java.lang.String类代表字符串
程序中所有双引号字符串,都是String对象(就算没有new,也是对象)
字符串特点:
1.字符串内容永不改变
2.由于字符串内容不改变,所以字符串可以共享使用(常量池)
3.字符串效果上相当于char[]字符数组,但是底层原理是byte[]字节数组
字符串创建方法:
1.public String():创建一个空白字符串,不含任何内容
String str = new String();
2.public String(char[] array):根据字符数组内容,来创建相应的字符串
char[] array = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str = new String(array)
3.public String(byte[] array):根据字节数组内容,来创建相应的字符串
byte[] array = {97, 98, 99};
String str = new String(array);
4.直接创建 String str = "abc";
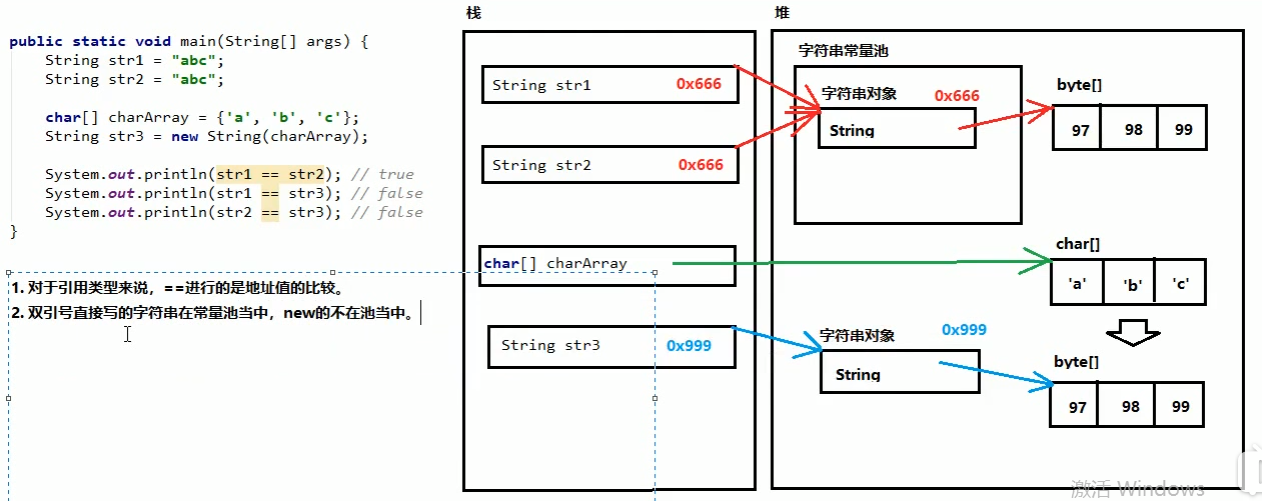
字符串常量池:程序当中直接写上的双引号字符串,就在字符串常量池中。
对于基本类型,==是对进行数值的比较
对于引用类型,==是对进行地址值的比较
注意:
String str = "hello";
sout(str); //输出为hello
str = "java";
sout(str); //输出为java
字符串没有发生改变,改变的只是地址值,str保存的是地址值
String类常用方法:
1.public boolean equals(object obj):参数可以是任何对象,只有参数是一个字符串并且内容相同才会给出true,否则false
任何对象都能被 obejct 接收
str1 = "hello";
char[] array = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str2 = new String(array);
sout(str1.equals(str2)); //false
sout("hello".equals(str1)); //true
一般常量放前面,变量放后面
这个方法区分大小写
2.public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(object obj):英文不区分大小写的比较
3.public int length():获取字符串中含字符个数,得到字符串长度
4.public String concat(String str):将当前字符串和参数字符串,拼接成为一个新的字符串并返回
String str1 = "hello"
String str2 = "world"
String str3 = str1.concat(str2); helloworld
5.public char charAt(int index):获取指定位置的单个字符(从0开始)
String str1 = "hello";
char ch = str1.charAt(1) // ch = e
6.public int indexOf(String str):查找参数字符串,在本字符串当中首次出现的索引位置,如果没有,返回值为-1
String str1 = "helloworld";
int num = str1.indexOf("llo"); // num = 2
int num = str1.indexOf("abc"); // num = -1
7.public String substring(int index):截取从参数位置一直到字符串末尾,返回新字符串
public String substring(int begin, int end):截取从 begin 开始,一直到 end 结束,中间的字符。[begin, end),包括左边,不包括右边
8.public char[] toCharArray():将当前字符串拆分为字符数组作为返回值
9.public byte[] getBytes():获得当前字符串底层的字节数组
10.public String replace(CharSequence oldString, CharSequence newString):
将所有出现的字符串替换成为新的字符串,返回替换之后的结果新字符串
String str1 = "会不会玩啊!你大爷的!"
String str2 = str1.replace("你大爷的", "****")
sout(str2); //输出为:会不会玩啊!****!
11.public String[] split(String regex):按照参数规则,将字符串切割成若干部分
若切割 "aaa bbb ccc" 可按空格划分,则参数 regex 为空格
split的参数实际是一个正则表达式,若要用 '.' 分割,必须写"\."(两个反斜杠)