))
{
_comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>)NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.WrappedAroundStringComparerOrdinal;
}
else if (ReferenceEquals(_comparer, StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
_comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>)NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.WrappedAroundStringComparerOrdinalIgnoreCase;
}
}
一般来说我们的key一般都是string,那么默认就是NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.WrappedAroundDefaultComparer。
如果遍历和_comparer 有关的话,那么NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.WrappedAroundDefaultComparer 就很重要,但是现在还不能确定,先不看。
先看一下添加元素的情况。
public void Add(TKey key, TValue value)
{
bool modified = TryInsert(key, value, InsertionBehavior.ThrowOnExisting);
Debug.Assert(modified); // If there was an existing key and the Add failed, an exception will already have been thrown.
}
TryInsert 比较长,那么就一部分一部分看。
if (key == null)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key);
}
if (_buckets == null)
{
Initialize(0);
}
Debug.Assert(_buckets != null);
Entry[]? entries = _entries;
Debug.Assert(entries != null, "expected entries to be non-null");
_buckets 一开始是是null,那么先来看一下Initialize。
private int Initialize(int capacity)
{
int size = HashHelpers.GetPrime(capacity);
int[] buckets = new int[size];
Entry[] entries = new Entry[size];
// Assign member variables after both arrays allocated to guard against corruption from OOM if second fails
_freeList = -1;
#if TARGET_64BIT
_fastModMultiplier = HashHelpers.GetFastModMultiplier((uint)size);
#endif
_buckets = buckets;
_entries = entries;
return size;
}
那么看一下初始化的时候dic 的size是多少,通过 HashHelpers.GetPrime(capacity)。
我们知道如果我们没有指定capacity,那么capacity默认是0;
public static int GetPrime(int min)
{
if (min < 0)
throw new ArgumentException(SR.Arg_HTCapacityOverflow);
foreach (int prime in s_primes)
{
if (prime >= min)
return prime;
}
// Outside of our predefined table. Compute the hard way.
for (int i = (min | 1); i < int.MaxValue; i += 2)
{
if (IsPrime(i) && ((i - 1) % HashPrime != 0))
return i;
}
return min;
}
这个s_primes 我贴一下。
private static readonly int[] s_primes =
{
3, 7, 11, 17, 23, 29, 37, 47, 59, 71, 89, 107, 131, 163, 197, 239, 293, 353, 431, 521, 631, 761, 919,
1103, 1327, 1597, 1931, 2333, 2801, 3371, 4049, 4861, 5839, 7013, 8419, 10103, 12143, 14591,
17519, 21023, 25229, 30293, 36353, 43627, 52361, 62851, 75431, 90523, 108631, 130363, 156437,
187751, 225307, 270371, 324449, 389357, 467237, 560689, 672827, 807403, 968897, 1162687, 1395263,
1674319, 2009191, 2411033, 2893249, 3471899, 4166287, 4999559, 5999471, 7199369
};
把0带入进去,那么结果应该是3,看来一开始是3个存储桶,那么我们可以思考一下这个存储桶数量是否和性能有关,如果动态指定后性能是否更好,后面会在细节篇介绍。
TryInsert 这个方法继续往下看:
IEqualityComparer<TKey>? comparer = _comparer;
uint hashCode = (uint)((comparer == null) ? key.GetHashCode() : comparer.GetHashCode(key));
uint collisionCount = 0;
ref int bucket = ref GetBucket(hashCode);
int i = bucket - 1; // Value in _buckets is 1-based
在TryInsert 出现了_comparer,每个comparer 有自己的hashcode 方式,那么这个hashcode 会决定存储到哪个存储桶里面吗。
这里我们假设是在string情况下, 如果我们在不填写comparer的情况下,默认是OrdinalComparer。
private sealed class OrdinalComparer : NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer
{
internal OrdinalComparer(IEqualityComparer<string> wrappedComparer)
: base(wrappedComparer)
{
}
public override bool Equals(string x, string y)
{
return string.Equals(x, y);
}
public override int GetHashCode(string obj)
{
return obj.GetNonRandomizedHashCode();
}
}
通过下面这个comparer.GetHashCode,获取了hashcode。
介绍一下GetNonRandomizedHashCode 这个哈,这个就是说每个string 每次生成的都是确定的hashcode,而且其碰撞的可能性非常低,如果想看的话可以看一下源码,这里非重点,或许会在后续的介绍hash中说明一下。
uint hashCode = (uint)((comparer == null) ? key.GetHashCode() : comparer.GetHashCode(key));
然后通过hashcode 获取在bucket:
ref int bucket = ref GetBucket(hashCode);
int i = bucket - 1; // Value in _buckets is 1-based
查看:GetBucket
[MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.AggressiveInlining)]
private ref int GetBucket(uint hashCode)
{
int[] buckets = _buckets!;
#if TARGET_64BIT
return ref buckets[HashHelpers.FastMod(hashCode, (uint)buckets.Length, _fastModMultiplier)];
#else
return ref buckets[hashCode % (uint)buckets.Length];
#endif
}
通过上面这两段代码得知,如果是第一次添加元素,那么bucket 是0,i 为-1;
继续在tryinsert 往下看。
while (true)
{
// Should be a while loop https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/issues/9422
// Test uint in if rather than loop condition to drop range check for following array access
if ((uint)i >= (uint)entries.Length)
{
break;
}
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key))
{
if (behavior == InsertionBehavior.OverwriteExisting)
{
entries[i].value = value;
return true;
}
if (behavior == InsertionBehavior.ThrowOnExisting)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowAddingDuplicateWithKeyArgumentException(key);
}
return false;
}
i = entries[i].next;
collisionCount++;
if (collisionCount > (uint)entries.Length)
{
// The chain of entries forms a loop; which means a concurrent update has happened.
// Break out of the loop and throw, rather than looping forever.
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException_ConcurrentOperationsNotSupported();
}
}
这里i 为-1 然后entries.Length 是3。
所以(uint)i >= (uint)entries.Length 是true。
第一次我们添加的时候就直接break了。
值得一提的是另外一件事情,那就是当我们反编译的时候,看到的是这样的。
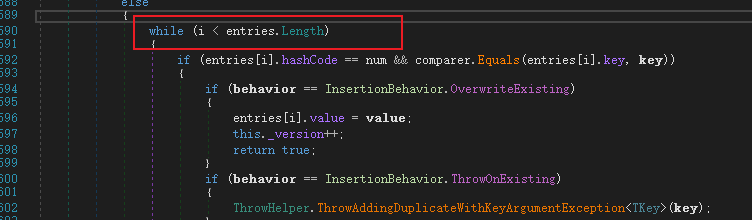
那么这里就有人问了,i = -1的时候,那么这个时候不是会出现异常吗?
实际上并不会,要知道当我们运行的时候比较的是二进制代码,故而建议编译后的调试的时候把16进制打开。

if (_freeCount > 0)
{
index = _freeList;
Debug.Assert((StartOfFreeList - entries[_freeList].next) >= -1, "shouldn't overflow because `next` cannot underflow");
_freeList = StartOfFreeList - entries[_freeList].next;
_freeCount--;
}
else
{
int count = _count;
if (count == entries.Length)
{
Resize();
bucket = ref GetBucket(hashCode);
}
index = count;
_count = count + 1;
entries = _entries;
}
ref Entry entry = ref entries![index];
entry.hashCode = hashCode;
entry.next = bucket - 1; // Value in _buckets is 1-based
entry.key = key;
entry.value = value; // Value in _buckets is 1-based
bucket = index + 1;
_version++;
// Value types never rehash
if (!typeof(TKey).IsValueType && collisionCount > HashHelpers.HashCollisionThreshold && comparer is NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer)
{
// If we hit the collision threshold we'll need to switch to the comparer which is using randomized string hashing
// i.e. EqualityComparer<string>.Default.
Resize(entries.Length, true);
}
这里_freeCount 是0,从这个命名(空闲数量)来看结合别人说的那个remove 之后顺序会变,猜测一下,是不是删除的时候保留了一个空位,然后如果有空位然后就往里面添加呢?
这个先不管只有知道如果一直添加那么其一直是0。
那么就按照_freeCount 是0的节奏走,那么就是判断是count == entries.Length 判断是否满了,如果满了肯定就是扩容一下,调整一下之类的了。
然后总量加1,同时设置了左边是最后一位,那么猜测一下,如果一直这样加的话,如果遍历的时候没有使用到comparer,那么就是按照添加的顺序了。
那么看一下字典的迭代步骤:
public bool MoveNext()
{
if (_version != _dictionary._version)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException_InvalidOperation_EnumFailedVersion();
}
// Use unsigned comparison since we set index to dictionary.count+1 when the enumeration ends.
// dictionary.count+1 could be negative if dictionary.count is int.MaxValue
while ((uint)_index < (uint)_dictionary._count)
{
ref Entry entry = ref _dictionary._entries![_index++];
if (entry.next >= -1)
{
_current = new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(entry.key, entry.value);
return true;
}
}
_index = _dictionary._count + 1;
_current = default;
return false;
}
_index 一开始默认是0,那么我们存储的值是一个数组,那么如果按照上面这样逻辑的遍历,那么是按照添加顺序来的。
这里有一个遍历出来的条件,entry.next >= -1,那么是否是如果删除的话那么就做一个标记呢?因为如果移动数组,那么的确是一件艰难的事情(性能)。
那么看remove了。
public bool Remove(TKey key)
{
// The overload Remove(TKey key, out TValue value) is a copy of this method with one additional
// statement to copy the value for entry being removed into the output parameter.
// Code has been intentionally duplicated for performance reasons.
if (key == null)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key);
}
if (_buckets != null)
{
Debug.Assert(_entries != null, "entries should be non-null");
uint collisionCount = 0;
uint hashCode = (uint)(_comparer?.GetHashCode(key) ?? key.GetHashCode());
ref int bucket = ref GetBucket(hashCode);
Entry[]? entries = _entries;
int last = -1;
int i = bucket - 1; // Value in buckets is 1-based
while (i >= 0)
{
ref Entry entry = ref entries[i];
if (entry.hashCode == hashCode && (_comparer?.Equals(entry.key, key) ?? EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default.Equals(entry.key, key)))
{
if (last < 0)
{
bucket = entry.next + 1; // Value in buckets is 1-based
}
else
{
entries[last].next = entry.next;
}
Debug.Assert((StartOfFreeList - _freeList) < 0, "shouldn't underflow because max hashtable length is MaxPrimeArrayLength = 0x7FEFFFFD(2146435069) _freelist underflow threshold 2147483646");
entry.next = StartOfFreeList - _freeList;
if (RuntimeHelpers.IsReferenceOrContainsReferences<TKey>())
{
entry.key = default!;
}
if (RuntimeHelpers.IsReferenceOrContainsReferences<TValue>())
{
entry.value = default!;
}
_freeList = i;
_freeCount++;
return true;
}
last = i;
i = entry.next;
collisionCount++;
if (collisionCount > (uint)entries.Length)
{
// The chain of entries forms a loop; which means a concurrent update has happened.
// Break out of the loop and throw, rather than looping forever.
ThrowHelper.ThrowInvalidOperationException_ConcurrentOperationsNotSupported();
}
}
}
return false;
}
这里就直接说明一下这个思路哈。
首先给出一张概念图:

这张是什么意思呢? 字典实际上默认情况下实际上是3个数据桶。
但是数据本身是存在数组中的,然后通过数据key的hashcode 来决定数据放在哪个数据桶中。
且同一个数据桶中是链状结构的,那么删除步骤就是下面这个概念图。
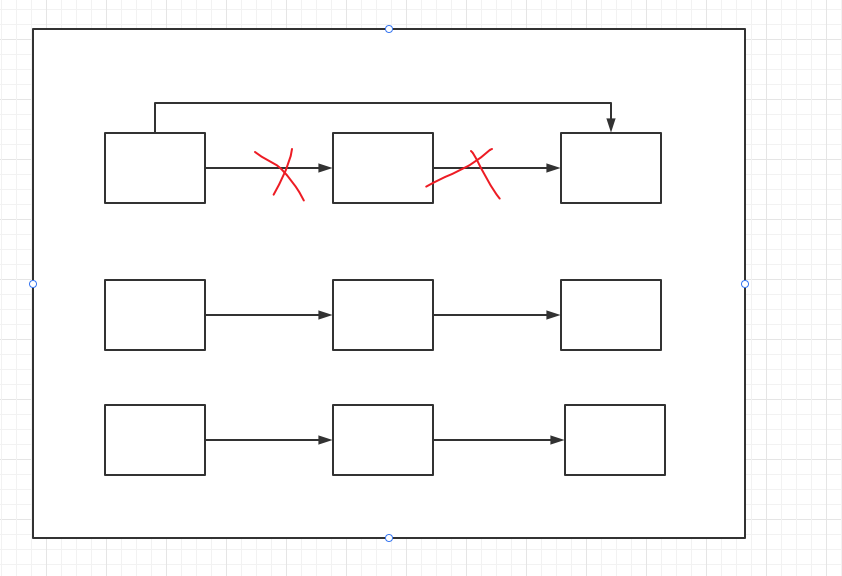
就是进行链表删除一样,同样把这个数据的key和value 清空,然后把next进行弄为比-1还小的数StartOfFreeList - _freeList,StartOfFreeList 默认是-3,_freeList 最小是-1,这样就在数组中标记删除了。
那么我们再来看添加的时候,如果有删除的位置的时候的代码。
if (_freeCount > 0)
{
index = _freeList;
Debug.Assert((StartOfFreeList - entries[_freeList].next) >= -1, "shouldn't overflow because `next` cannot underflow");
_freeList = StartOfFreeList - entries[_freeList].next;
_freeCount--;
}
如果有删除的位置那么会顶替删除的位置。
那么删除的模型是怎么样的?看StartOfFreeList - entries[_freeList].next。
这里删除逻辑其实是这样的。

删除的我们指定只是做了标记,但是这个标记可不是这么简单的标记,而是形成了链状结构,每次如果添加的时候就替补了最后一个删除为,然后最后一个删除位又得到了更新。
这里给出一个例子。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
Dictionary<string, string> keys = new Dictionary<string, string>();
keys.Add("aaa","aaa");
keys.Add("cccc", "cccc");
keys.Add("ddddd", "ddddd");
keys.Remove("aaa");
keys.Remove("cccc");
keys.Add("xxxx", "bbbbb");
keys.Add("zzzz", "bbbbb");
foreach (var a in keys)
{
Console.WriteLine(a.Key);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
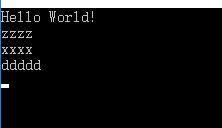
结
那么得出结论。
1. 字典foreach 顺序是字典添加的顺序
2. 字典删除元素后,字典顺序将会改变
如果字典一直只添加,那么会foreach 会是原来的顺序。
如果字典进行了删除,那么这个最后一个删除位将会成为下一个添加位。
整理查找我就不介绍了,也是通过定位在哪个存储桶,然后进行链状查询。
在该系列,在后面应该也会介绍一下list源码。