要专业系统地学习EF推荐《你必须掌握的Entity Framework 6.x与Core 2.0》。这本书作者(汪鹏,Jeffcky)的博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/CreateMyself/
既然弄到了NLog就不得不去弄弄它,那么我了解到NLog可以将日志输出到控制台、文件、数据库,还有其他的目标地址。
那么我现在就来记录一下控制台、文件、数据库的配置方式,并且能够立马生效。
在NLog.Config配置文件中进行如下配置
输出到控制台

<targets>
<!--输出到控制台-->
<target name="logConsole" xsi:type="Console"/>
</targets>

<!--这里就是告诉他logger对象所在的位置,然后将日志写到上面配置的某个目标地址--> <logger name="_201901212.NLog.NLogCommandInterceptor" writeTo="logConsole"/>
我的logger对象写在拦截类里面,并将拦截到的SQL语句写入到日志里面

public class NLogCommandInterceptor : IDbCommandInterceptor
{
private static readonly Logger Logger = LogManager.GetCurrentClassLogger();
public void NonQueryExecuted(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<int> interceptionContext)
{
LogIfError(command,interceptionContext);
}
public void NonQueryExecuting(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<int> interceptionContext)
{
LogIfNonAsync(command,interceptionContext);
}
public void ReaderExecuted(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<DbDataReader> interceptionContext)
{
LogIfError(command,interceptionContext);
}
public void ReaderExecuting(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<DbDataReader> interceptionContext)
{
LogIfNonAsync(command, interceptionContext);
}
public void ScalarExecuted(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<object> interceptionContext)
{
LogIfError(command, interceptionContext);
}
public void ScalarExecuting(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<object> interceptionContext)
{
LogIfNonAsync(command,interceptionContext);
}
private void LogIfNonAsync<TResult>(DbCommand command,DbCommandInterceptionContext<TResult> interceptionContext)
{
if (!interceptionContext.IsAsync)
{
Console.WriteLine(Logger.Name);
Console.WriteLine($"张四海{Logger}");
Logger.Warn("Non-async command used:{0}{1}",Environment.NewLine, command.CommandText);
}
}
private void LogIfError<TResult>(DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<TResult> interceptionContext)
{
if (interceptionContext.Exception != null)
{
Logger.Error("Command {0} failed with exception {1}",command.CommandText,interceptionContext.Exception);
}
}
}
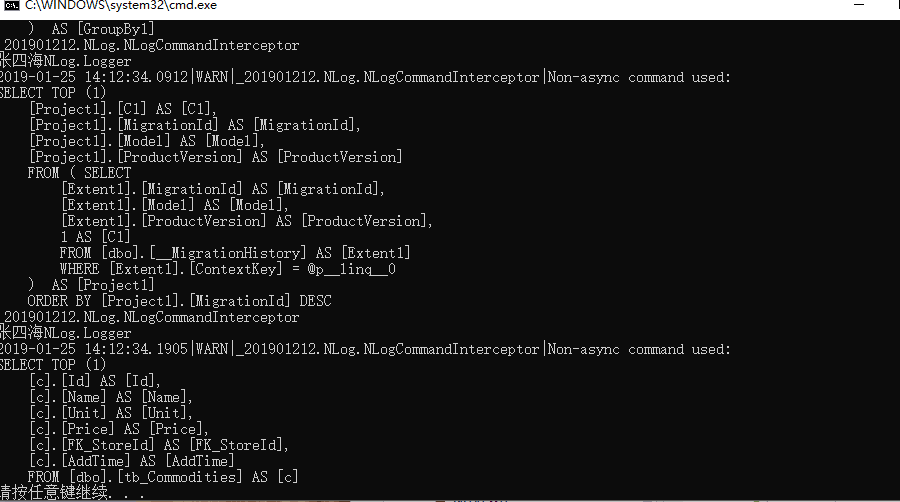
写入到文件 ${basedir}Logslog.txt 这表示它会在binDebug里面创建Logs文件夹并写入log.txt文件

<target name="logfile" xsi:type="File" fileName="${basedir}Logslog.txt"/>

<logger name="_201901212.NLog.NLogCommandInterceptor" writeTo="logfile"/>
也可以设置为其他的地址:../../Logs/sihai.txt

或者绝对路径:D:sihai.txt
写入到数据库中,这个就复杂点,要设置连接字符串、inset语句、参数

<target name="db" xsi:type="Database" dbProvider="System.Data.SqlClient" connectionString="Data Source=LAPTOP-G81QJ856SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=_201901212.EFDbContext;Integrated Security=True;user id=sa;password=111111"
commandText="INSERT INTO tb_Logs2(Id) VALUES(@id);">
<parameter name="@id" layout="${guid}" />

<logger name="_201901212.NLog.NLogCommandInterceptor" writeTo="db"/>
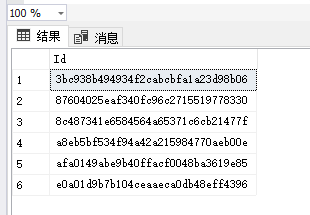
先要在数据库中把表建好,我建议是先弄一个列看看行不行。我就是搞了半天不知道哪里出了问题。最后重新建个表只有Id列,然后就成功了。
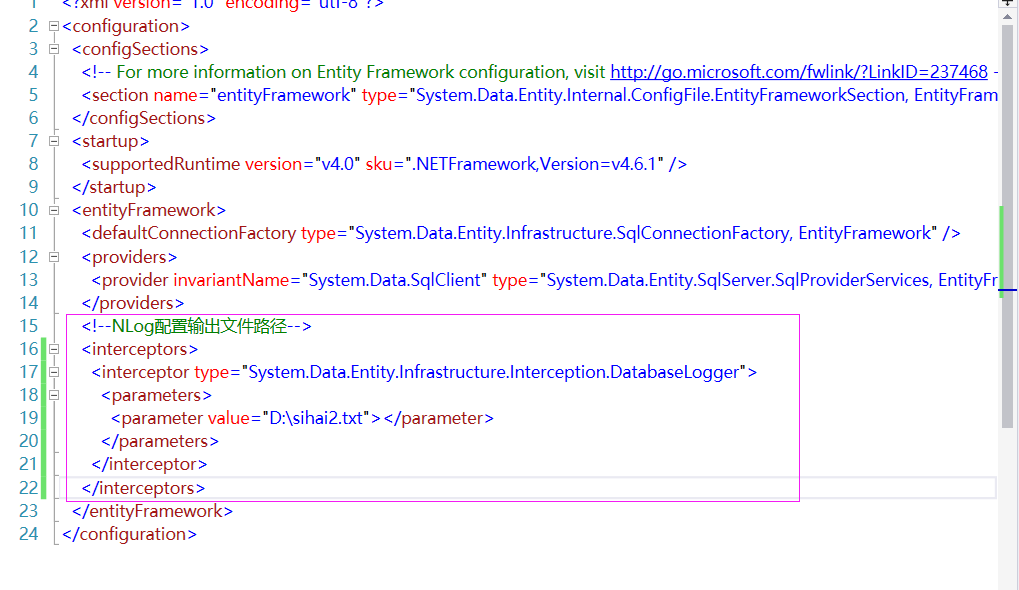
配置也可以不用写在NLog.config文件中,可以写在app.config或者web.config文件中
如果你配置了控制台也配置了文件或者数据库,那么这三种都会有效。
