每个Node节点包含两个内容
1.保存数据
2.下一个节点引用
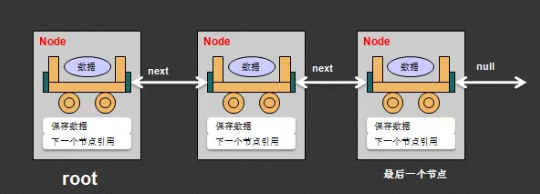
定义一个Node类
假设本次保存的数据是String型数据,同时拥有下一个引用;
// 每一个链表实际上就是由多个节点组成的 class Node { // 定义一个节点 private String data; // 要保存的数据 private Node next; //要保存的下一个节点 // 每一个Node类对象都必须保存有相应的数据 public Node (String data){ // 必须有数据才有Node this.data = data; } public void setNext(Node next){ this.next = next; } public Node getNext(){ return this.next; } public String getData(){ return this.data; } }
以上只是一个专门负责保存节点关系的类,但是至于怎么保存的的关系,现在并不是由Node类进行。需要由其他类来负责Node的关系匹配。
使用第一种形式设置和取出数据 while循环
// 每一个链表实际上就是由多个节点组成的 class Node { // 定义一个节点 private String data; // 要保存的数据 private Node next; //要保存的下一个节点 // 每一个Node类对象都必须保存有相应的数据 public Node (String data){ // 必须有数据才有Node this.data = data; } public void setNext(Node next){ this.next = next; } public Node getNext(){ return this.next; } public String getData(){ return this.data; } } public class LinkDemo{ public static void main(String args[]){ // 第一步:准备出所有的数据 Node root = new Node("火车头"); Node n1 = new Node("车厢A"); Node n2 = new Node("车厢B"); root.setNext(n1); n1.setNext(n2); // 第二步:取出所有数据 Node currentNode = root ; // 从当前根结点开始读取 while(currentNode != null) { //当前结点存在有数据 System.out.println(currentNode.getData()); // 将下一个结点设置为当前结点 currentNode = currentNode.getNext(); } } }
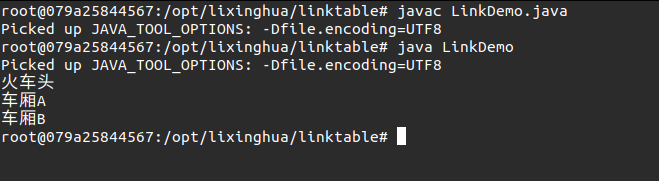
实际上以上的操作使用的循环并不方便,最好的做法还是应该使用递归操作完成
使用第二种方式设置和取得数据 递归调用
// 每一个链表实际上就是由多个节点组成的 class Node { // 定义一个节点 private String data; // 要保存的数据 private Node next; //要保存的下一个节点 // 每一个Node类对象都必须保存有相应的数据 public Node (String data){ // 必须有数据才有Node this.data = data; } public void setNext(Node next){ this.next = next; } public Node getNext(){ return this.next; } public String getData(){ return this.data; } } public class LinkDemo{ public static void main(String args[]){ // 第一步:准备出所有的数据 Node root = new Node("火车头"); Node n1 = new Node("车厢A"); Node n2 = new Node("车厢B"); root.setNext(n1); n1.setNext(n2); // 第二步:取出所有数据 print(root); } public static void print(Node current){ if (current == null){ return ; } System.out.println(current.getData()); print(current.getNext()); } }
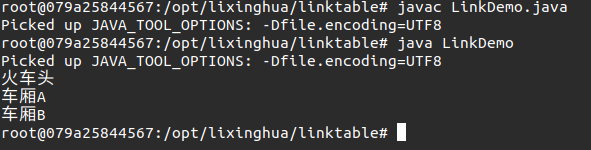
对于所有的节点操作,由于我们并不知道具体的循环次数,所以只能够使用while循环,但是在节点操作中,要比直接使用while循环,从代码上更加直观
疑问?整个过程里面实际上它完成的功能就是一个设置和取出数据的过程。为什么需要Node?
由于数据本身不具备先后的关系,所以使用Node类来封装数据,同时使用Node类指向下一个节点